Emergency Update Released for Microsoft Office Zero-Day Vulnerability CVE-2026-21509 Amid Active Exploits
Published on: 2026-01-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Microsoft Office Zero-Day CVE-2026-21509 – Emergency Patch Issued for Active Exploitation
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
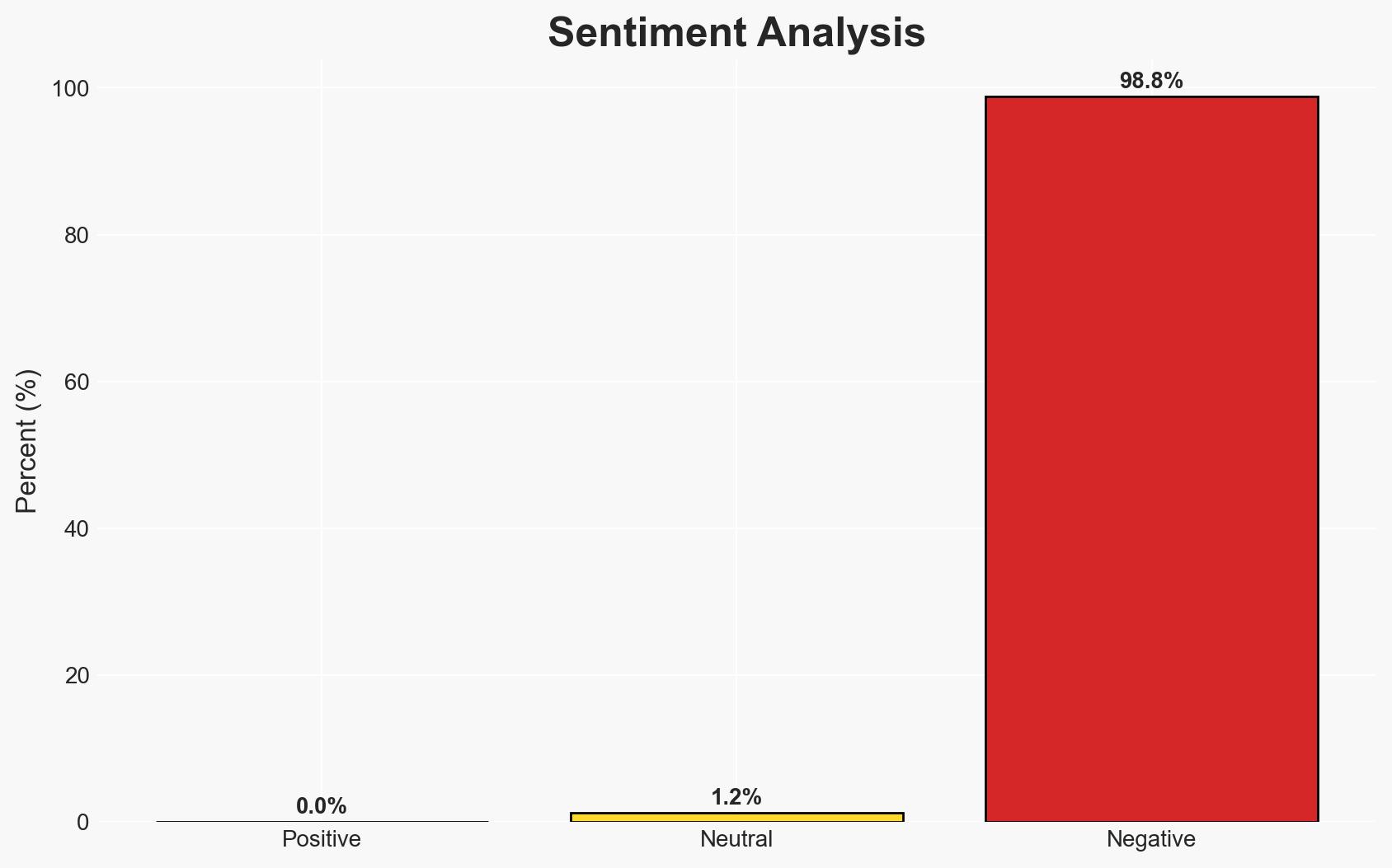
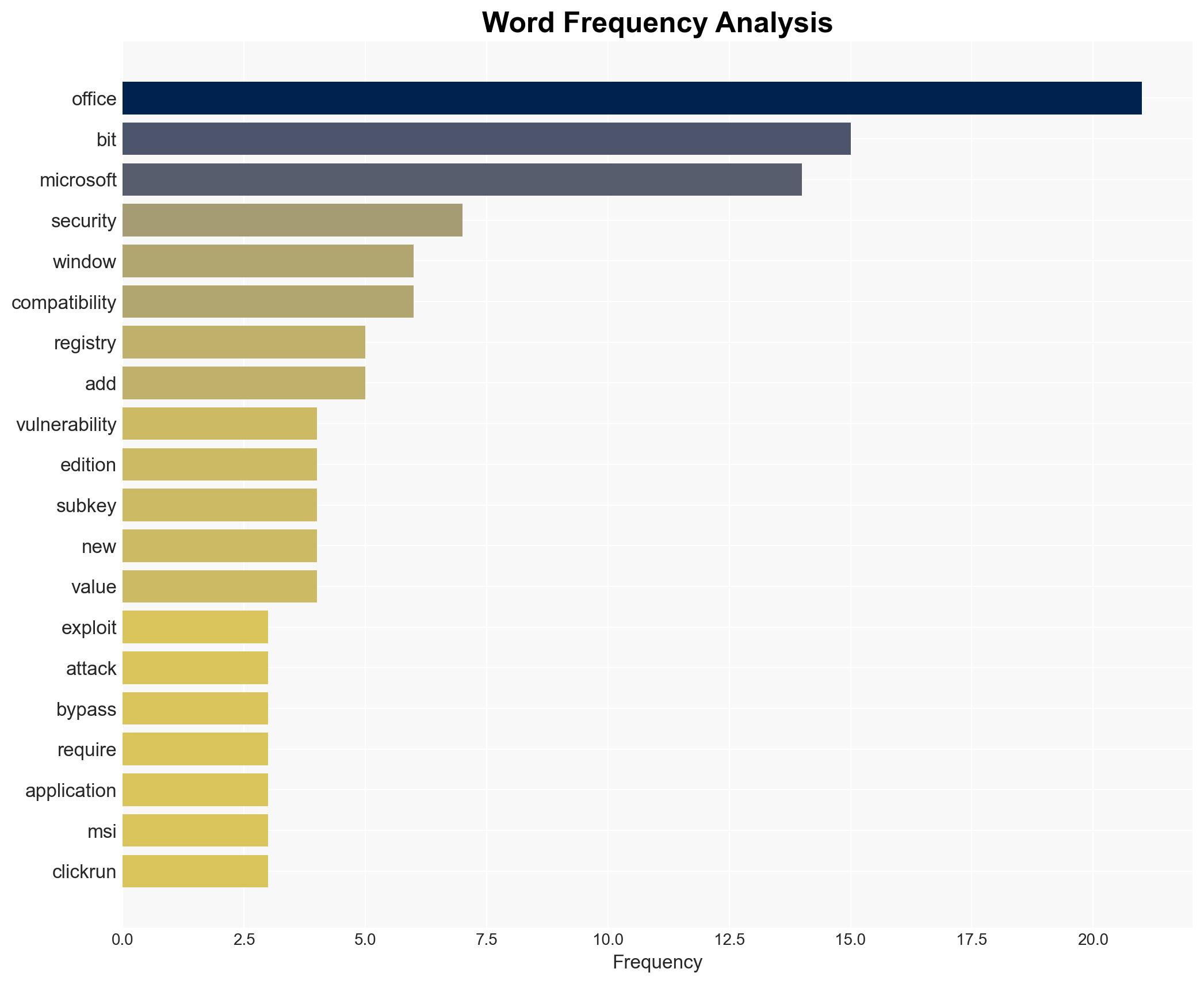
The CVE-2026-21509 zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft Office, with a CVSS score of 7.8, is actively exploited, necessitating immediate patching. The vulnerability allows attackers to bypass security features through specially crafted Office files. Microsoft has issued patches and mitigation steps, but the scope of exploitation remains unclear. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the lack of detailed attack data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is being exploited by state-sponsored actors targeting specific high-value organizations. This is supported by the high-severity rating and the nature of the vulnerability, which suggests a sophisticated threat actor. However, the lack of detailed attack information limits certainty.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation is opportunistic, carried out by cybercriminals targeting a broad range of users for financial gain. The requirement for user interaction (opening a file) aligns with typical cybercriminal tactics. Contradicting this is the absence of widespread reports of such attacks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the typical exploitation method involving user interaction, which is common in cybercrime. Indicators such as targeted attack reports could shift this judgment towards Hypothesis A.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is actively exploited; Microsoft’s patches are effective; user interaction is required for exploitation; the scope of exploitation is limited to Office versions specified.
- Information Gaps: Details on the nature and scope of the attacks exploiting this vulnerability; identification of threat actors involved; effectiveness of mitigation steps in diverse environments.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating the sophistication of the threat actor; reliance on Microsoft’s advisory without independent verification; possible deception in the reported scope of exploitation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of CVE-2026-21509 could lead to broader cybersecurity challenges if not contained. The situation could evolve with increased sophistication of attacks or discovery of additional vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored involvement is confirmed, particularly if linked to geopolitical adversaries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for organizations in critical sectors; potential for increased cyber threat levels.
- Cyber / Information Space: Risk of data breaches and information leaks; potential for misinformation if attacks are misattributed.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected organizations; disruption to business operations and public trust in software security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Ensure all systems are patched; educate users on phishing risks; monitor for unusual activity related to Office applications.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience through regular security audits; enhance threat intelligence sharing; strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity entities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid containment and patching prevent further exploitation.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Continued opportunistic attacks with moderate impact, mitigated by patch adoption.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC)
- Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC)
- Office Product Group Security
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerability, Microsoft Office, patch management, threat intelligence, cybercrime, state-sponsored threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us