Evolving Cyber Resilience: A Critical Business Strategy Amid Rising Threats and Costs in the UK
Published on: 2025-11-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cyber resilience is a business imperative skills and strategy must evolve
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
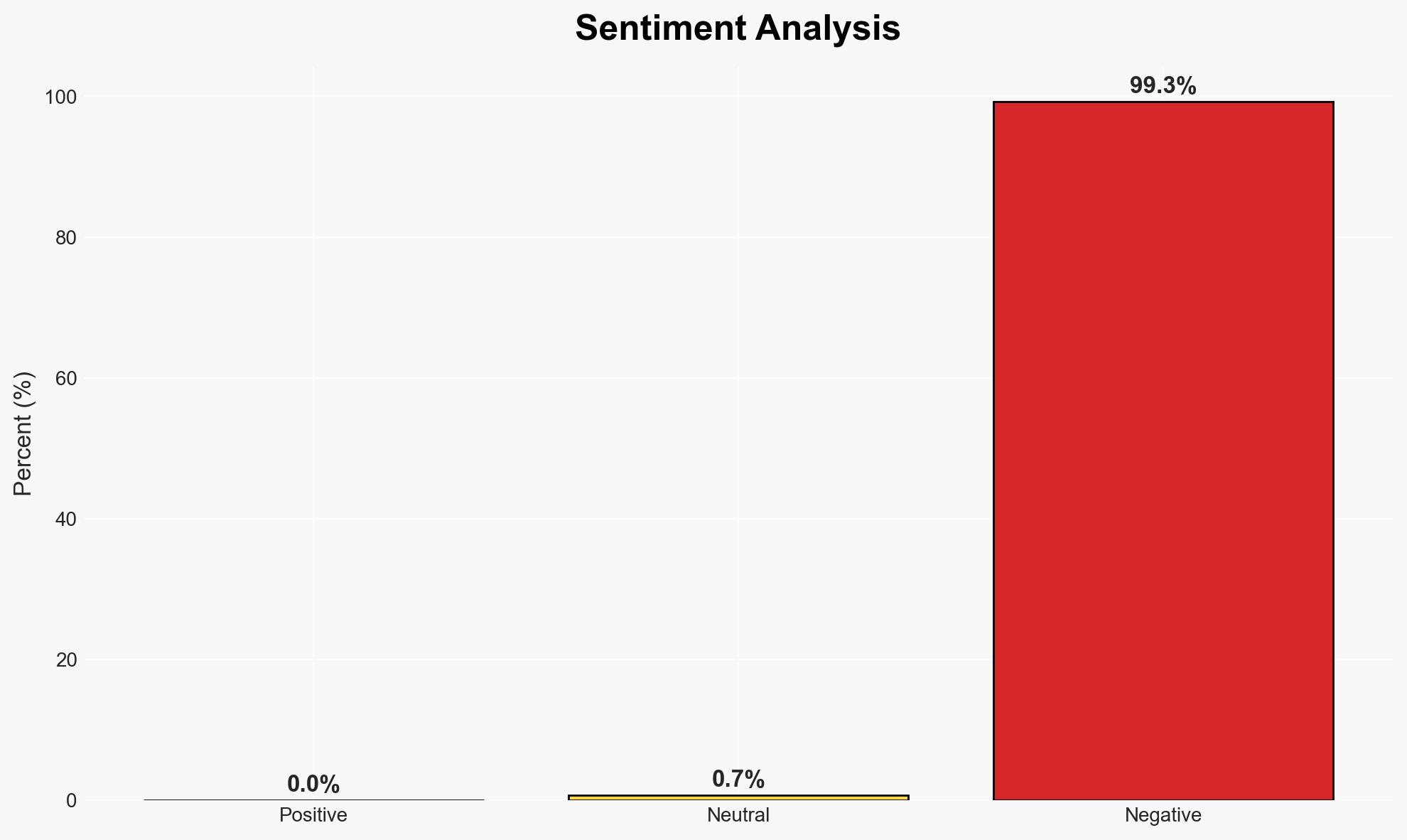
The UK faces significant cybersecurity challenges, with recent breaches highlighting vulnerabilities in both public and private sectors. The proposed ransomware payment ban aims to protect critical national infrastructure but may inadvertently increase private sector risks. The current assessment, with moderate confidence, suggests that the private sector must urgently enhance cyber resilience to mitigate these threats.
2. Competing Hypotheses
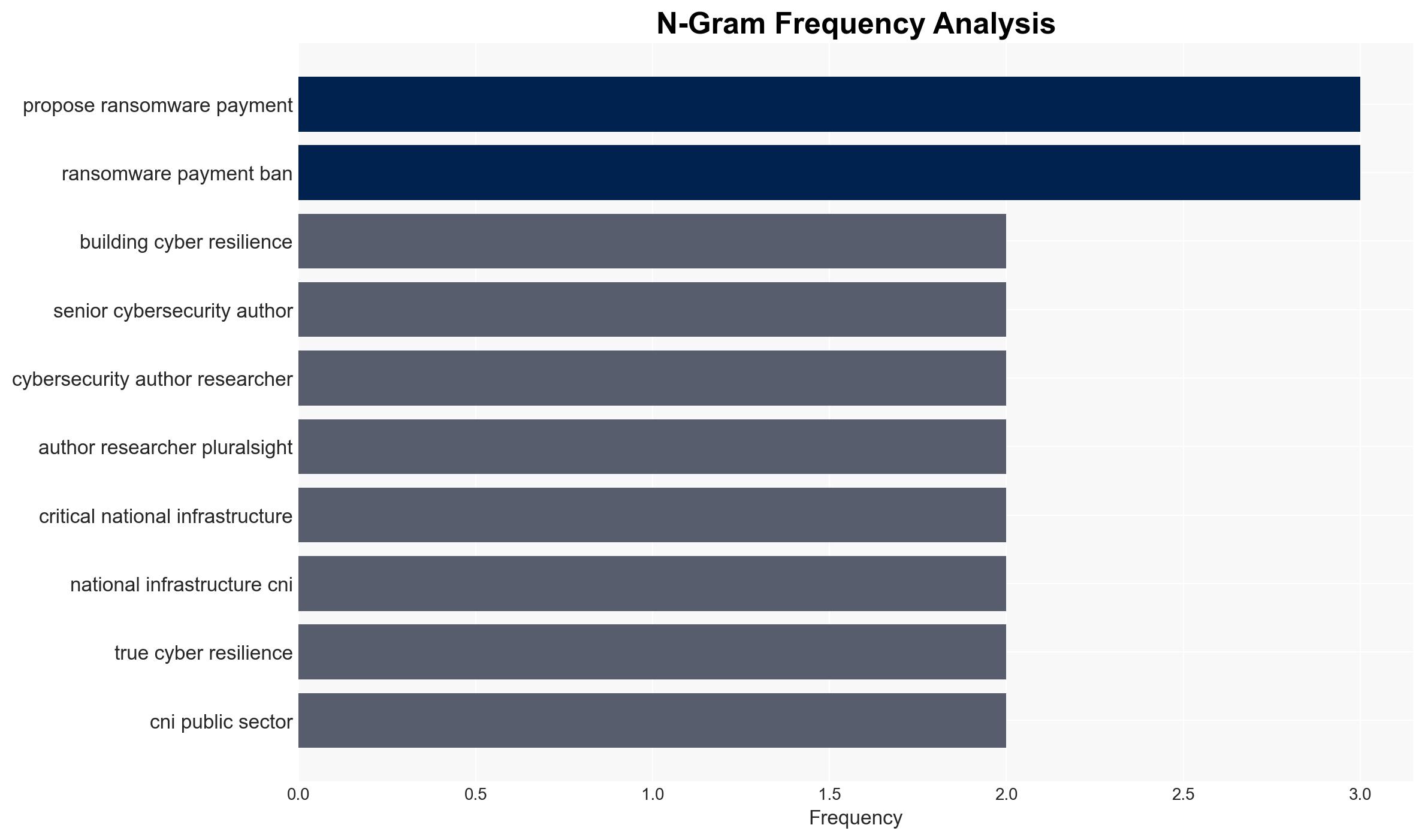
- Hypothesis A: The proposed ransomware payment ban will effectively reduce cybercrime profitability and shift attacker focus away from critical national infrastructure. This is supported by the theory that reducing ransom payouts will decrease the incentive for targeting essential services. However, it is uncertain how attackers will adapt and whether they will increase focus on the private sector.
- Hypothesis B: The ransomware payment ban will lead to increased targeting of the private sector, as attackers seek alternative revenue streams. This is supported by the assumption that attackers will exploit perceived weaknesses in private sector defenses. Contradicting evidence includes potential private sector improvements in cyber resilience, though this remains speculative.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the private sector’s existing vulnerabilities and the likelihood of attackers adapting to the ban by shifting focus. Indicators such as increased private sector breaches or changes in attack patterns could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions:
- The ransomware payment ban will be effectively enforced.
- Attackers will adapt their strategies in response to the ban.
- The private sector currently lacks sufficient cyber resilience.
- Cyber skills and training are critical to enhancing resilience.
- Information Gaps:
- Specific details on the enforcement mechanisms for the ransomware payment ban.
- Data on private sector cyber resilience capabilities and gaps.
- Trends in attacker behavior post-ban implementation.
- Bias & Deception Risks:
- Potential bias in assuming uniform attacker behavior across sectors.
- Risk of underestimating private sector adaptation capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolving cyber threat landscape necessitates strategic adjustments across sectors. The ransomware payment ban may alter attacker incentives, leading to a redistribution of cyber threats.
- Political / Geopolitical: The UK government may face pressure to balance public and private sector protections, potentially affecting international cybersecurity collaborations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased private sector targeting could elevate national security risks if critical supply chains are disrupted.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced cyber defenses may lead to more sophisticated cyber operations and potential escalation in cyber warfare tactics.
- Economic / Social: Significant financial impacts on businesses could lead to broader economic instability and affect public trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of cyber threats to private sector entities, provide guidance on enhancing cyber defenses, and initiate public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop comprehensive cyber resilience strategies, invest in workforce upskilling, and establish clear incident response protocols.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Effective adaptation by both sectors reduces overall cybercrime impact.
- Worst Case: Significant increase in private sector breaches leads to economic disruption.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in resilience with intermittent high-profile breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
- UK Government
- Private Sector Enterprises
- Critical National Infrastructure Operators
- Cybersecurity Training Providers (e.g., Pluralsight)
7. Thematic Tags
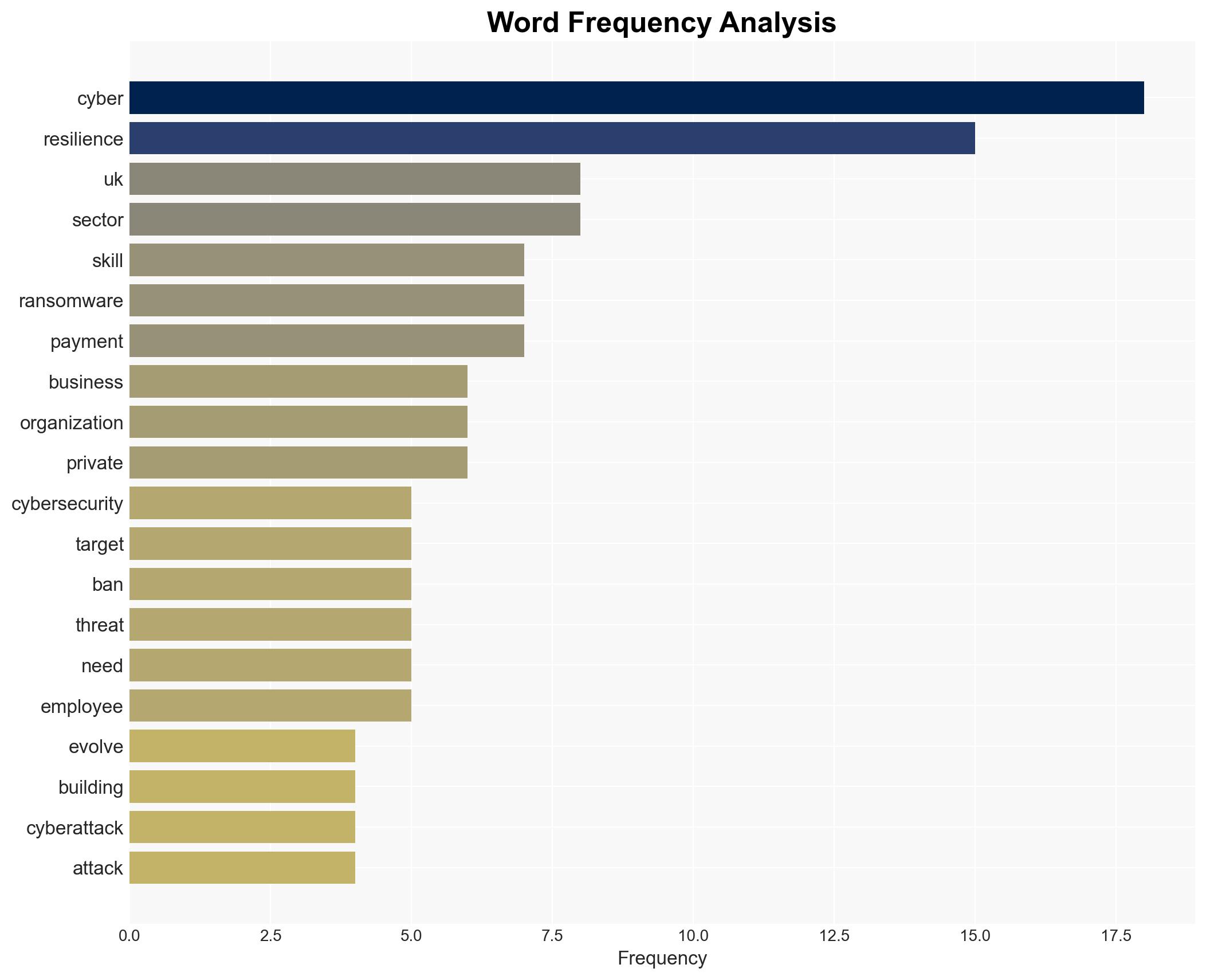
Cybersecurity, cyber resilience, ransomware, private sector, critical infrastructure, cybersecurity skills, cyber threat landscape, public-private partnership
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us