Differences Between Syncing and Backing Up Data – MakeUseOf
Published on: 2025-04-04
Intelligence Report: Differences Between Syncing and Backing Up Data – MakeUseOf
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
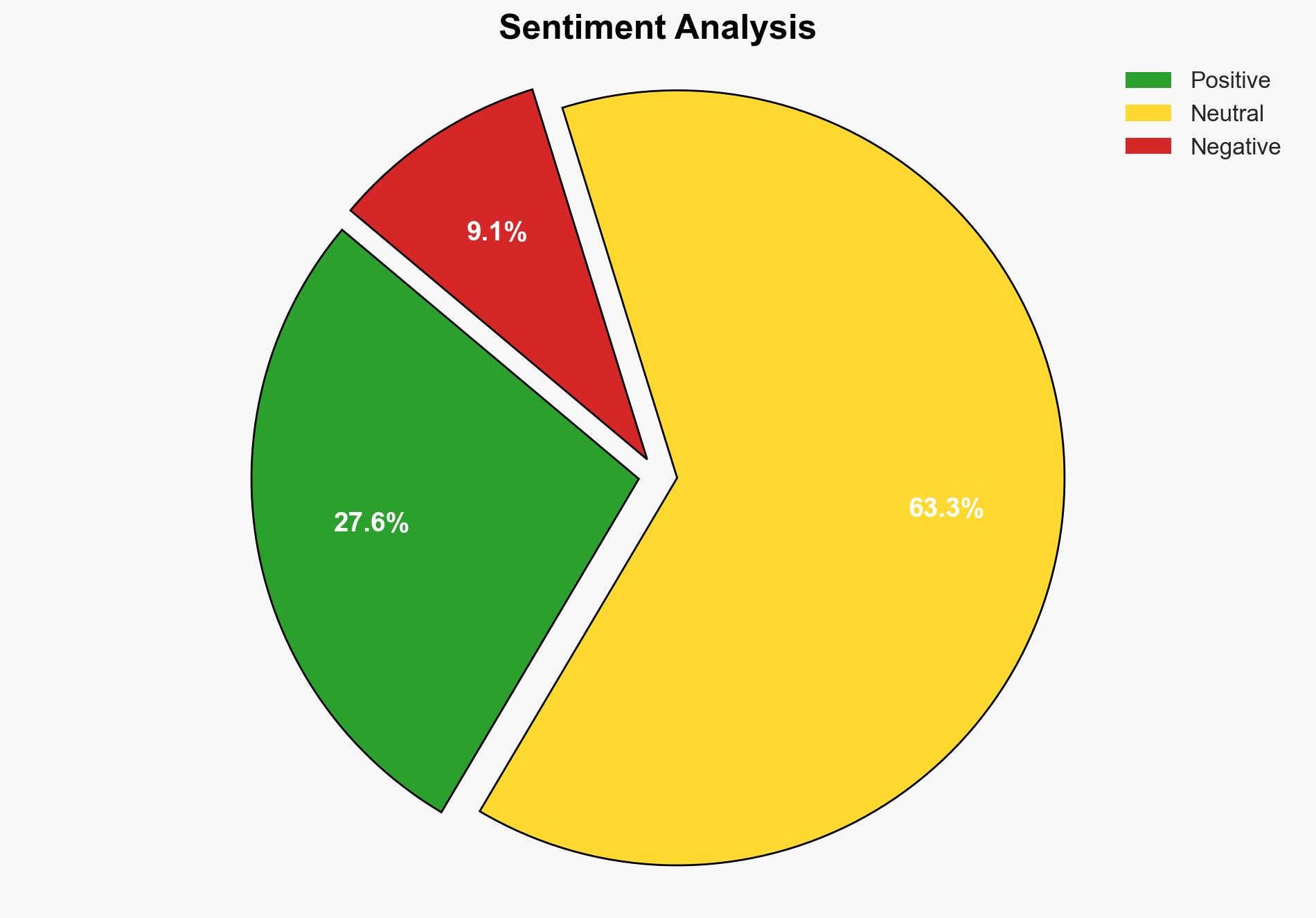
The analysis highlights the critical differences between data syncing and backing up. Syncing ensures data is updated across devices in real-time, providing convenience but lacking in security. Conversely, backing up data offers a secure, offline copy that remains unaffected by changes or deletions. Stakeholders are advised to implement a dual strategy utilizing both syncing for accessibility and backups for data integrity and security.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied for this analysis:
General Analysis
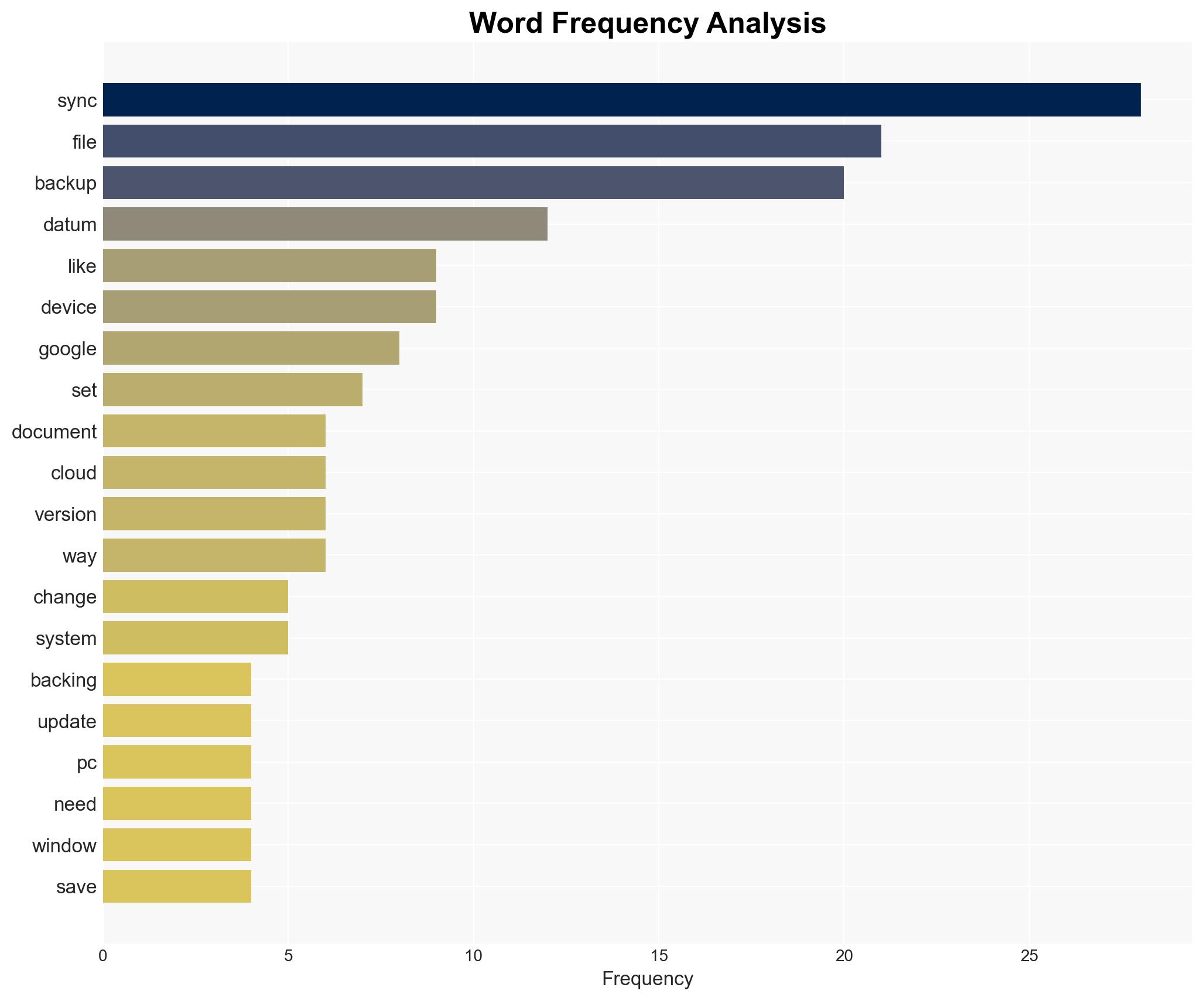
Syncing and backing up data serve distinct purposes. Syncing keeps files updated across multiple devices, which is beneficial for users needing constant access to their data. However, it mirrors any deletions or corruptions, posing a security risk. Backing up data, on the other hand, involves creating a separate, offline copy that remains unchanged regardless of alterations to the original files. This method protects against data loss due to accidental deletion, corruption, or malware.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary risk associated with relying solely on syncing is the potential for data loss or corruption to propagate across all synced devices. This could have significant implications for individuals and organizations, particularly if sensitive or critical data is involved. The lack of a robust backup system could lead to increased vulnerability to ransomware and other cyber threats, impacting national security, regional stability, and economic interests.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
Recommendations:
- Implement a comprehensive data management strategy that includes both syncing and regular backups.
- Encourage the use of cloud services with robust version history and recovery options.
- Promote awareness of the limitations of syncing and the importance of maintaining separate backups.
- Consider regulatory measures to ensure organizations adhere to best practices in data management.
Outlook:
In the best-case scenario, widespread adoption of dual data management strategies will reduce data loss incidents and improve overall data security. The worst-case scenario involves continued reliance on syncing alone, leading to increased data breaches and losses. The most likely outcome is a gradual shift towards integrating both methods as awareness of their complementary roles grows.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The report does not mention specific individuals or organizations by name. However, it emphasizes the importance of stakeholders in technology, cybersecurity, and data management sectors to address the identified risks and implement recommended strategies.