EU Faces Growing Challenges from Spyware and AI Amidst Ongoing Digital Rights Concerns in 2025
Published on: 2026-01-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 2025 Digital rights review Spyware AI war EU regulations
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
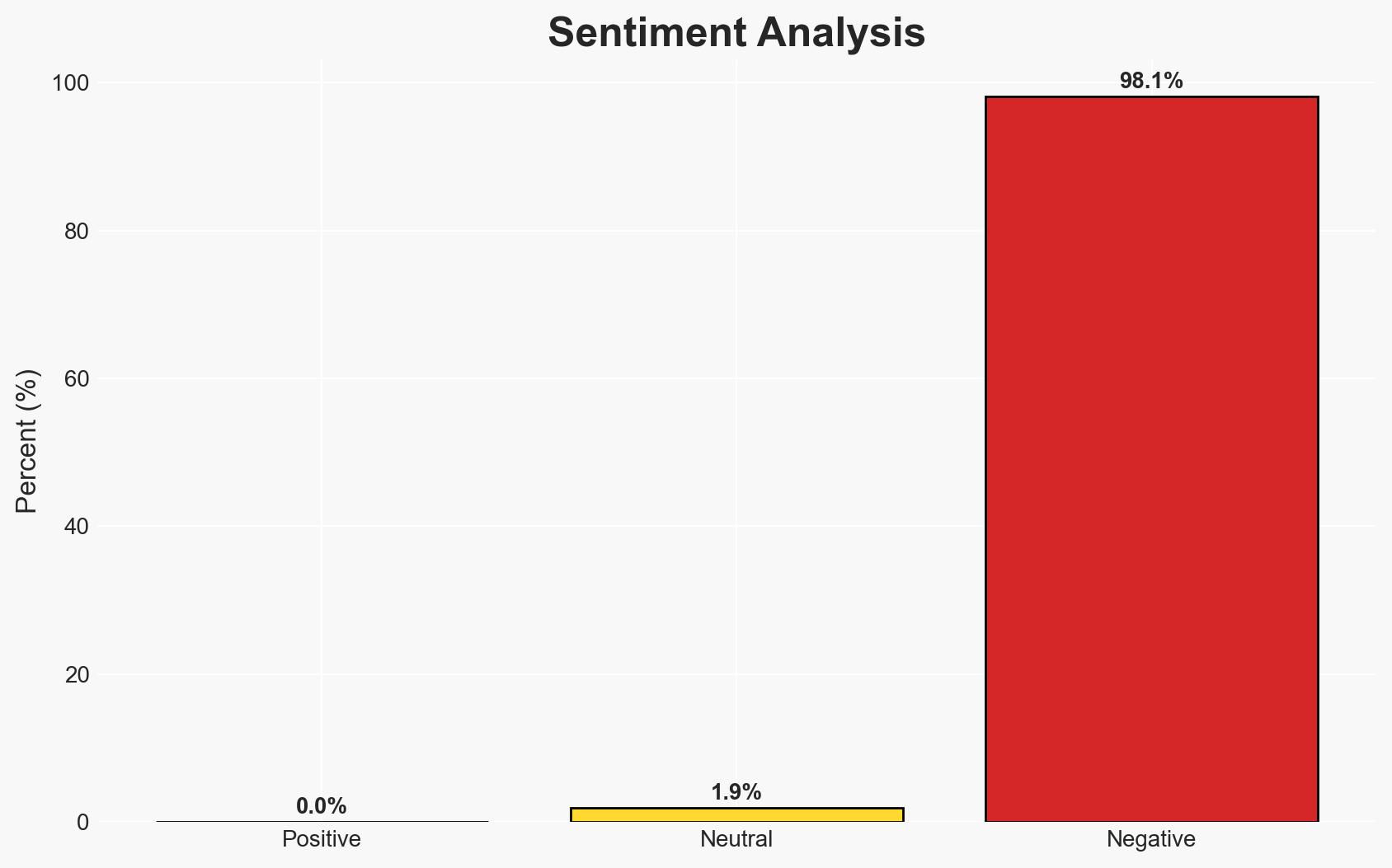
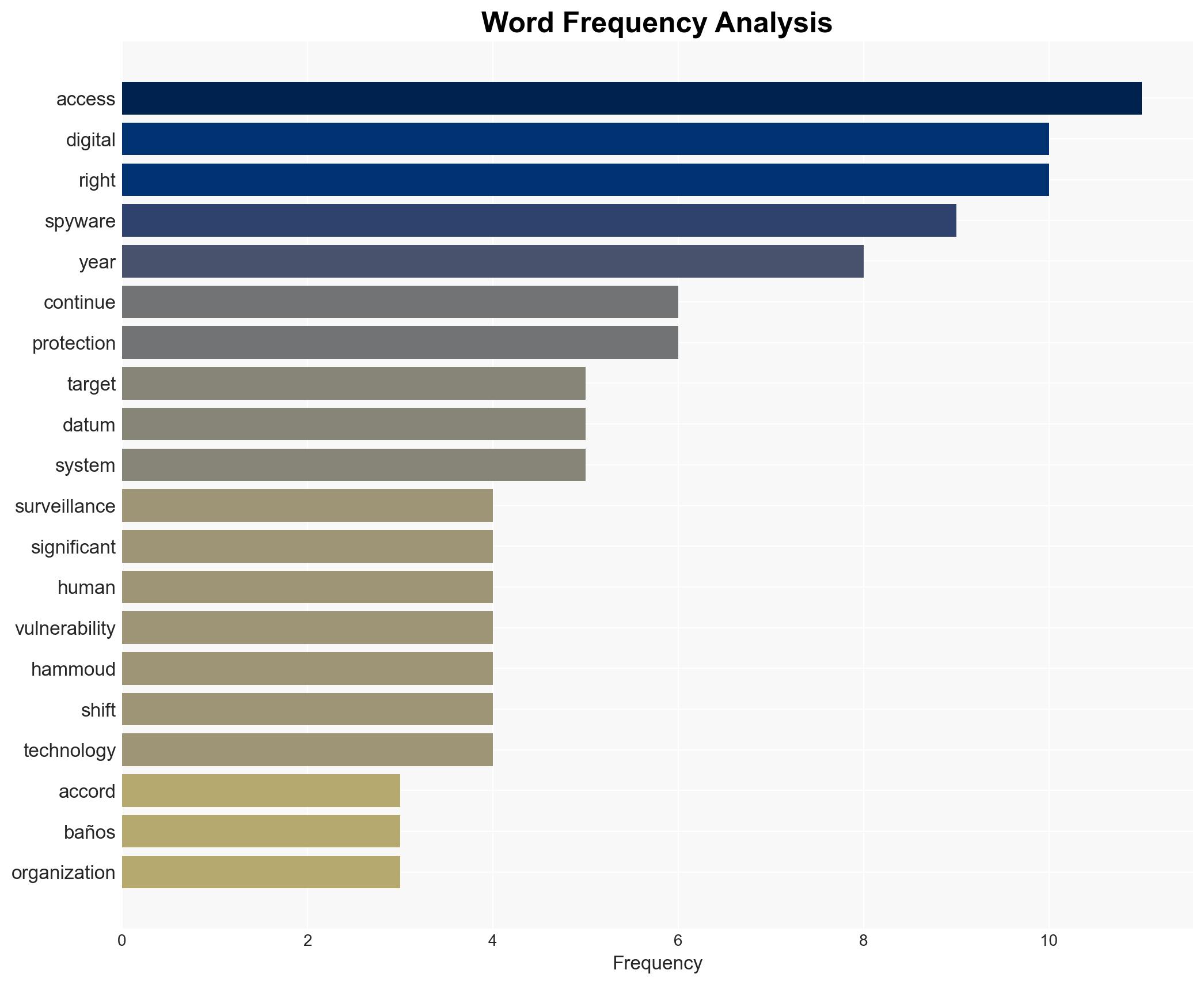
The proliferation of spyware, particularly zero-day exploits, continues to pose a significant threat to privacy and digital rights, despite regulatory efforts. The resilience of the mercenary spyware industry undermines these efforts, with moderate confidence in the assessment that current safeguards are insufficient. This affects journalists, activists, and potentially broader civil society.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The proliferation of spyware is primarily driven by state actors seeking to suppress dissent and monitor journalists and activists. Supporting evidence includes the use of spyware by governments, as reported by the Italian parliamentary committee. However, there is uncertainty regarding the full extent of state involvement.
- Hypothesis B: The proliferation is driven by private sector demand and the lucrative market for zero-day vulnerabilities. This is supported by the resilience of the mercenary spyware industry and the international market for vulnerabilities. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of transparency in private sector motivations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the documented resilience and adaptability of the spyware market. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of direct state sponsorship or changes in international regulatory frameworks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Governments and private entities continue to prioritize access to zero-day vulnerabilities; regulatory frameworks remain non-binding; digital rights organizations maintain current levels of advocacy.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the financial flows within the zero-day vulnerability market; comprehensive list of state actors involved in spyware procurement.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from digital rights organizations emphasizing threats to civil liberties; possible underreporting by governments on their use of spyware.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing development and deployment of spyware could lead to increased tensions between states and civil society, potentially escalating into broader geopolitical conflicts over digital sovereignty.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic friction over digital rights and surveillance practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced surveillance capabilities could be leveraged for counter-terrorism but risk misuse against non-violent actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Continued exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities may undermine trust in digital platforms and services.
- Economic / Social: Potential chilling effects on journalism and activism, impacting social cohesion and democratic processes.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of zero-day markets; engage with tech companies to enhance vulnerability patching processes.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop international partnerships to strengthen regulatory frameworks; invest in cybersecurity education and awareness campaigns.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Enhanced international cooperation leads to effective regulation and reduced spyware proliferation.
- Worst: Escalation of state-sponsored surveillance leads to widespread civil liberties violations.
- Most-Likely: Continued resilience of spyware industry with incremental regulatory improvements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Alejandro Mayoral Baños – Executive Director, Access Now
- Rand Hammoud – Surveillance Campaigns Lead, Access Now
- Paragon Solutions – Developer of Graphite spyware
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, digital rights, spyware, zero-day vulnerabilities, EU regulations, surveillance, civil liberties
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us