Dutch government says it’s relinquishing control of Chinese-owned chipmaker Nexperia – ABC News
Published on: 2025-11-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Strategic Analysis of Dutch Government’s Relinquishment of Control over Nexperia
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
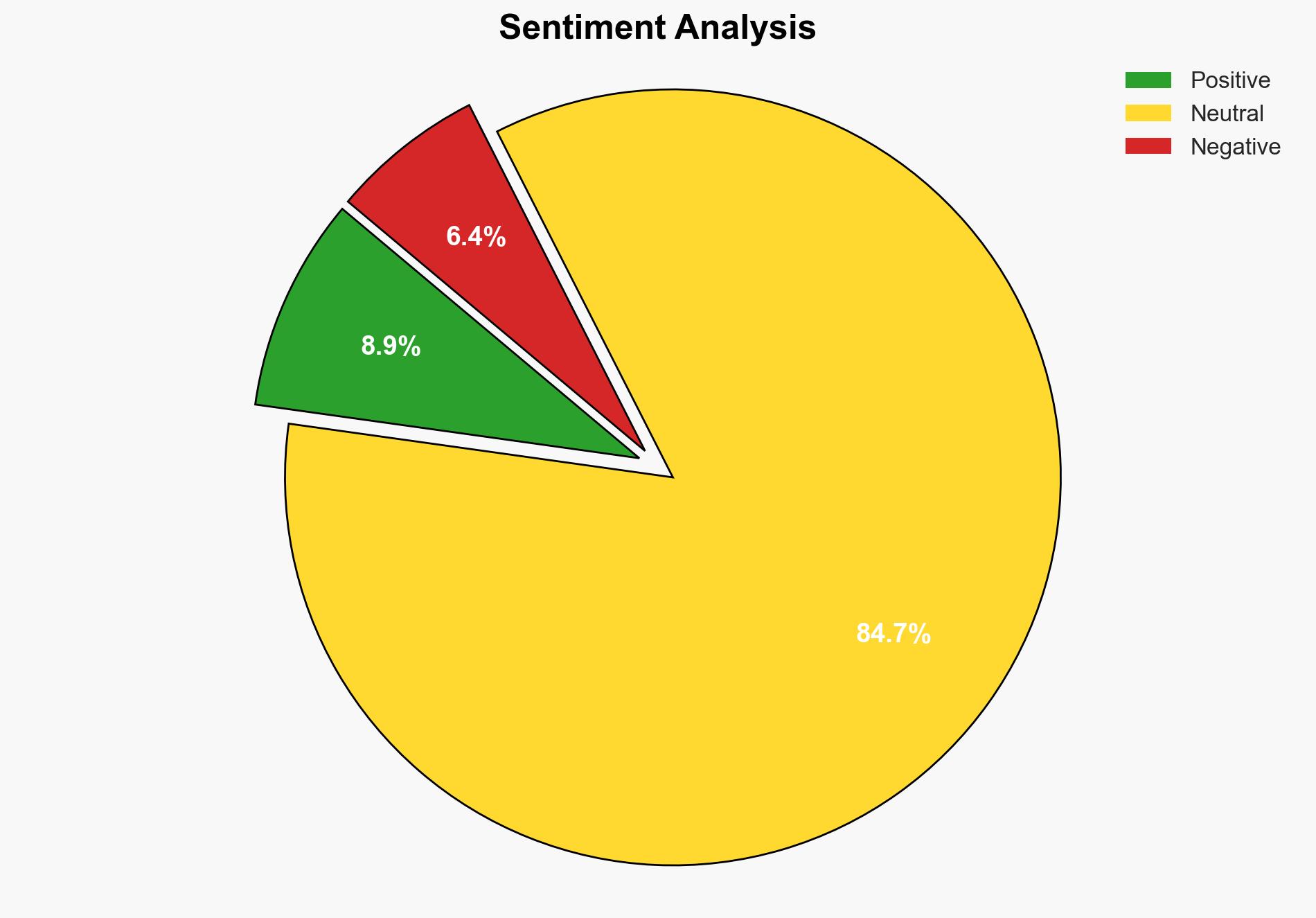
The Dutch government’s decision to relinquish control over Nexperia, a Chinese-owned chipmaker, appears to be a strategic move to ease tensions with China and ensure semiconductor supply stability. The most supported hypothesis is that this decision is a calculated diplomatic gesture to balance national security concerns with economic interests. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes monitoring the situation closely for any shifts in geopolitical dynamics and preparing contingency plans for potential supply chain disruptions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The Dutch government is relinquishing control over Nexperia primarily to de-escalate tensions with China and secure a stable supply of semiconductors crucial for the global automotive industry.
Hypothesis 2: The decision is driven by internal political pressures and economic considerations, with less emphasis on international diplomatic relations.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the context of recent diplomatic engagements and the critical nature of semiconductor supply chains. The involvement of high-level meetings and the timing of the decision following constructive discussions with Chinese authorities support this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: The Dutch government has assessed that the risks associated with relinquishing control are outweighed by the benefits of improved diplomatic relations and semiconductor supply stability.
Red Flags: The potential for miscommunication or misinterpretation of the Dutch government’s intentions by other international stakeholders, particularly the United States, which may view this move as undermining broader efforts to limit Chinese influence in critical technology sectors.
Deception Indicators: The possibility that Chinese authorities may not fully honor commitments to ensure supply chain stability, using the situation to gain leverage in broader geopolitical negotiations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The decision could lead to improved short-term semiconductor supply stability but may also embolden China to exert more influence over European technology sectors. There is a risk of political backlash from allies, particularly the U.S., which could result in strained transatlantic relations. Additionally, there is a potential for cyber and informational threats if the situation is perceived as a weakening of European resolve against Chinese technological expansion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Engage in diplomatic dialogues with key allies to clarify the rationale behind the decision and mitigate any potential misunderstandings. Develop contingency plans for semiconductor supply chain disruptions.
- Best Scenario: The decision leads to stabilized semiconductor supplies and improved diplomatic relations with China without significant backlash from allies.
- Worst Scenario: The move is perceived as capitulation to Chinese pressure, leading to strained relations with the U.S. and potential supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Most-likely Scenario: Short-term improvements in semiconductor supply are achieved, but long-term geopolitical tensions persist, requiring ongoing diplomatic and strategic management.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
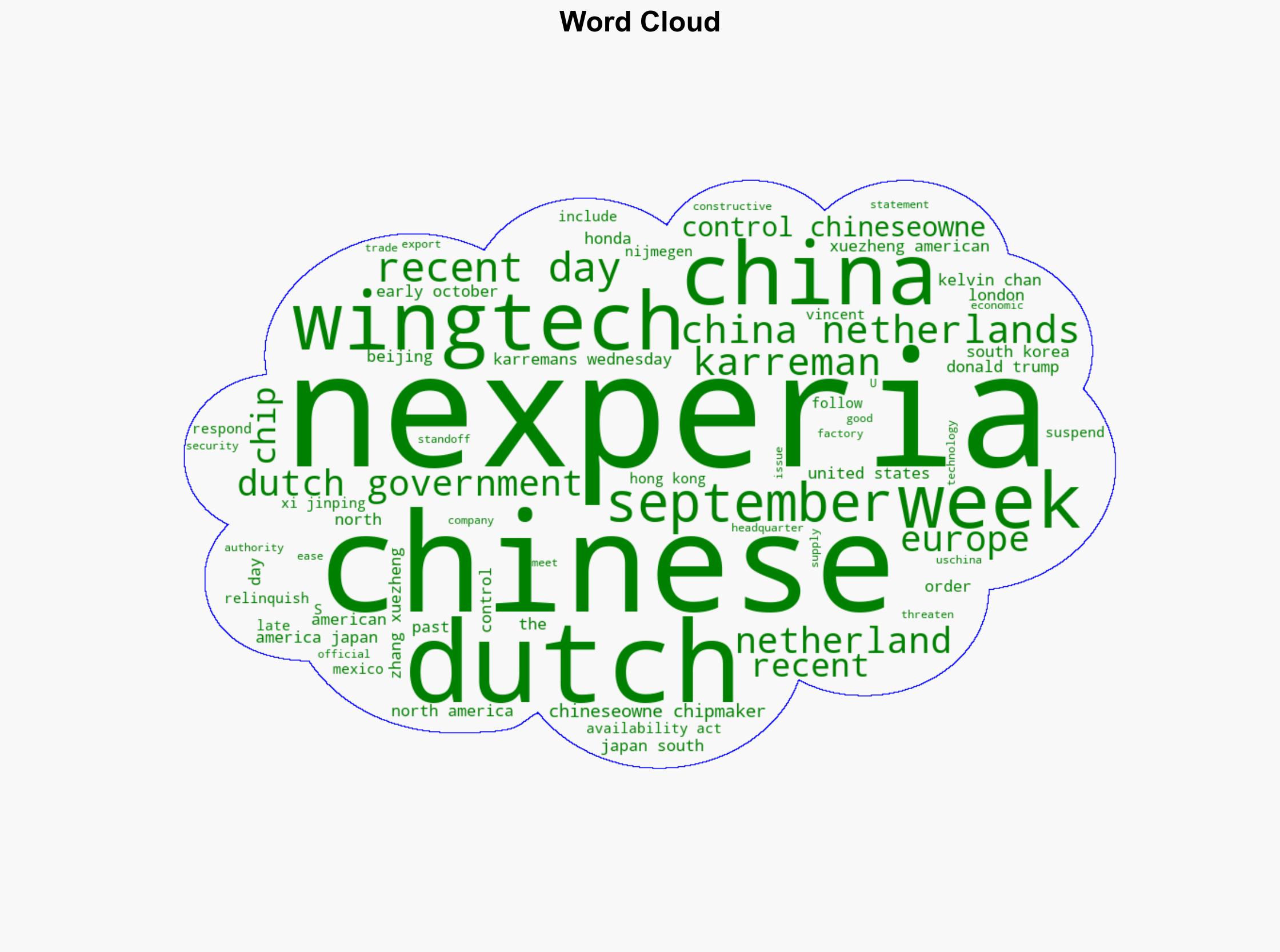
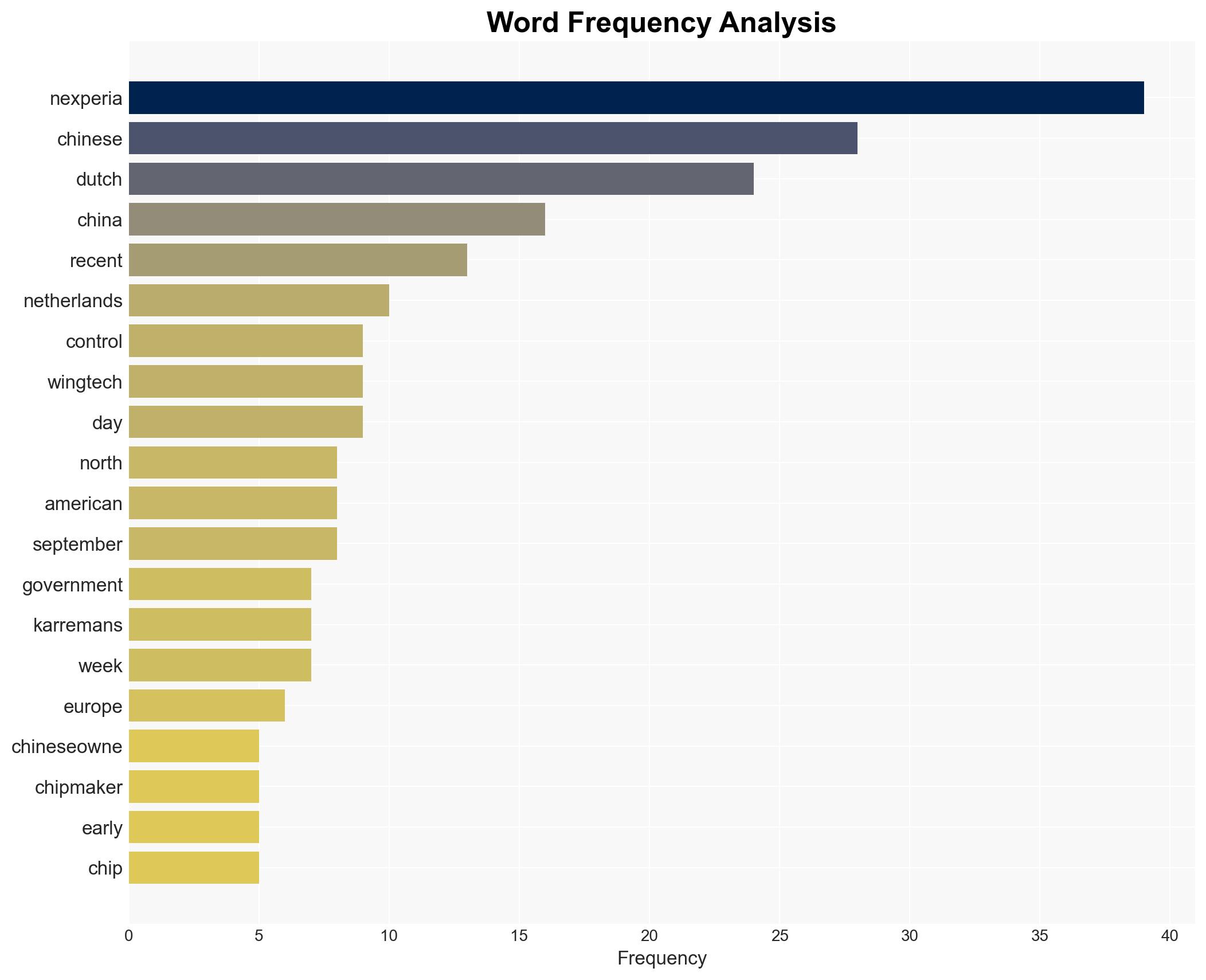
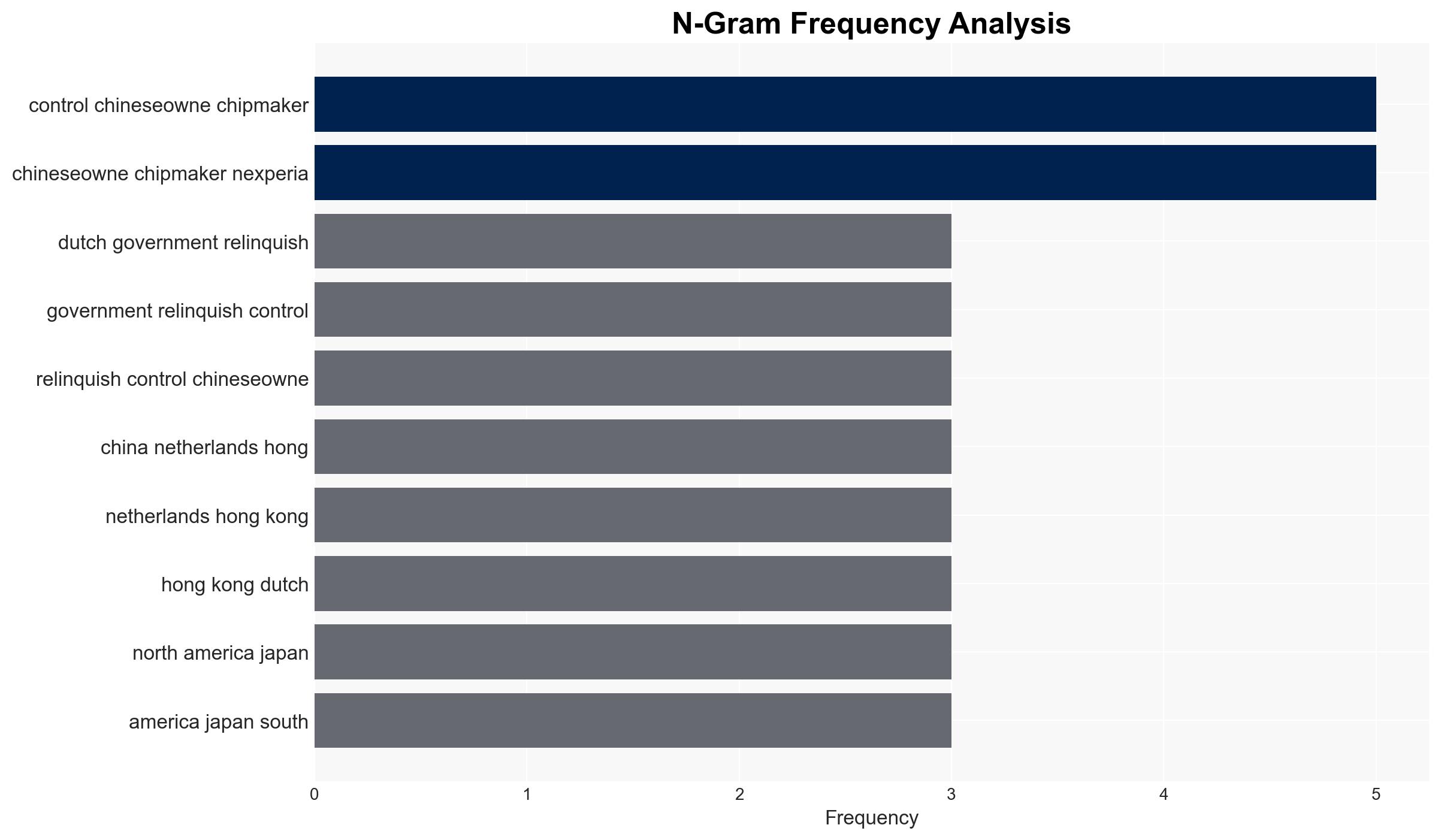
Vincent Karremans, Economic Affairs Minister; Wingtech Technology; Zhang Xuezheng, Wingtech Founder; Nexperia.
7. Thematic Tags
National Security Threats, Semiconductor Supply Chain, Geopolitical Relations, Economic Diplomacy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us