Data Theft Vulnerability in Microsoft Copilot Exploited by Reprompt Attack Method
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
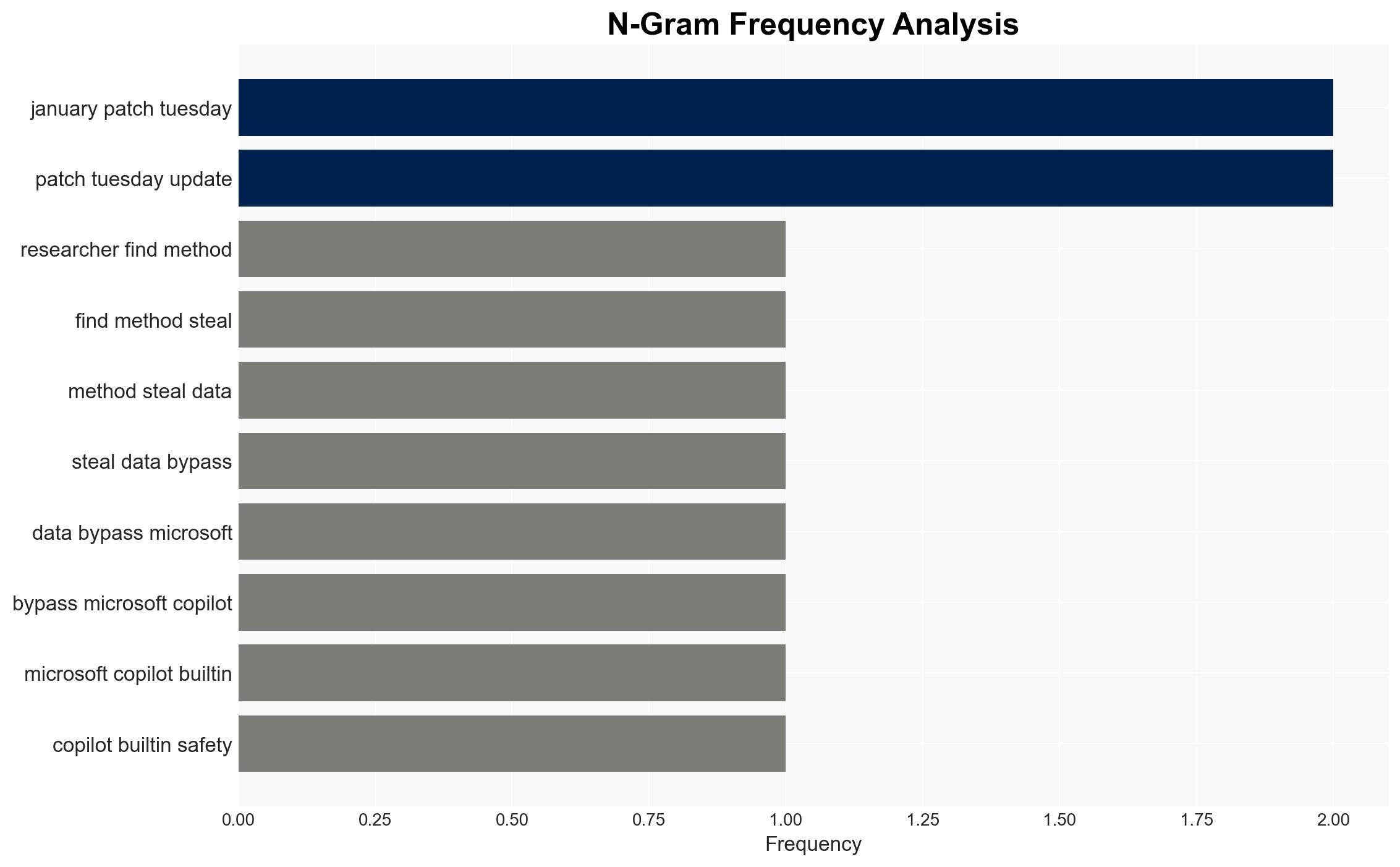
Intelligence Report: Reprompt attack lets attackers steal data from Microsoft Copilot
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
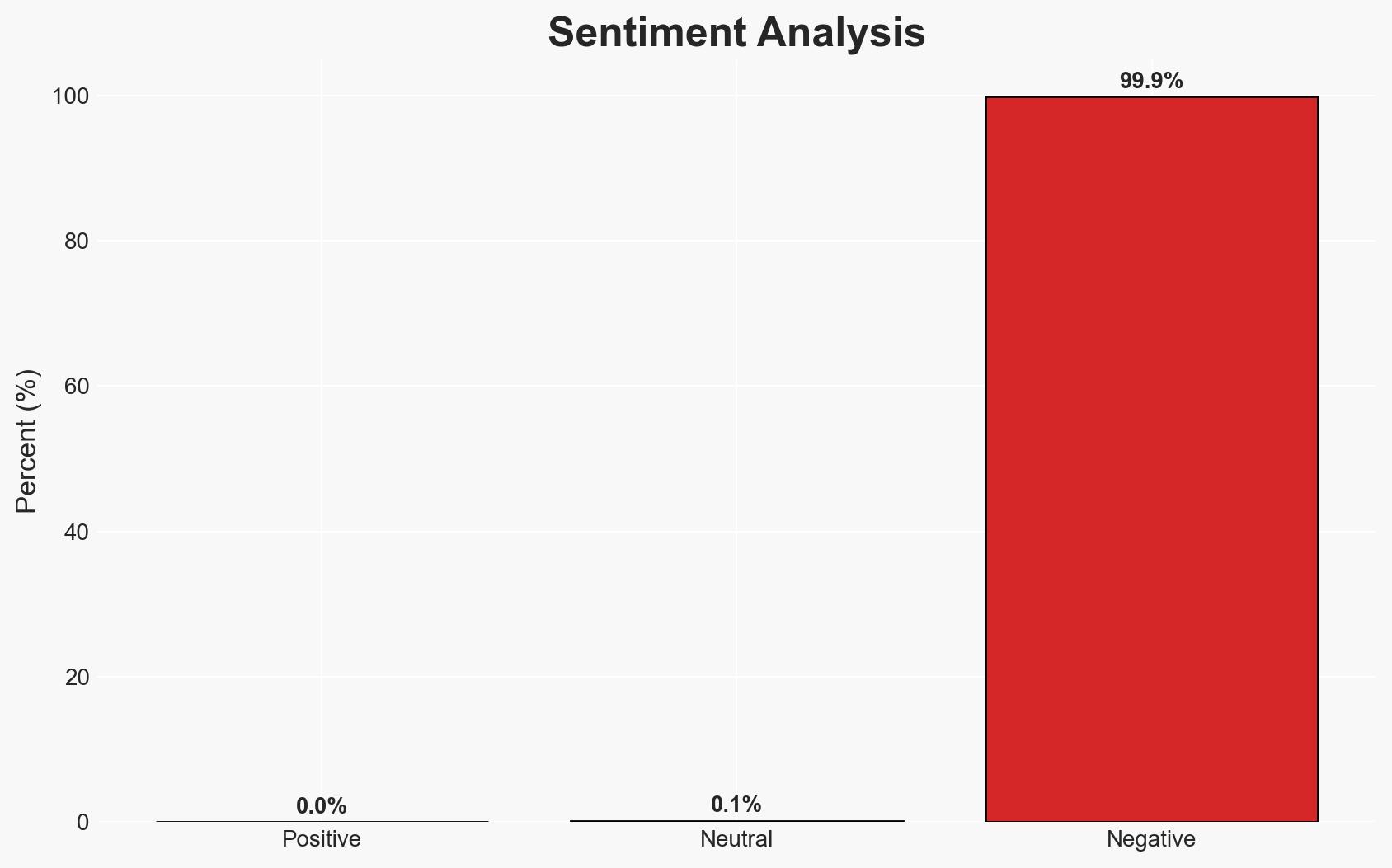
The Reprompt attack exploits a vulnerability in Microsoft Copilot, allowing attackers to hijack user sessions through URL parameter manipulation. This vulnerability, although patched, highlights ongoing risks associated with AI integration in consumer applications. The attack’s simplicity and potential impact on user data security necessitate vigilance. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Reprompt attack is an isolated incident due to a specific oversight in Copilot’s URL handling, now mitigated by the January patch. Supporting evidence includes the lack of reported in-the-wild exploitation and the patch’s release. However, uncertainties remain about similar vulnerabilities in other AI systems.
- Hypothesis B: The Reprompt attack indicates a broader systemic vulnerability in AI assistants’ security frameworks, potentially exploitable in other applications beyond Copilot. This hypothesis is supported by the attack’s fundamental simplicity and the general trend of AI security challenges. Contradicting evidence includes the specific nature of the vulnerability to Copilot’s URL handling.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific nature of the vulnerability and the absence of exploitation evidence. However, vigilance is needed for indicators of broader systemic issues, such as similar vulnerabilities in other AI platforms.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Microsoft’s patch effectively mitigates the vulnerability; No other similar vulnerabilities exist in Copilot; Users will apply security updates promptly; Attackers have not exploited the vulnerability in the wild.
- Information Gaps: Lack of data on potential exploitation attempts before the patch; Details on Microsoft’s internal security assessments post-patch; Information on similar vulnerabilities in other AI systems.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in assuming the patch fully resolves the issue; Source bias from reliance on Microsoft’s reported data; Deception risk from attackers potentially masking exploitation attempts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The Reprompt attack underscores the need for robust security measures in AI applications, with potential long-term impacts on user trust and AI adoption. The incident could influence regulatory scrutiny and security standards for AI technologies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased regulatory focus on AI security, potentially affecting international tech policy discussions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness of AI vulnerabilities could lead to increased targeting by cyber adversaries.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for similar attacks on other AI platforms, necessitating enhanced cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Erosion of consumer trust in AI technologies could slow adoption and impact market dynamics.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Ensure all systems are updated with the latest patches; Monitor for any signs of exploitation attempts; Educate users on recognizing phishing attempts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI developers for security best practices; Invest in AI security research and development; Enhance regulatory frameworks for AI technologies.
- Scenario Outlook: Best-case: Increased security measures prevent further incidents; Worst-case: Similar vulnerabilities are found in other AI systems, leading to widespread exploitation; Most-likely: Gradual improvement in AI security with sporadic incidents prompting ongoing vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft (Developer of Copilot)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
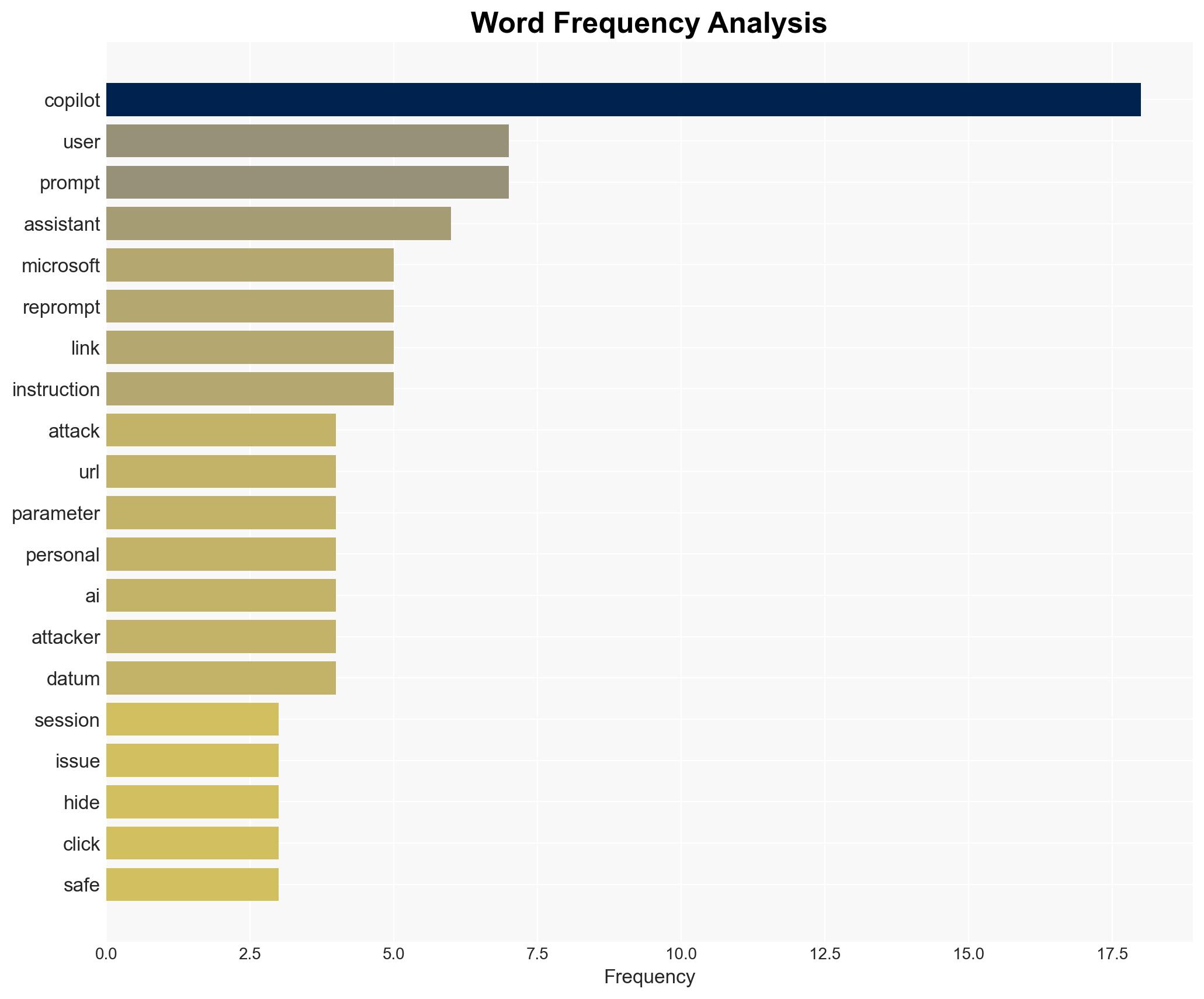
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, Microsoft Copilot, phishing attacks, software patches, user data protection, AI integration risks
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us