DRC Rwanda-backed M23 sign framework deal for peace after talks in Qatar – Al Jazeera English
Published on: 2025-11-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
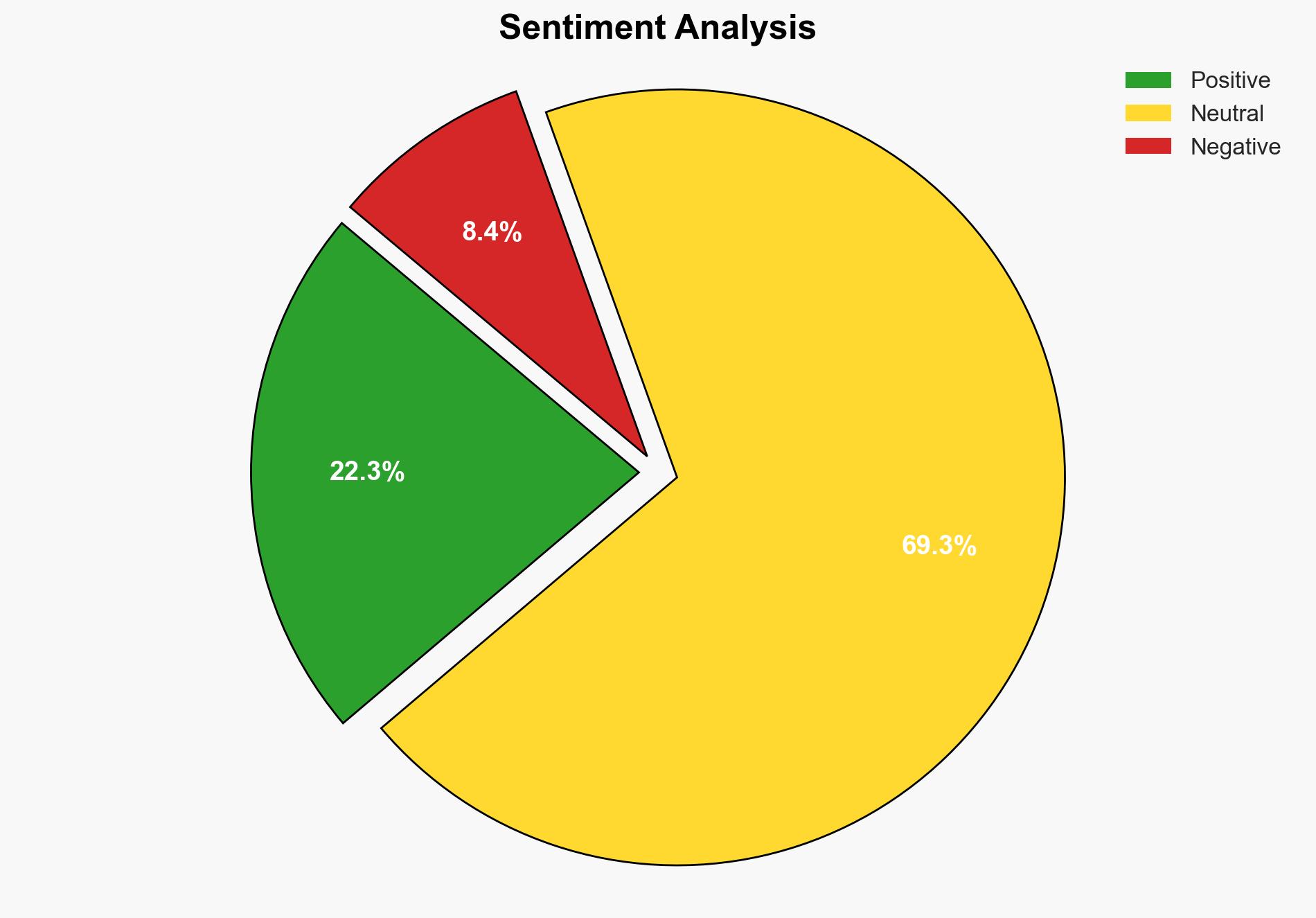
The signing of a framework peace deal between the DRC government and the Rwanda-backed M23 rebel group in Qatar represents a potentially significant step towards resolving long-standing conflict in the region. However, the success of this agreement is contingent upon effective implementation and monitoring, which remains uncertain. The most supported hypothesis is that the peace process will face significant challenges, but may lead to incremental improvements in stability if supported by robust international oversight. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The peace agreement will lead to a sustained reduction in violence and improved humanitarian conditions in the DRC.
Hypothesis 2: The peace agreement will face implementation challenges, leading to a temporary reduction in violence but ultimately failing to achieve long-term stability.
Hypothesis 2 is more likely due to historical precedents of failed agreements in the region, the complexity of the conflict, and the potential for spoilers to undermine the process.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: All parties are genuinely committed to peace; international stakeholders will provide necessary support and oversight; local populations will support the peace process.
Red Flags: Previous agreements have failed; potential for non-compliance by rebel factions; regional actors may have conflicting interests.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The peace agreement, if not effectively implemented, could lead to renewed violence, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis and destabilizing the region further. There is a risk of escalation if rebel groups perceive the agreement as a threat to their interests or if regional actors intervene to protect their strategic interests.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Increase international monitoring and support for the implementation process; engage local communities to build grassroots support for peace; ensure transparent communication between all stakeholders.
- Best Scenario: Successful implementation leads to lasting peace and regional stability.
- Worst Scenario: Breakdown of the agreement results in intensified conflict and humanitarian disaster.
- Most-likely Scenario: Partial implementation with intermittent violence, requiring ongoing international engagement.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Mohammed bin Abdulaziz Al Khulaifi, Massad Boulo, Alain Uakyani.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Regional Focus: Central Africa, DRC, Rwanda, Peace Process, Conflict Resolution
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·