Dutch Police Detain 21-Year-Old for Selling Access to JokerOTP Phishing Tool Targeting Financial Accounts
Published on: 2026-02-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Police arrest seller of JokerOTP MFA passcode capturing tool
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
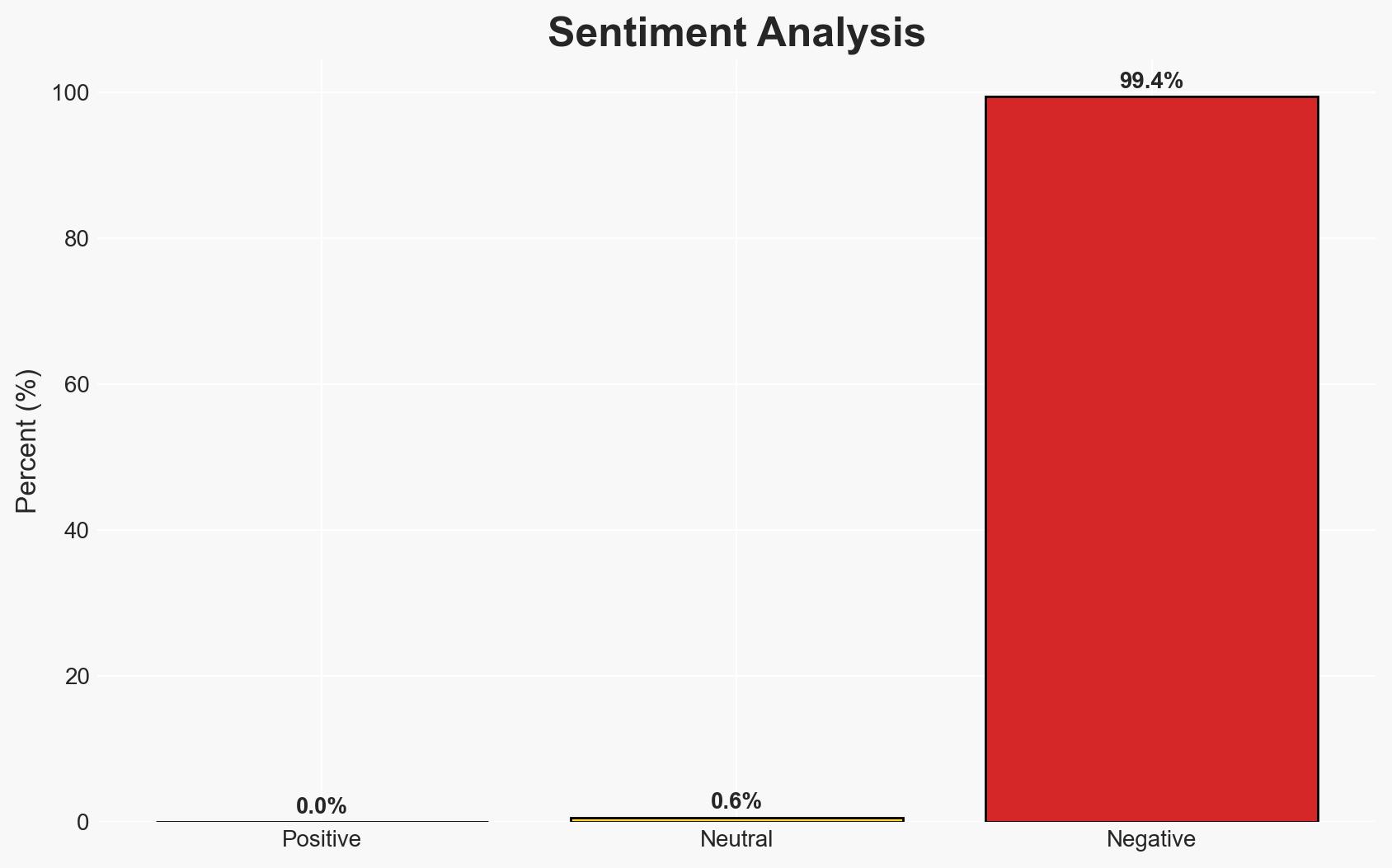
The arrest of a 21-year-old in the Netherlands for selling access to the JokerOTP phishing tool highlights ongoing vulnerabilities in multi-factor authentication systems. The operation has resulted in significant financial losses and affected users in multiple countries. The most likely hypothesis is that the dismantling of this operation will temporarily disrupt similar cybercriminal activities, but the underlying threat persists. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The arrest and dismantling of the JokerOTP operation will significantly disrupt similar phishing-as-a-service operations. Supporting evidence includes the arrest of key individuals and the identification of numerous buyers. However, the persistence of similar tools and techniques in the cybercriminal ecosystem contradicts this view.
- Hypothesis B: The disruption is temporary, and similar operations will quickly adapt or re-emerge. This is supported by the widespread availability of similar tools and the adaptability of cybercriminal networks. The ongoing investigation and potential prosecution of buyers may deter some actors but is unlikely to eliminate the threat entirely.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the resilience and adaptability of cybercriminal networks. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant decrease in similar phishing attacks or the emergence of new, more effective law enforcement strategies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The JokerOTP tool was a significant player in the phishing-as-a-service market; law enforcement actions will have a deterrent effect; cybercriminals will continue to seek new methods to bypass MFA.
- Information Gaps: The full extent of the network of buyers and their capabilities; the potential existence of other similar tools not yet identified.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of the tool’s market share; reliance on law enforcement sources may introduce bias; cybercriminals may use misinformation to mislead investigations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to temporary disruption in phishing operations but may also drive innovation in cybercriminal tactics. The broader dynamics of cybercrime and law enforcement efforts will continue to evolve.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation in cybercrime investigations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and potential for improved security measures in MFA systems.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible shifts in cybercriminal strategies to target other vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Continued financial losses and erosion of trust in digital services could impact economic stability and consumer behavior.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of phishing-as-a-service platforms; increase public awareness campaigns on MFA vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies to improve MFA security; invest in law enforcement cyber capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Significant reduction in phishing attacks due to improved security measures and law enforcement success.
- Worst: Emergence of more sophisticated tools that bypass current MFA systems.
- Most-Likely: Continued adaptation by cybercriminals, with periodic disruptions by law enforcement.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
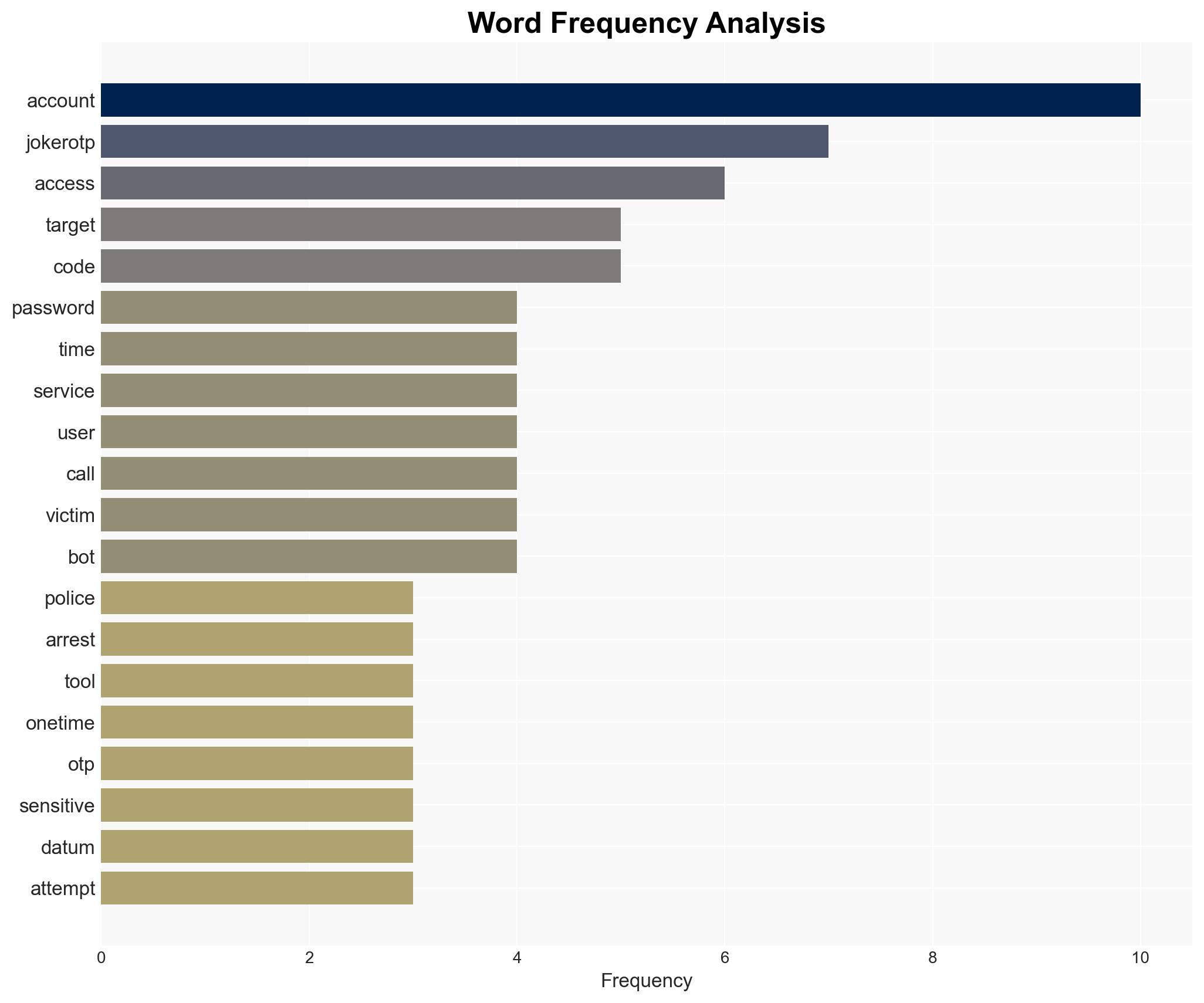
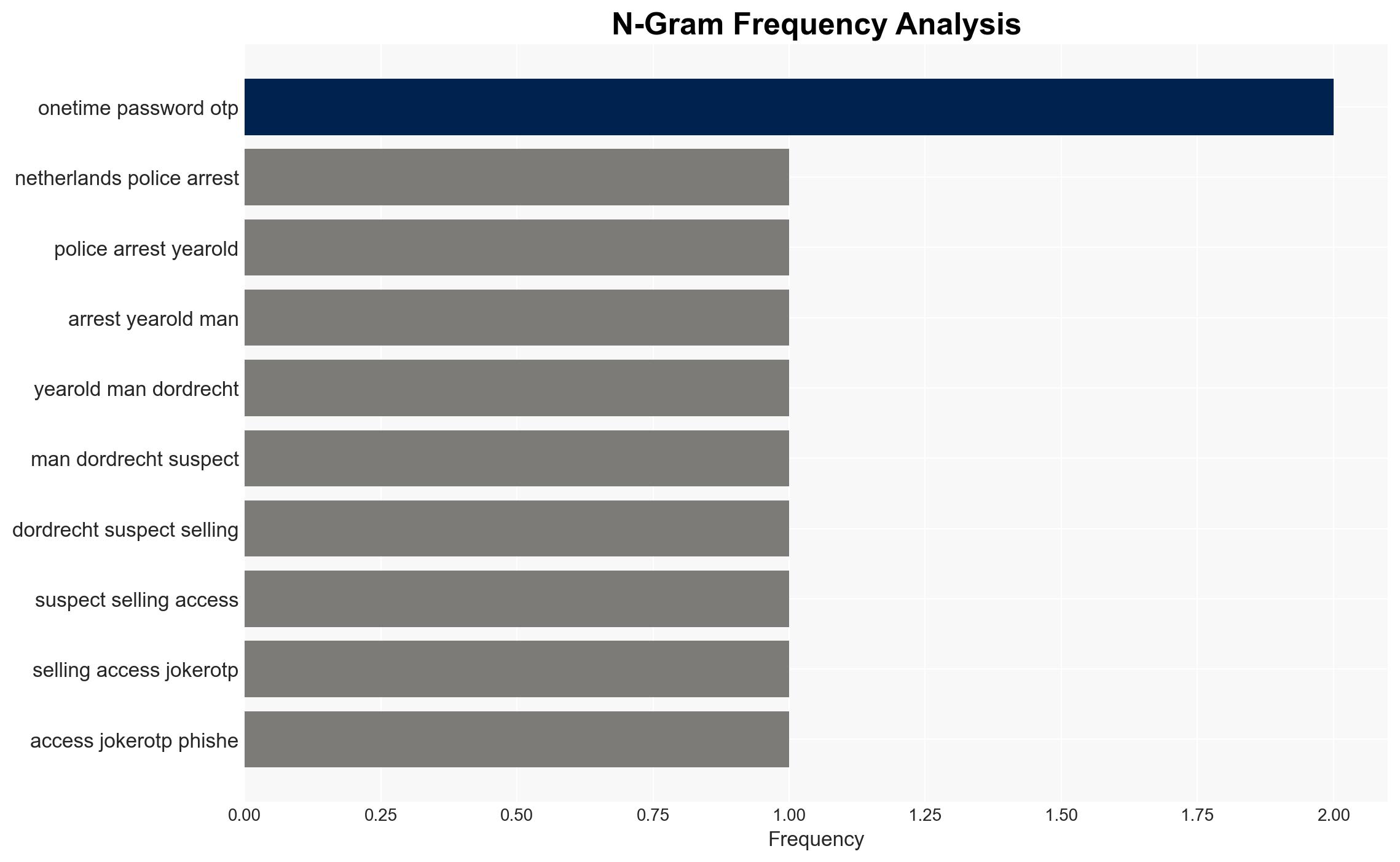
- 21-year-old suspect from Dordrecht (name undisclosed)
- JokerOTP developer (arrested in April 2025)
- Co-developer known as ‘spit’ and ‘defone123’ (arrested in August)
- Anouk Bonekamp, team leader of Cybercrime Oost-Brabant
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, phishing-as-a-service, multi-factor authentication, law enforcement, financial fraud, cyber security, international cooperation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us