Emerging Trends in Economic Warfare: The Subtle Shift in Global Conflict Dynamics
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: A New Era of Economic Warfare Arrives
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The current era of economic warfare is characterized by strategic exploitation of interdependence, particularly through cyber-enabled intellectual property theft and supply chain manipulation. The United States’ openness in research and innovation is being weaponized against it, posing significant risks to national security and economic stability. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the complexity and evolving nature of the threat landscape.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The strategic exploitation of openness in U.S. innovation ecosystems is primarily driven by state-sponsored actors aiming to gain economic and technological superiority. This is supported by documented cases of intellectual property theft and supply chain disruptions. However, the precise attribution to specific state actors remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The observed economic warfare tactics are primarily opportunistic actions by non-state actors, including corporate competitors, seeking to gain a competitive edge. While this could explain some incidents, the coordinated nature of activities and the scale of operations suggest a more organized effort, likely involving state actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the systematic and strategic nature of the activities observed, which align with known state-sponsored economic espionage patterns. Indicators such as increased cyber intrusions and targeted supply chain disruptions could further validate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. innovation model remains vulnerable to exploitation; state-sponsored actors have the capability and intent to engage in economic warfare; supply chain dependencies are critical vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: Specific attribution of cyber activities to state actors; detailed understanding of adversaries’ strategic objectives; comprehensive mapping of vulnerable supply chains.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias in attributing activities to state actors; potential misinformation from adversaries to obscure true intentions; reliance on open-source data that may be incomplete or outdated.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of economic warfare tactics could lead to increased geopolitical tensions, particularly between major global powers. The persistence of these tactics may destabilize economic systems and undermine trust in international trade and cooperation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for escalation into broader geopolitical conflicts; erosion of alliances due to mistrust in shared innovation ecosystems.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased vulnerability to cyber-attacks targeting critical infrastructure; potential for economic destabilization to fuel extremist narratives.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened cyber threat landscape with persistent intrusions; potential for misinformation campaigns to obscure attribution and intent.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of supply chains leading to economic instability; potential loss of competitive edge in key industries; social unrest due to economic impacts.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cyber activities targeting innovation sectors; initiate diplomatic engagements to address state-sponsored economic espionage; conduct supply chain vulnerability assessments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to protect critical supply chains; strengthen public-private partnerships for cybersecurity; invest in counterintelligence capabilities focused on economic threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: International cooperation leads to reduced economic warfare activities.
- Worst: Escalation into broader geopolitical conflict and significant economic disruption.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-level economic warfare with periodic escalations and ongoing vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
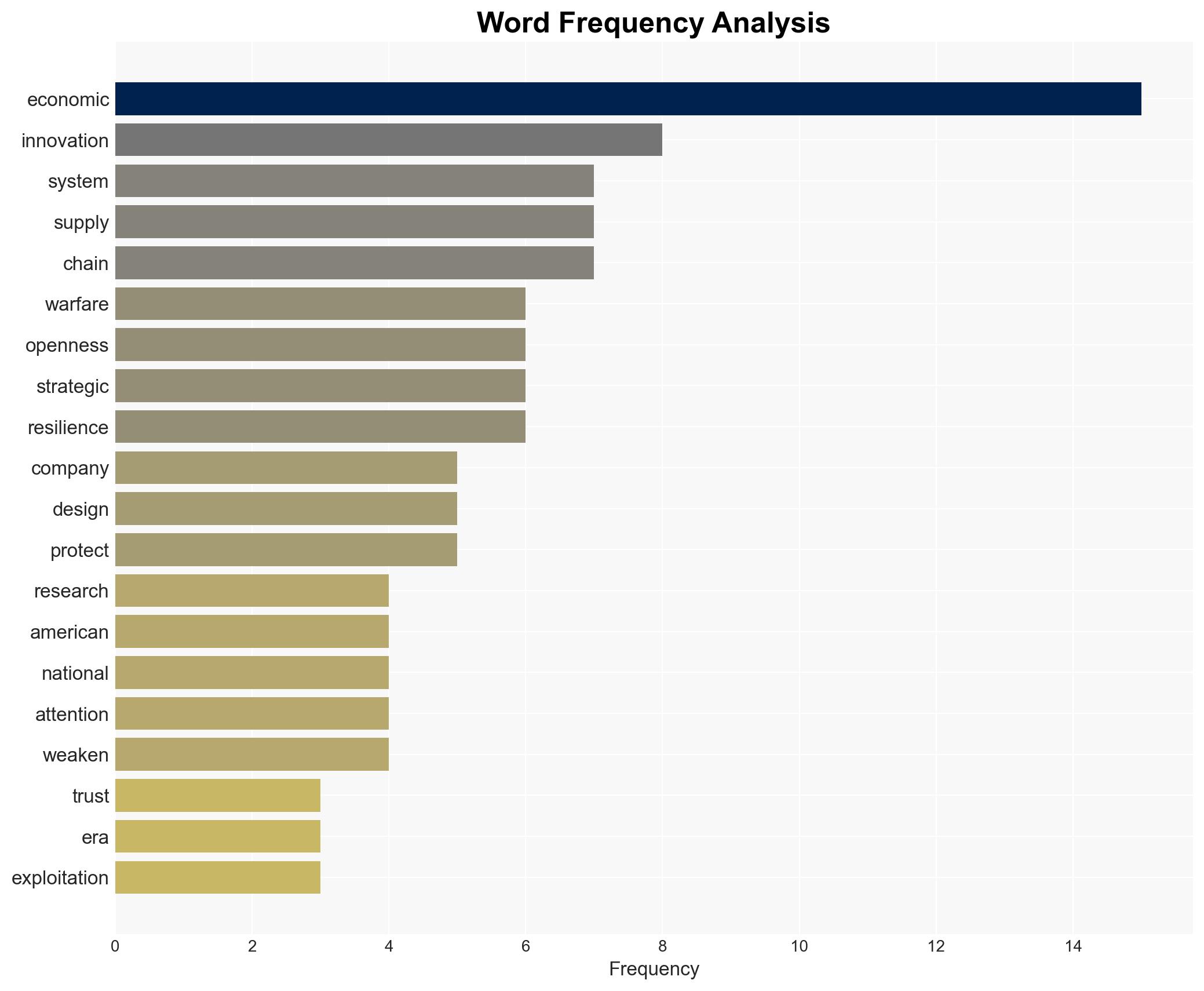
cybersecurity, economic warfare, cyber-espionage, supply chain security, intellectual property theft, state-sponsored threats, innovation ecosystems, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us