Empowering Afghan Resistance: Strategies to Undermine Taliban Control Amidst Ongoing Crisis
Published on: 2026-01-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Lawrences Shadow How Afghan Resistance Can Topple the Taliban
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The current geopolitical and internal dynamics in Afghanistan present an opportunity for the United States to support anti-Taliban resistance groups, potentially destabilizing Taliban control. The most likely hypothesis is that indirect support and strategic enablement could lead to significant erosion of Taliban power, aligning with U.S. security interests. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, acknowledging the complex and fluid nature of the situation.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. can effectively empower Afghan resistance groups to destabilize and potentially topple the Taliban through indirect support, such as intelligence sharing and deniable funding. Supporting evidence includes current Taliban vulnerabilities and historical precedents of successful insurgencies. Key uncertainties involve the cohesion and capability of resistance groups.
- Hypothesis B: Efforts to empower resistance groups will fail to achieve strategic objectives due to potential Taliban countermeasures, lack of resistance cohesion, and regional geopolitical complexities, particularly involving Pakistan. Contradicting evidence includes the Taliban’s ongoing control over significant parts of Afghanistan and potential external support from sympathetic states.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the Taliban’s internal and external pressures, including economic collapse and conflict with Pakistan. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Taliban cohesion, external support dynamics, and resistance group effectiveness.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Taliban’s control is sufficiently weakened to be vulnerable to insurgency; resistance groups can be unified and effectively supported; U.S. support will not provoke significant international backlash.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the strength and cohesion of resistance groups; Taliban’s internal stability and external support mechanisms.
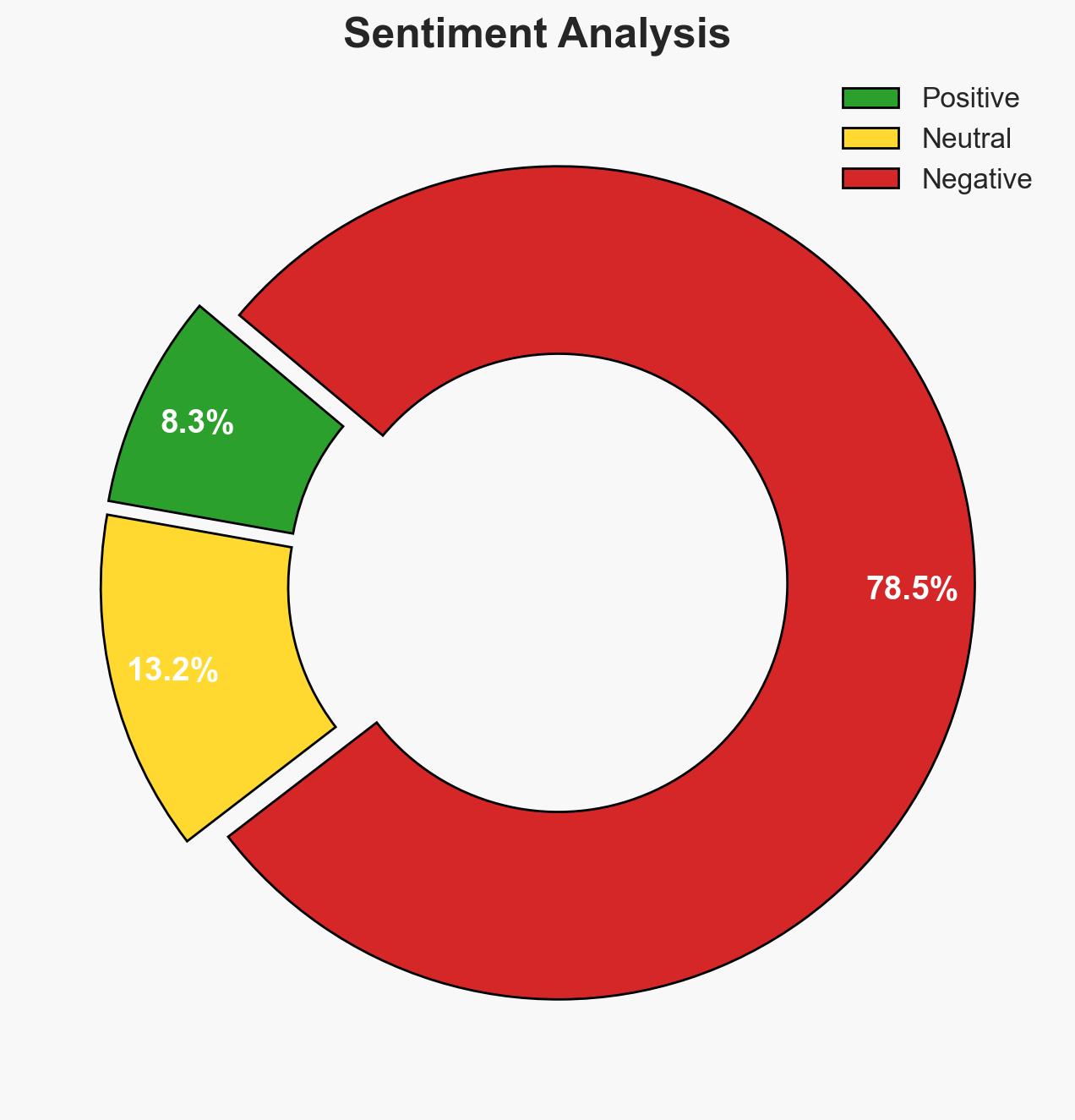
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of resistance capabilities; underestimation of Taliban resilience; source bias from resistance-aligned entities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The empowerment of Afghan resistance groups could lead to a protracted conflict, affecting regional stability and U.S. strategic interests. The situation may evolve with significant geopolitical, security, and economic repercussions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation of regional tensions, particularly with Pakistan, and shifts in alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased insurgency activity could lead to a more volatile security environment, with potential spillover effects.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased propaganda and misinformation campaigns by both Taliban and resistance groups.
- Economic / Social: Further economic destabilization could exacerbate humanitarian issues and social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on resistance groups; initiate discreet diplomatic engagements with regional partners.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to counter potential Taliban retaliation; strengthen partnerships with key regional actors.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Resistance gains significant ground, leading to Taliban concessions or collapse.
- Worst Case: Taliban consolidates power, resistance efforts collapse, leading to increased regional instability.
- Most Likely: Protracted conflict with fluctuating control, requiring sustained U.S. strategic engagement.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
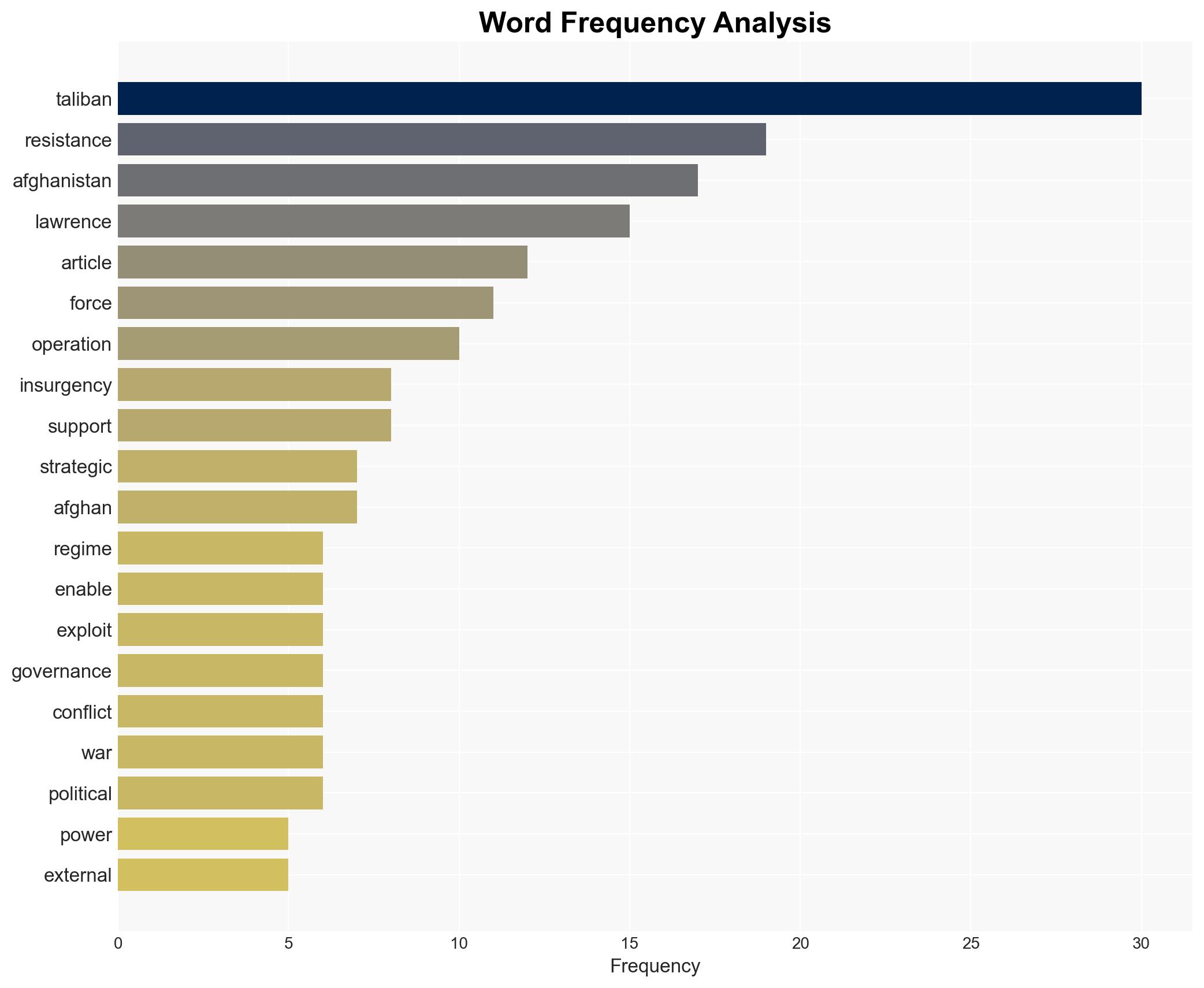
Counter-Terrorism, insurgency, geopolitical strategy, Taliban, Afghanistan, regional stability, intelligence operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us