Emerging Trends in Automated Exploit Development Using Advanced Language Models
Published on: 2026-01-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The coming industrialisation of exploit generation with LLMs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The industrialization of exploit generation using large language models (LLMs) like GPT-5.2 and Opus 4.5 is likely to significantly enhance the capabilities of state and non-state actors in cyber operations. This development may reduce the dependency on human hackers, shifting the focus to computational resources. The most likely hypothesis is that LLMs will become a central tool in offensive cyber operations, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: LLMs will enable the rapid development of sophisticated exploits, reducing the need for skilled human hackers. This is supported by the experiment’s success in generating multiple exploits under complex constraints. However, uncertainties include the scalability of these methods and potential countermeasures by defenders.
- Hypothesis B: The complexity and unpredictability of real-world environments will limit the effectiveness of LLM-generated exploits, maintaining the need for human expertise. This is contradicted by the experiment’s results but supported by the inherent unpredictability of real-world systems.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the demonstrated capability of LLMs to solve complex tasks efficiently. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include advancements in defensive technologies or significant failures of LLMs in real-world applications.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: LLMs will continue to improve in capability; computational resources will remain accessible; adversaries will prioritize LLMs in their cyber arsenals.
- Information Gaps: The scalability of these methods to diverse real-world systems and the effectiveness of potential countermeasures are not well understood.
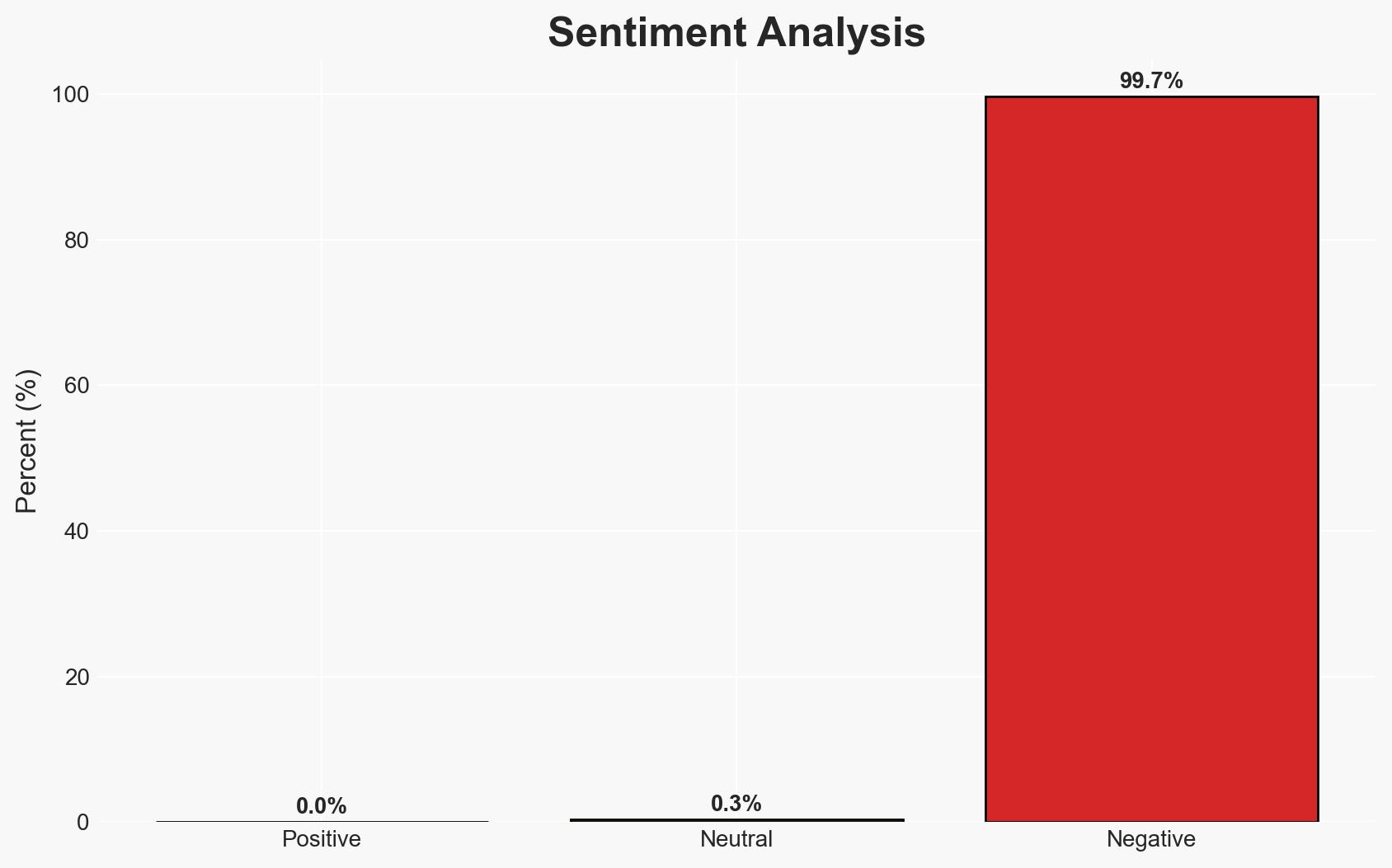
- Bias & Deception Risks: The source may have a vested interest in promoting LLM capabilities; results may not fully represent real-world complexities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The industrialization of exploit generation could significantly alter the cyber threat landscape, potentially lowering the barrier to entry for sophisticated cyber operations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased cyber capabilities could escalate tensions between states, leading to a cyber arms race.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced exploit capabilities could be leveraged by terrorist groups, increasing the threat of cyber-terrorism.
- Cyber / Information Space: Widespread use of LLMs in cyber operations could lead to more frequent and sophisticated cyber attacks.
- Economic / Social: Potential disruptions to critical infrastructure could have severe economic and social impacts.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of LLM developments, enhance cyber defenses, and engage with international partners to discuss norms and regulations.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, invest in defensive AI technologies, and establish partnerships with tech companies for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures reduce the impact of LLM-generated exploits.
- Worst: Widespread adoption of LLMs leads to a surge in cyber attacks.
- Most-Likely: Gradual integration of LLMs into cyber operations with periodic significant incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
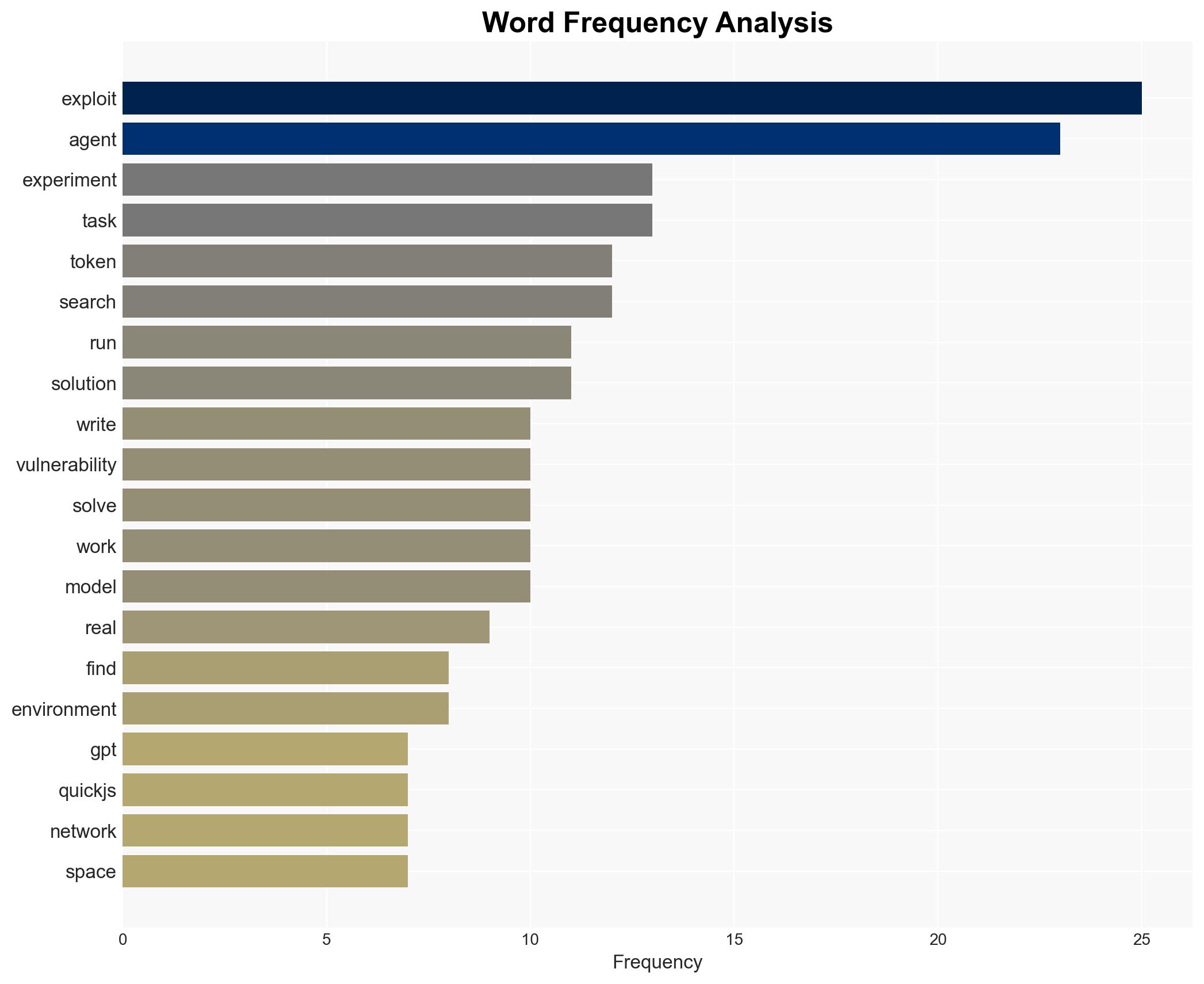
cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, exploit generation, LLMs, cyber operations, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us