European Space Agency Faces Major Data Breach as Cybercriminals Steal Hundreds of Gigabytes of Sensitive Info…
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cyberthieves hit European Space Agency stealing hundreds of gigabytes of data
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
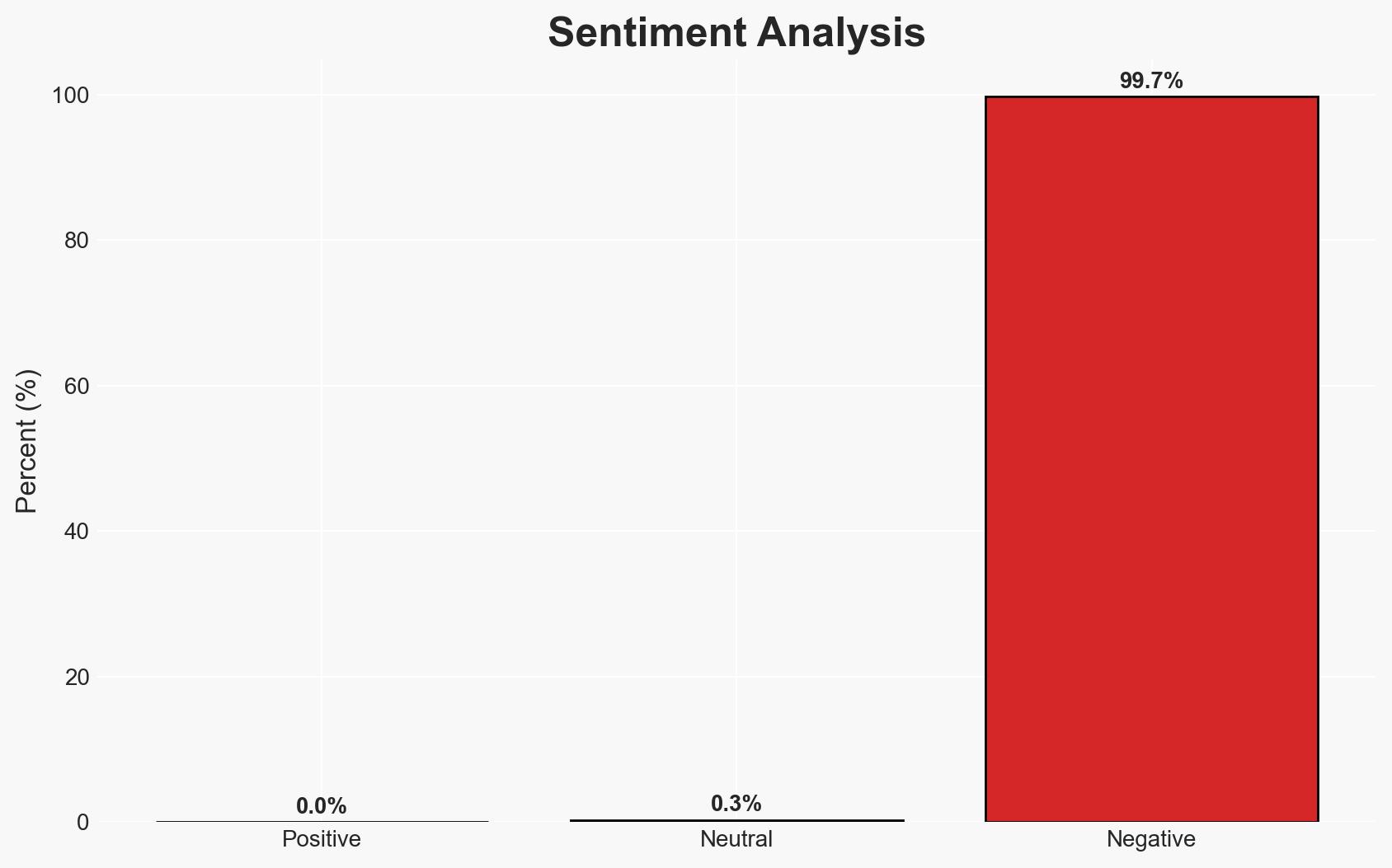
The European Space Agency (ESA) has suffered significant data breaches, exposing sensitive information on dark web forums. The breaches highlight vulnerabilities in ESA’s cybersecurity posture, potentially impacting international space collaboration. The most likely hypothesis is that the breaches result from inadequate cyber hygiene and unpatched vulnerabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The data breaches were facilitated by inadequate cyber hygiene among ESA staff, leading to compromised credentials. Supporting evidence includes frequent sales of ESA credentials on dark web forums and the use of infostealer malware. Key uncertainties include the specific methods used to obtain the credentials.
- Hypothesis B: The breaches were orchestrated by a sophisticated cybercrime group exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities in ESA’s systems. This is supported by the rapid succession of breaches and the substantial volume of data stolen. Contradicting evidence includes ESA’s initial minimization of the breach impact.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the scale and timing of the breaches, suggesting a coordinated attack. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of internal negligence or further breaches exploiting similar vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: ESA’s cybersecurity measures were insufficient; the breaches involved external threat actors; the data exposed is sensitive and valuable.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the vulnerabilities exploited; the identity and motives of the attackers; the full extent of the data compromised.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting by ESA to minimize reputational damage; reliance on open-source information which may be incomplete or inaccurate.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ESA data breaches could undermine trust in international space collaboration and expose sensitive technological information to adversaries. Over time, this may lead to increased scrutiny of ESA’s cybersecurity practices and potential geopolitical tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strain on international partnerships, particularly with entities like NASA and private contractors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of espionage and targeted cyberattacks on space infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for further exploitation of exposed data, leading to more sophisticated cyber threats.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for ESA and its partners; erosion of public confidence in space agencies’ data security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive security audit; patch identified vulnerabilities; enhance monitoring of dark web activity for further data leaks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop robust cyber hygiene training for staff; strengthen international cybersecurity cooperation; invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: ESA successfully mitigates vulnerabilities, restoring trust and security.
- Worst: Continued breaches lead to significant geopolitical fallout and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: ESA improves cybersecurity posture, but faces ongoing threats requiring sustained vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Eric Morel de Westgaver, ESA’s director of European, legal and international matters
- Clémence Poirier, cybersecurity researcher at the Center for Security Studies, ETH Zurich
- Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters, cybercrime group
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other individuals/entities.
7. Thematic Tags
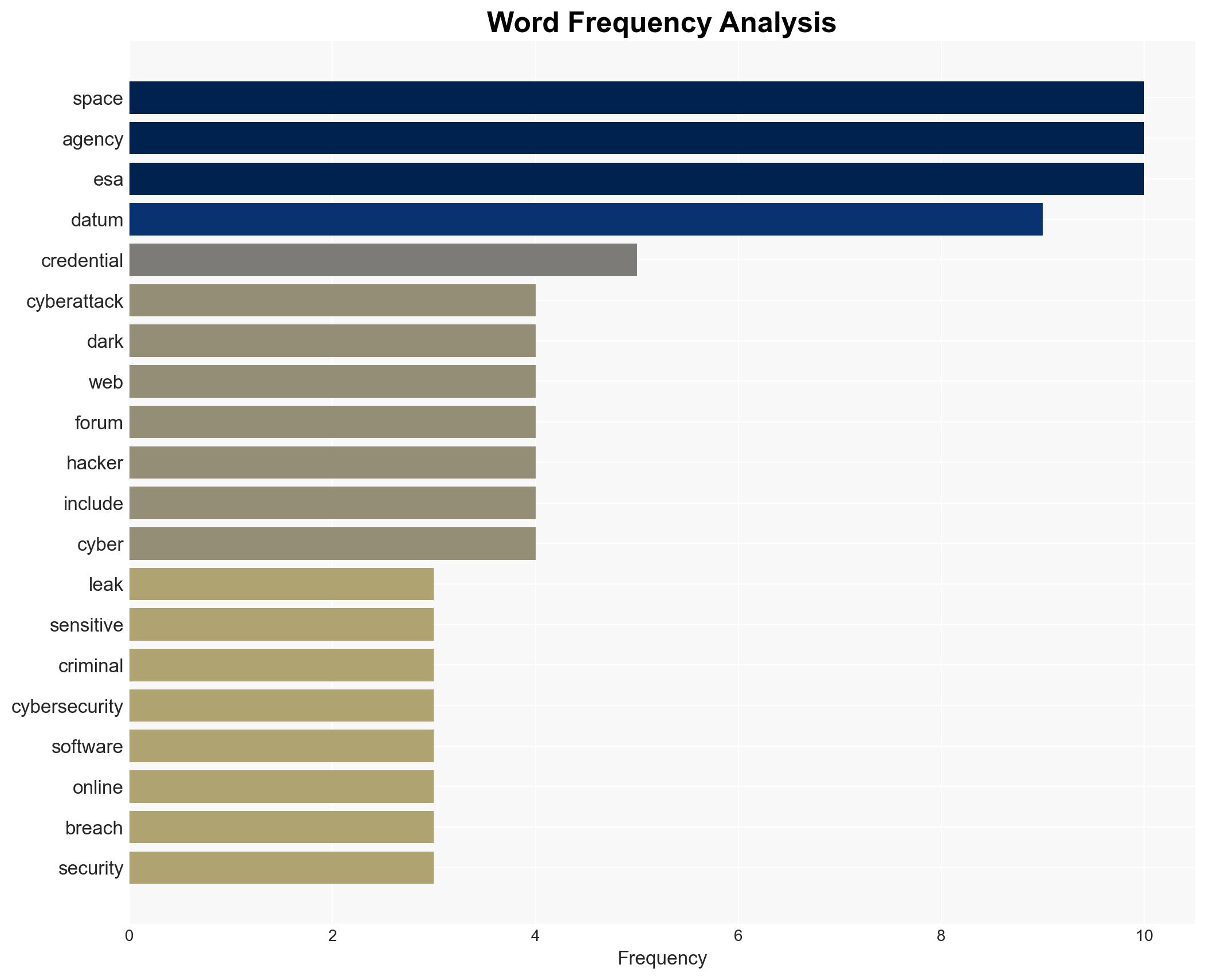
cybersecurity, data breach, space agency, international cooperation, cyber-espionage, information security, dark web
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us