Death toll from Hurricane Melissa climbs to 49 with many still missing – Al Jazeera English
Published on: 2025-10-31
Intelligence Report: Death toll from Hurricane Melissa climbs to 49 with many still missing – Al Jazeera English
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
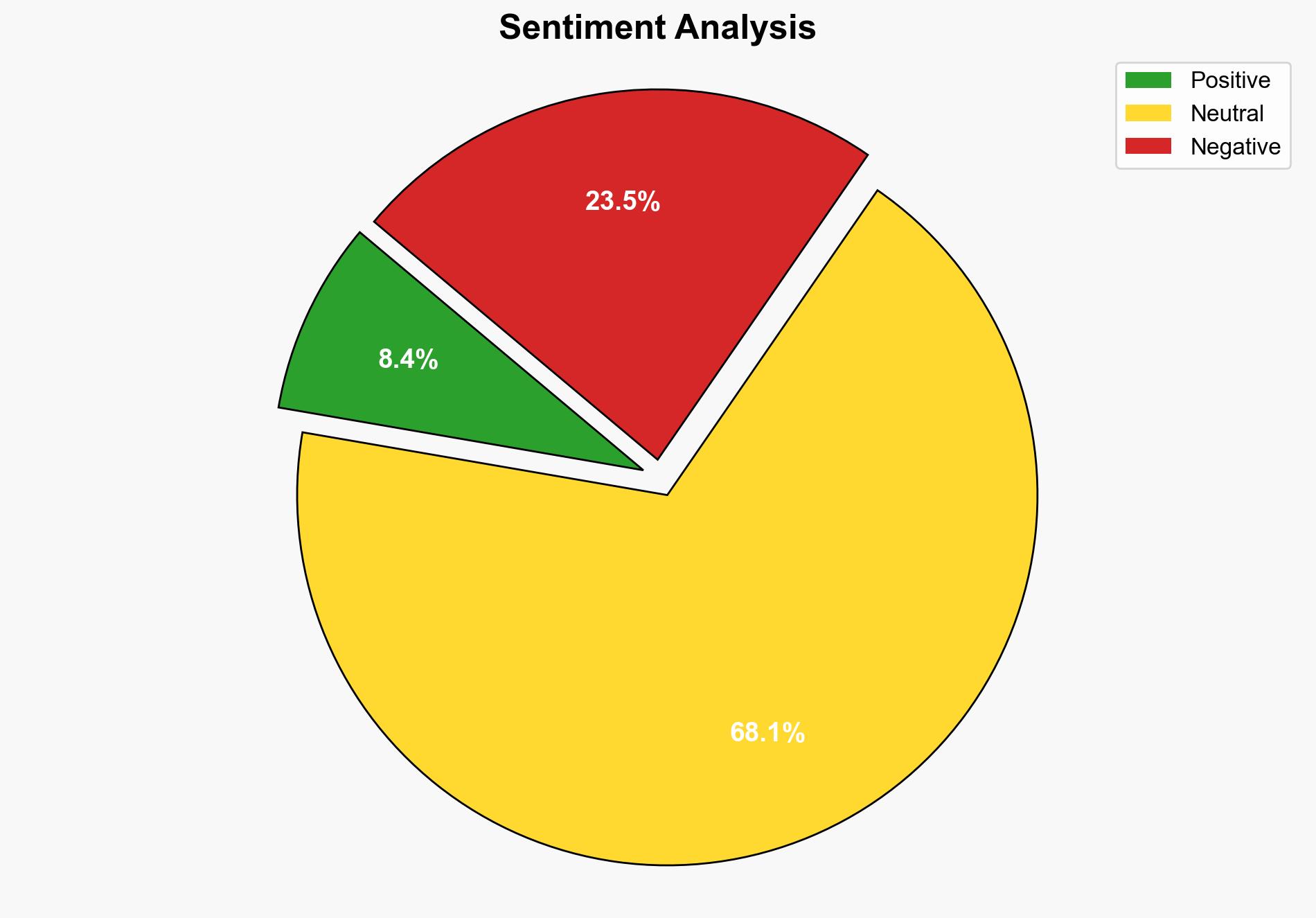
The most supported hypothesis is that Hurricane Melissa’s impact was exacerbated by inadequate infrastructure and emergency preparedness in the affected regions, particularly in Haiti and Jamaica. This conclusion is drawn with a moderate confidence level due to the consistency of reports on infrastructure damage and the historical context of similar events. Recommended actions include enhancing international aid coordination and infrastructure resilience in vulnerable Caribbean nations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The high death toll and destruction from Hurricane Melissa are primarily due to the storm’s unprecedented strength and trajectory, which directly hit vulnerable regions with insufficient time for preparation.
Hypothesis 2: The impact of Hurricane Melissa was significantly worsened by pre-existing vulnerabilities such as inadequate infrastructure, poor emergency response systems, and socio-economic challenges in the affected regions.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 2 is better supported. The evidence of widespread infrastructure damage and historical patterns of disaster response inadequacies in these regions align more closely with this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– Assumption: The reported figures and damage assessments are accurate and not subject to significant underreporting or exaggeration.
– Red Flag: Potential bias in reporting due to political or economic interests in affected countries.
– Blind Spot: Lack of detailed information on the effectiveness of local government and international aid response efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– Economic: Significant economic losses estimated between $1-3 billion could destabilize local economies, increasing dependency on international aid.
– Geopolitical: The disaster may strain regional relations if aid distribution is perceived as unequal or politically motivated.
– Psychological: Prolonged recovery efforts could lead to public discontent and social unrest in affected areas.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance infrastructure resilience through international partnerships focused on sustainable development and disaster preparedness.
- Improve early warning systems and community-based disaster response training in vulnerable regions.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Effective international aid and local recovery efforts lead to rapid stabilization and infrastructure improvements.
- Worst Case: Prolonged recovery efforts exacerbate economic and social instability, leading to increased migration and regional tensions.
- Most Likely: Gradual recovery with intermittent challenges due to ongoing socio-economic vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Dennis Zulu (UN Resident Coordinator)
– Marco Rubio (U.S. Secretary of State)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, disaster response, regional stability, humanitarian aid