European Commission’s mobile management platform breached; swift containment prevents major data loss
Published on: 2026-02-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: European Commission hit by cyberattackers targeting mobile management platform
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
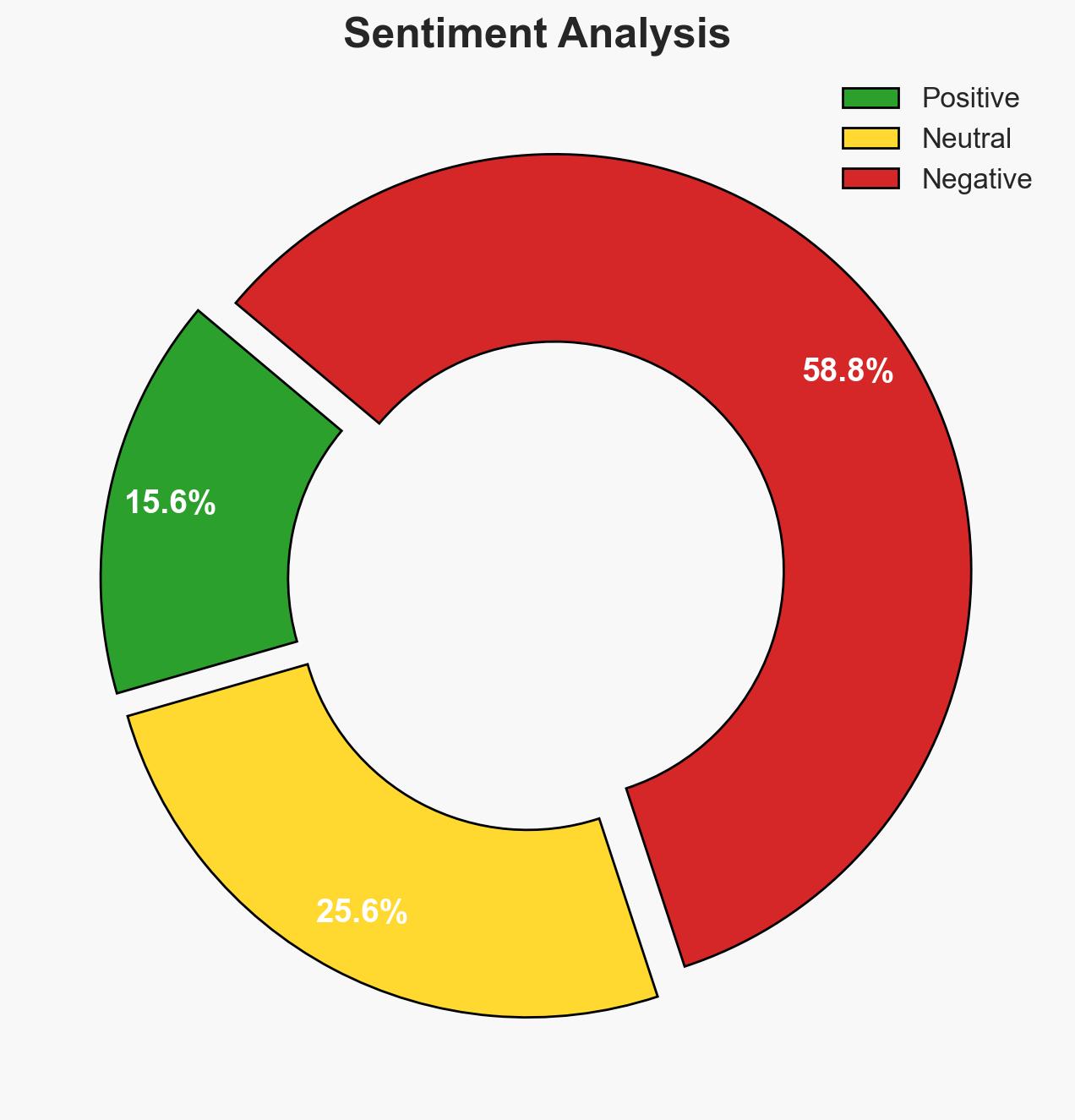
The European Commission’s mobile device management platform was compromised, likely due to a vulnerability in the Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM). The breach was contained quickly, with no mobile devices compromised, but some staff data may have been accessed. This incident highlights vulnerabilities in widely used mobile management systems. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was a targeted attack exploiting known vulnerabilities in the Ivanti EPMM platform. This is supported by the timing of the vulnerability disclosure and similar breaches in other European institutions. However, the specific intent and identity of the attackers remain unclear.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was an opportunistic attack by cybercriminals exploiting a zero-day vulnerability for financial gain or data theft. While possible, there is less direct evidence linking this motive to the breach, and the swift containment suggests a lack of deeper infiltration.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the correlation with known vulnerabilities and similar incidents. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include identification of the attackers or evidence of broader targeting patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The breach was limited to data access; Ivanti EPMM was the platform used; attackers exploited known vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: Identity and motives of the attackers; extent of data accessed; confirmation of the platform used.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in assuming a single platform was compromised; reliance on public disclosures which may omit sensitive details.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This incident underscores the vulnerability of critical IT infrastructure to known exploits, potentially encouraging further attacks on similar systems. The breach could lead to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure on mobile management platforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for strained relations if state-sponsored actors are implicated; increased EU focus on cybersecurity policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and defensive postures across EU institutions; potential for copycat attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased attention on patch management and vulnerability disclosures; potential for misinformation if details are misrepresented.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial impact on affected vendors; public concern over data privacy and institutional security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct thorough forensic analysis; enhance monitoring of mobile management systems; communicate transparently with stakeholders.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms; invest in staff training on cyber hygiene; review and update incident response plans.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No further incidents; vulnerabilities patched; improved security posture.
- Worst: Additional breaches occur; sensitive data leaked; significant reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Continued vigilance leads to improved defenses; minor incidents continue but are contained.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- European Commission
- Ivanti
- Arno Rutte, State Secretary for Justice and Security
- National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
- Dutch Data Protection Authority (AP)
- Council for the Judiciary (Rvdr)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, EU institutions, mobile management, vulnerability exploitation, incident response, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us