Enterprise security grapples with AI threats, cybercrime escalation, and supply chain vulnerabilities
Published on: 2026-01-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Enterprise security faces a three-front war cybercrime AI misuse and supply chains
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
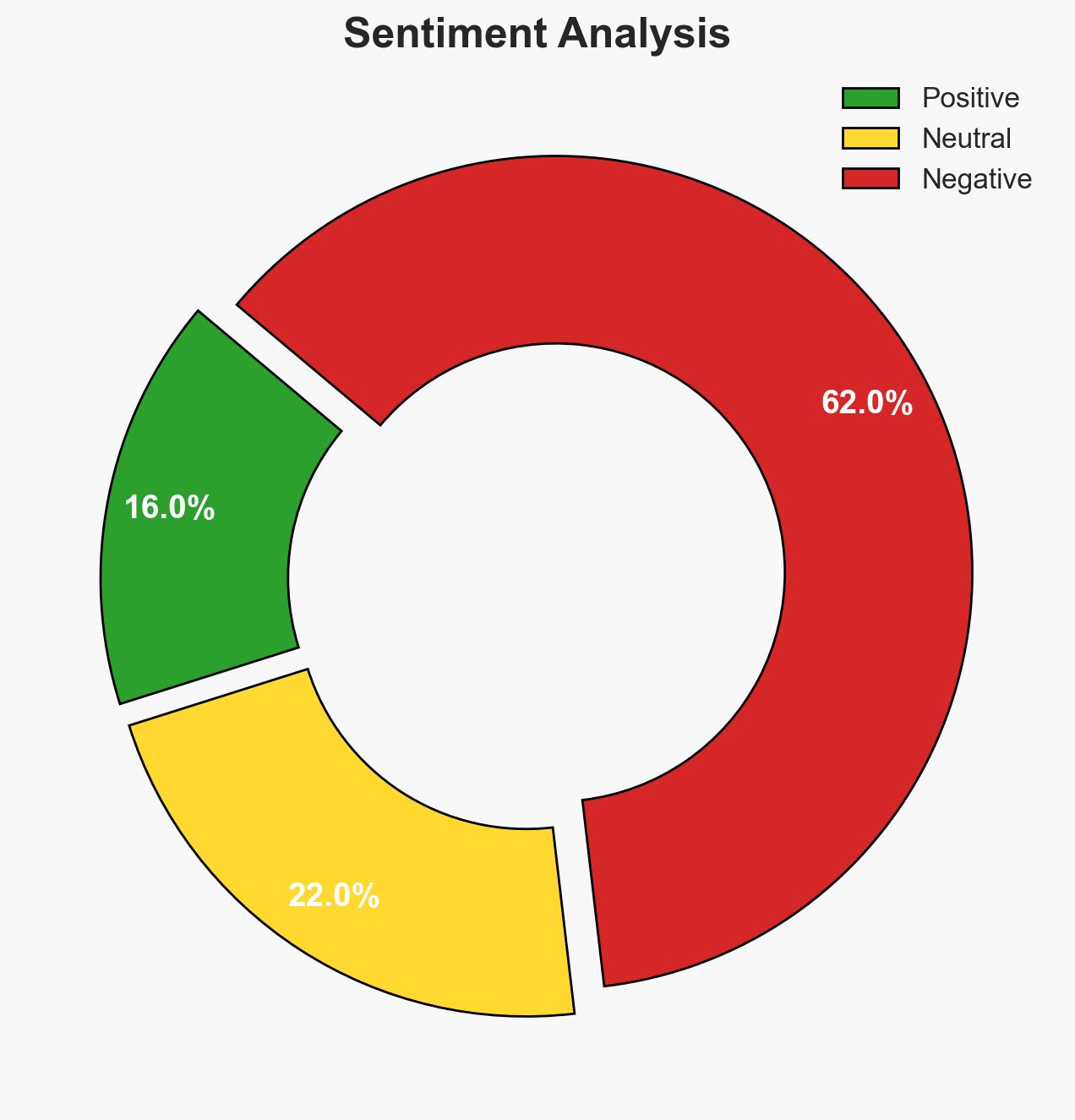
Organizations are increasingly vulnerable due to the convergence of AI misuse, geopolitical instability, and cybercrime, necessitating a shift from traditional cybersecurity to AI-driven defenses. The most likely scenario involves escalating AI-driven threats impacting global enterprises, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to uneven preparedness and response capabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI misuse and cybercrime are the primary drivers of increased security risks, with geopolitical factors playing a secondary role. This is supported by the rapid adoption of AI tools and their vulnerabilities, although geopolitical impacts are acknowledged. Key uncertainties include the pace of AI adoption and effectiveness of defensive measures.
- Hypothesis B: Geopolitical instability is the primary driver of increased security risks, with AI misuse and cybercrime as secondary factors. This is supported by organizations adjusting strategies in response to nation-state activities. However, the direct impact of AI misuse and cybercrime cannot be discounted.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate and tangible impacts of AI misuse and cybercrime on enterprise security, as evidenced by the rapid evolution of AI-driven threats. Indicators such as increased geopolitical tensions or significant regulatory changes could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI adoption will continue to outpace the development of adequate security measures; geopolitical tensions will persist; organizations will prioritize AI-driven defenses.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of AI-driven security measures; comprehensive assessments of geopolitical impacts on specific sectors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from organizations with vested interests in AI solutions; manipulation of threat data by adversaries to mislead defenders.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The convergence of AI misuse, geopolitical instability, and cybercrime could lead to a significant restructuring of enterprise security strategies. Over time, this may result in increased collaboration between private and public sectors and a shift in investment priorities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation or conflict over cybersecurity norms and AI regulation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment as AI tools are weaponized by both state and non-state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in AI-driven cyber operations, including misinformation and cyber-espionage.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruption due to increased security costs and potential loss of consumer trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of AI tool deployments; enhance threat intelligence sharing with government partners; conduct rapid vulnerability assessments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop AI-specific security protocols; invest in workforce training for AI management; establish international partnerships for AI governance.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective AI defenses reduce threat levels, with international cooperation on AI regulation.
- Worst: AI-driven attacks cause significant disruptions, with geopolitical tensions exacerbating security challenges.
- Most-Likely: Continued adaptation to AI threats, with uneven progress across sectors and regions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Paolo Dal Cin, global lead, Accenture Cybersecurity
- World Economic Forum
- Accenture
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
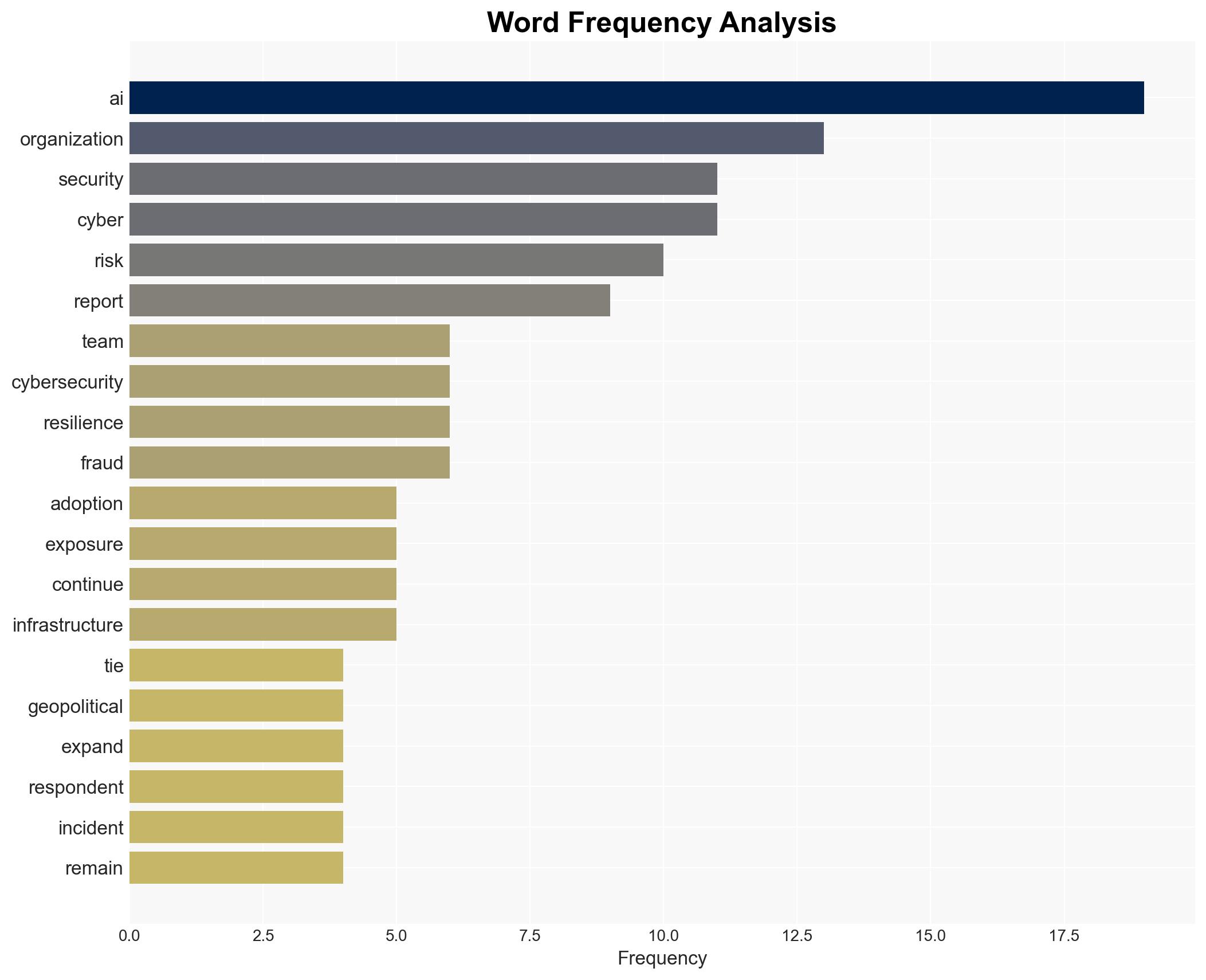
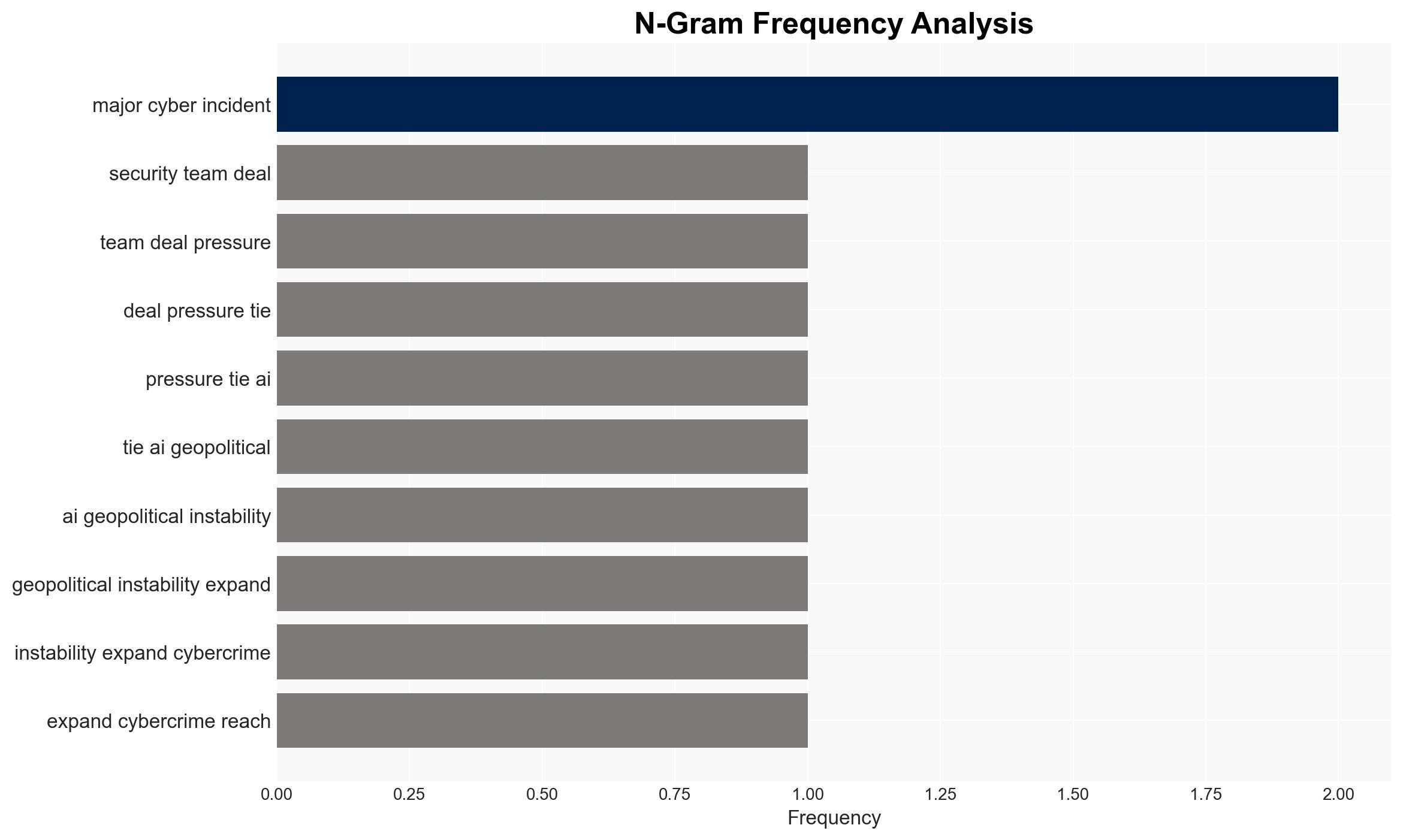
cybersecurity, AI security, cybercrime, geopolitical instability, enterprise risk, cybersecurity strategy, AI governance, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us