European Commission investigates cyber intrusion on mobile device management system, staff data potentially a…
Published on: 2026-02-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
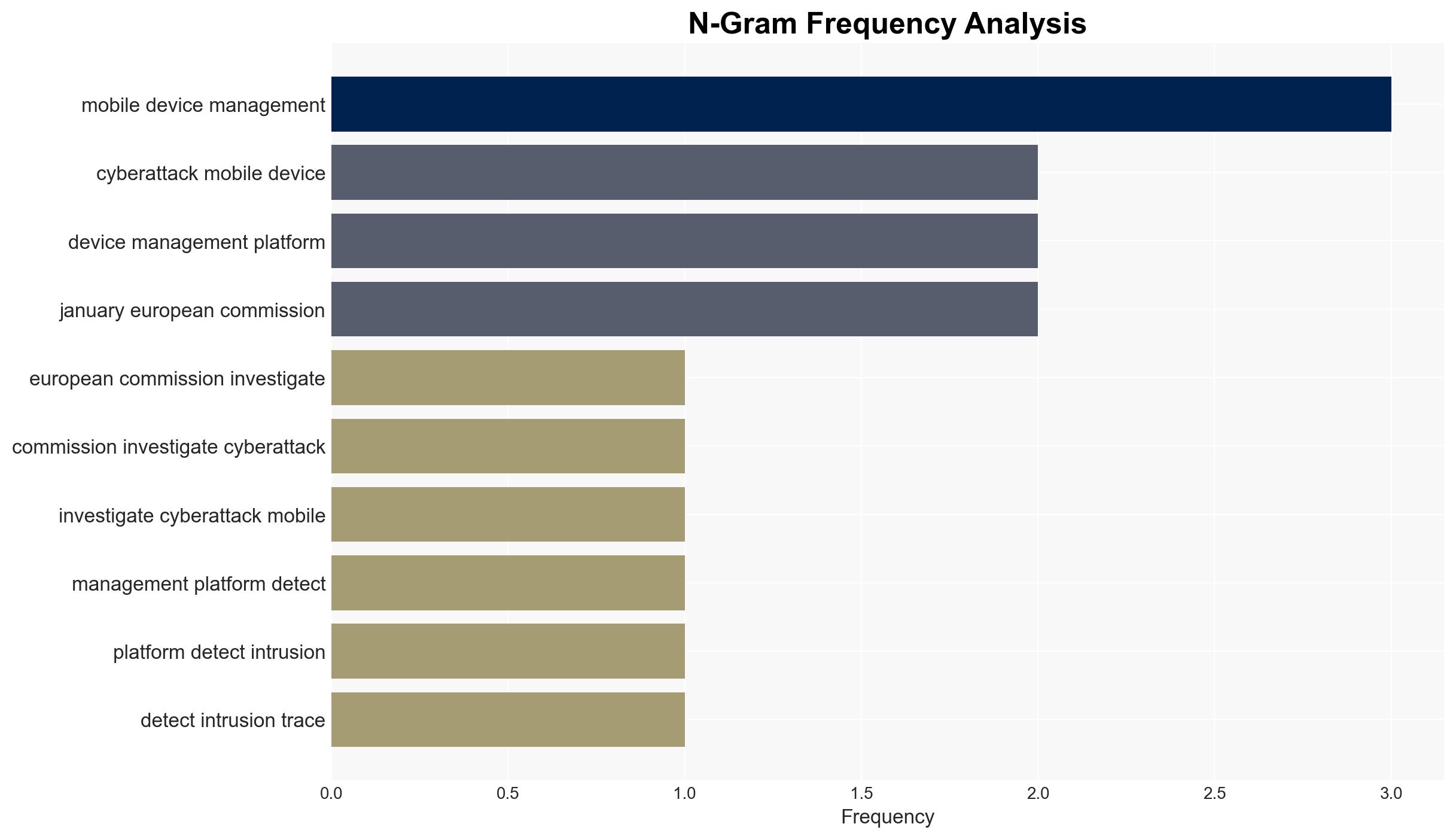
Intelligence Report: European Commission probes cyberattack on mobile device management system
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
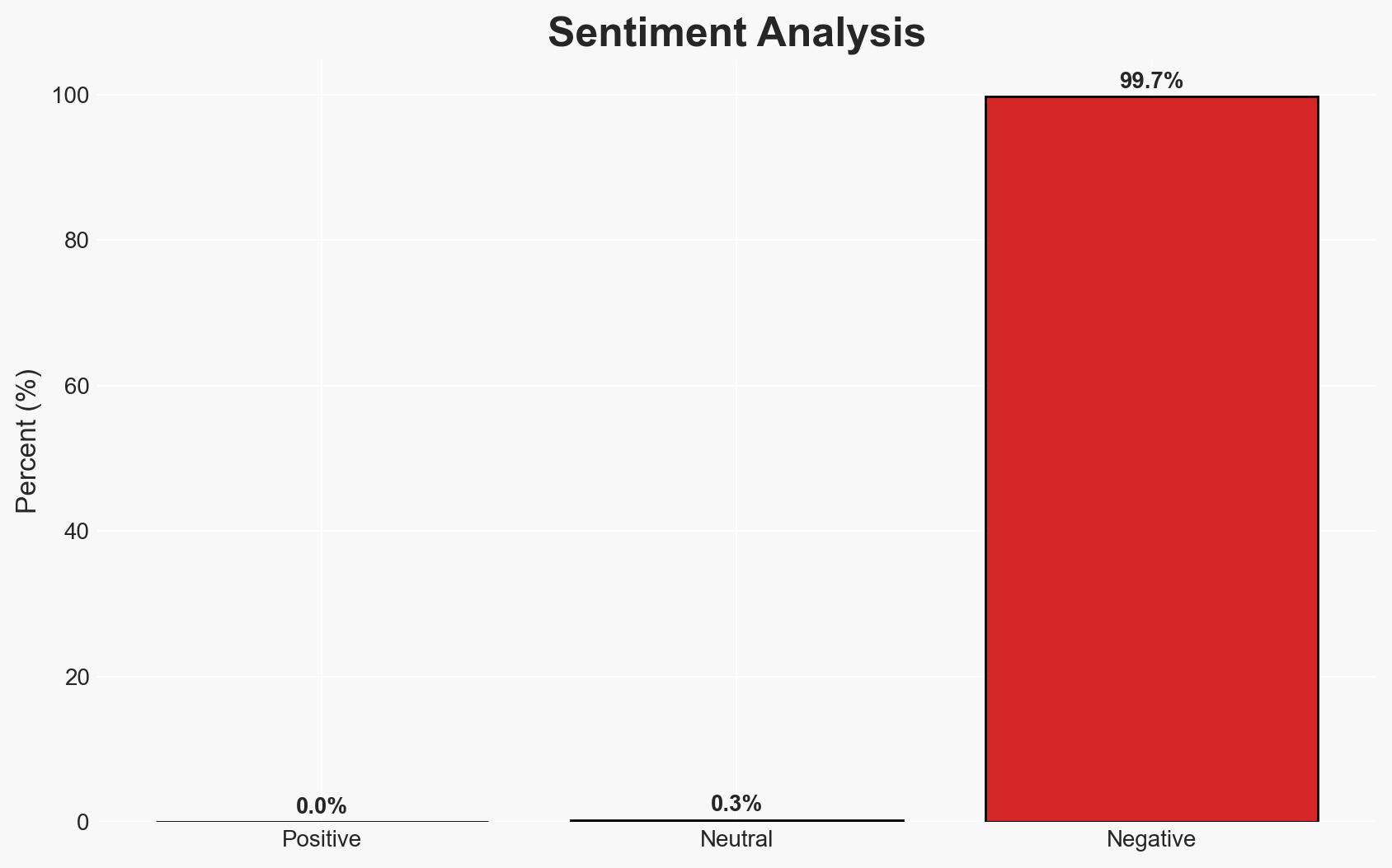
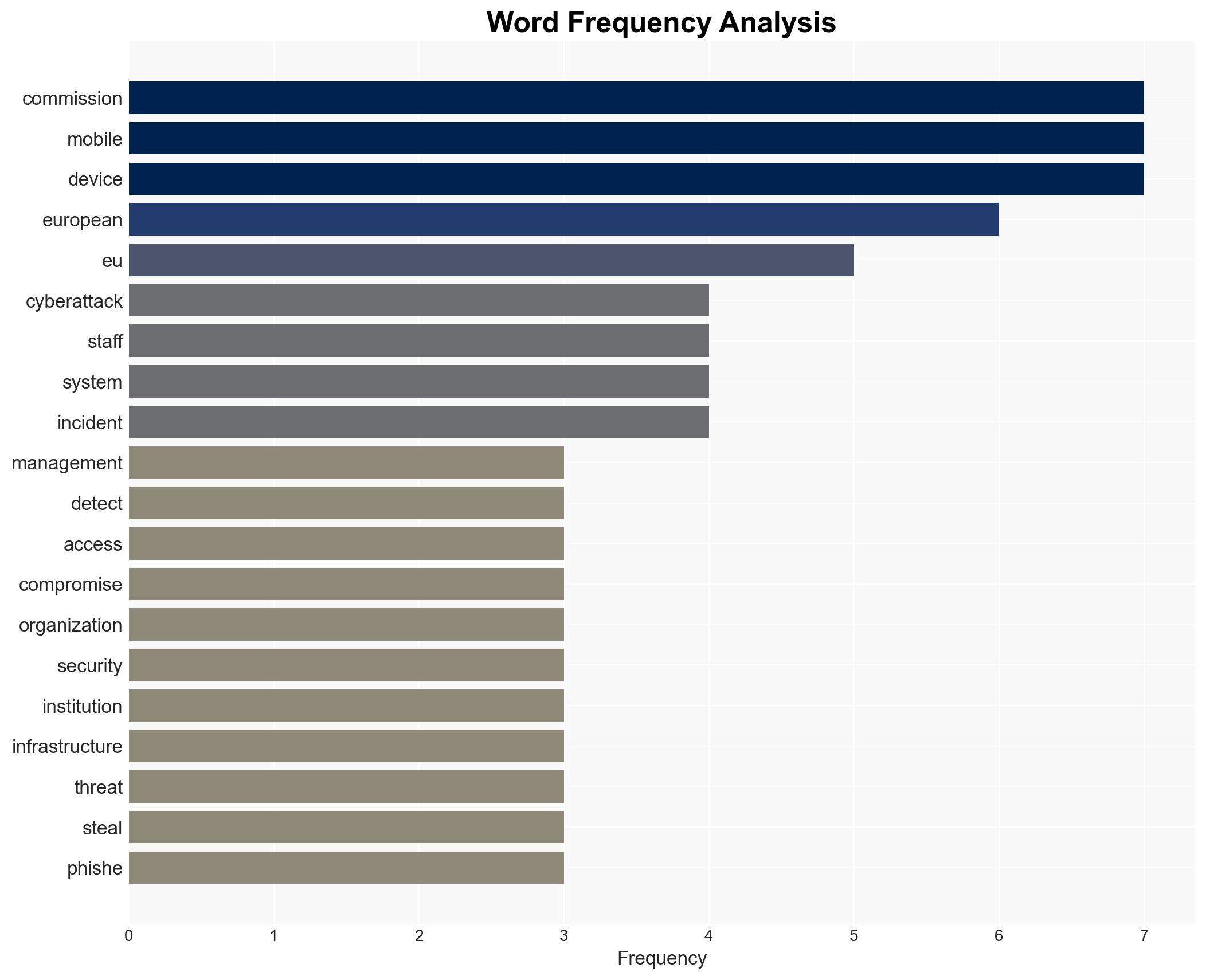
The European Commission is investigating a cyberattack on its mobile device management system, which may have exposed some staff data. The incident was contained within nine hours, with no devices compromised. This attack could facilitate future phishing attempts. Overall, there is moderate confidence that the attack aimed at reconnaissance rather than immediate disruption.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was primarily for reconnaissance, aiming to gather data for future targeted phishing or vishing attacks. Supporting evidence includes the limited data accessed and no devices being compromised. However, the exact method of access remains unknown, creating uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was an attempted breach to disrupt EU operations, but it was thwarted before achieving its objectives. The rapid containment and lack of device compromise contradict this, but the severity of past attacks suggests potential for more aggressive intent.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the nature of the data accessed and the absence of immediate operational impact. Indicators such as future phishing attempts targeting EU staff could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers’ primary goal was data collection; the European Commission’s cybersecurity measures are generally effective; no insider threat facilitated the attack.
- Information Gaps: Specific methods of access and identity of the threat actors remain unknown; potential links to previous attacks are unclear.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias may lead to underestimating the potential for more severe attacks; reliance on internal reports could overlook external threat indicators.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased phishing attacks targeting EU staff, potentially compromising sensitive information. The breach highlights vulnerabilities in EU cybersecurity that could be exploited by more sophisticated actors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential erosion of trust in EU institutions’ ability to protect data, impacting diplomatic relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of targeted attacks on EU personnel, necessitating enhanced security protocols.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage activities targeting EU institutions.
- Economic / Social: Possible reputational damage could affect public confidence in EU digital infrastructure.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring for phishing attempts, conduct a thorough forensic analysis, and update staff on security protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms, invest in advanced threat detection technologies, and conduct regular security audits.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No further incidents occur, and security measures are strengthened (trigger: successful audits).
- Worst: A major breach occurs, leading to significant data loss (trigger: increased phishing success rates).
- Most-Likely: Ongoing minor phishing attempts with no major breaches (trigger: continued vigilance and training).
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, EU institutions, phishing, data breach, cyber espionage, information security, reconnaissance
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us