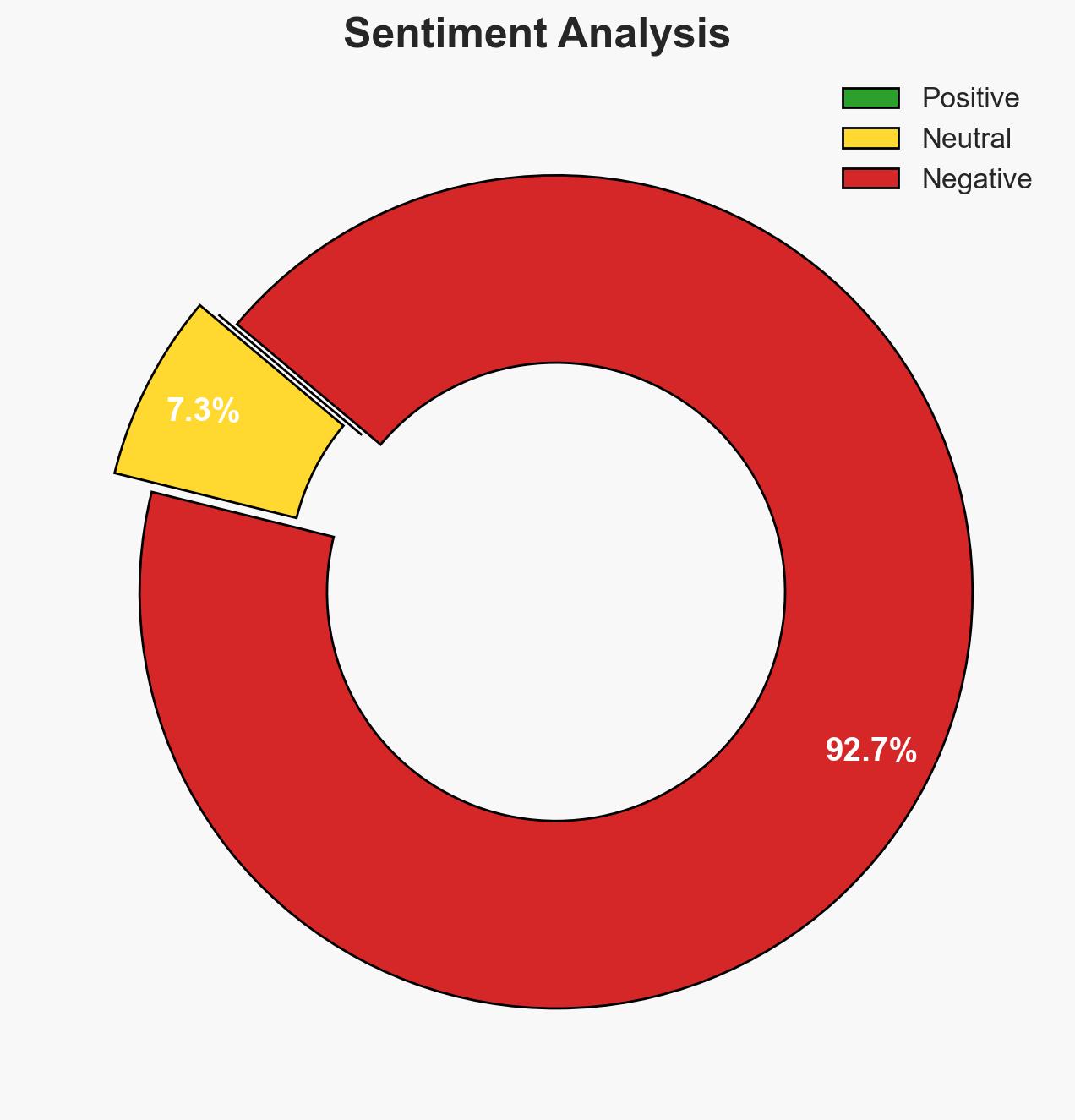
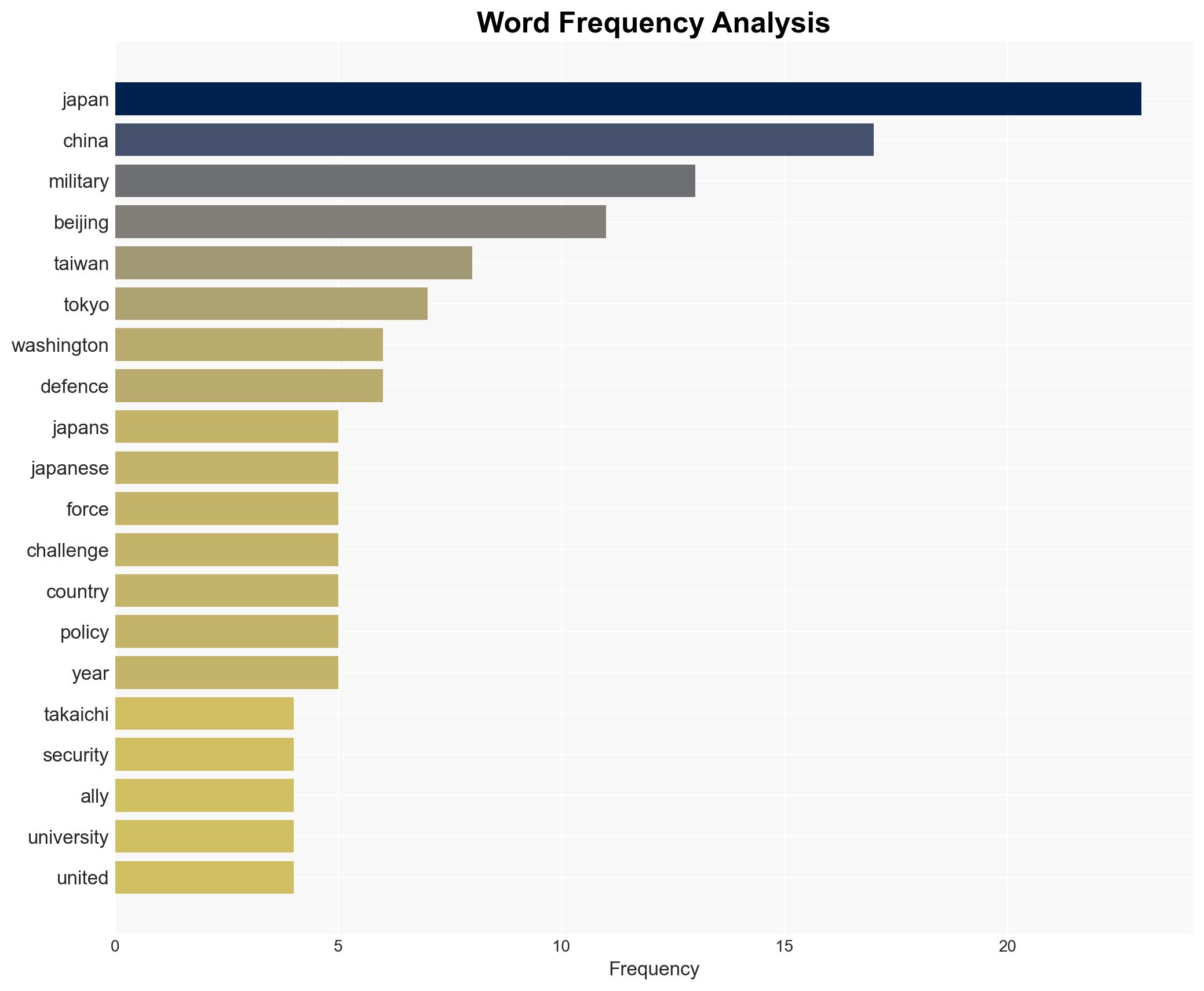
Escalating Tensions: Japan’s Military Remarks on Taiwan Strain Relations with China Amid Ongoing Diplomatic F…
Published on: 2025-12-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why the feud between Tokyo and Beijing could rage on for a while yet
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The ongoing diplomatic and military tensions between Japan and China, exacerbated by Japan’s recent assertive stance on Taiwan, are likely to persist due to strategic interests and regional security dynamics. The situation is influenced by the US-China-Japan triangle, with moderate confidence that Japan’s proactive role in regional security will continue to provoke strong responses from China.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Japan’s assertive stance on Taiwan is primarily driven by a strategic shift towards balancing China’s influence in the region, supported by its alliances with the US and other countries. Evidence includes Japan’s recent policy changes and military posture. However, uncertainties remain about the extent of US influence on Japan’s decisions.
- Hypothesis B: Japan’s actions are largely reactive to US pressure, with Tokyo following Washington’s lead in regional security matters. This hypothesis is contradicted by statements suggesting Japan is independently shaping its security policy. Key uncertainties include the internal decision-making processes within Japan’s government.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, as Japan appears to be actively shaping its security policy and engaging with multiple regional partners. Indicators such as Japan’s independent diplomatic initiatives could further validate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Japan will maintain its current security policy trajectory; US-Japan security ties remain strong; China perceives Japan’s actions as a direct challenge.
- Information Gaps: Detailed insights into Japan’s internal policy deliberations and China’s strategic calculus regarding Japan.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Chinese sources downplaying Japan’s autonomy; risk of misinterpretation of Japan’s intentions by external analysts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The Japan-China tensions could lead to increased regional instability, affecting diplomatic relations and security dynamics in East Asia. The situation may evolve with broader geopolitical shifts, particularly involving US-China relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic escalation or realignment of regional alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened military readiness and potential for miscalculations or skirmishes.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber operations targeting critical infrastructure or information campaigns to sway public opinion.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic sanctions or trade disruptions affecting regional economies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor diplomatic communications and military movements; engage in confidence-building measures to reduce tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances and partnerships; invest in cyber defense capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution and stabilization of relations.
- Worst: Military confrontation or significant economic fallout.
- Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic and military posturing with periodic escalations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Sanae Takaichi – Japanese Prime Minister
- Wu Xinbo – Dean, Institute of International Studies, Fudan University
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, regional security, US-China relations, Japan-China tensions, Taiwan, military strategy, diplomatic relations, economic sanctions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us