Explosion in Bandar Abbas kills child and injures 14 ahead of Iran’s naval exercise in the Strait of Hormuz
Published on: 2026-02-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Explosion in Iranian port city ahead of Iran’s naval drill in the Strait of Hormuz
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
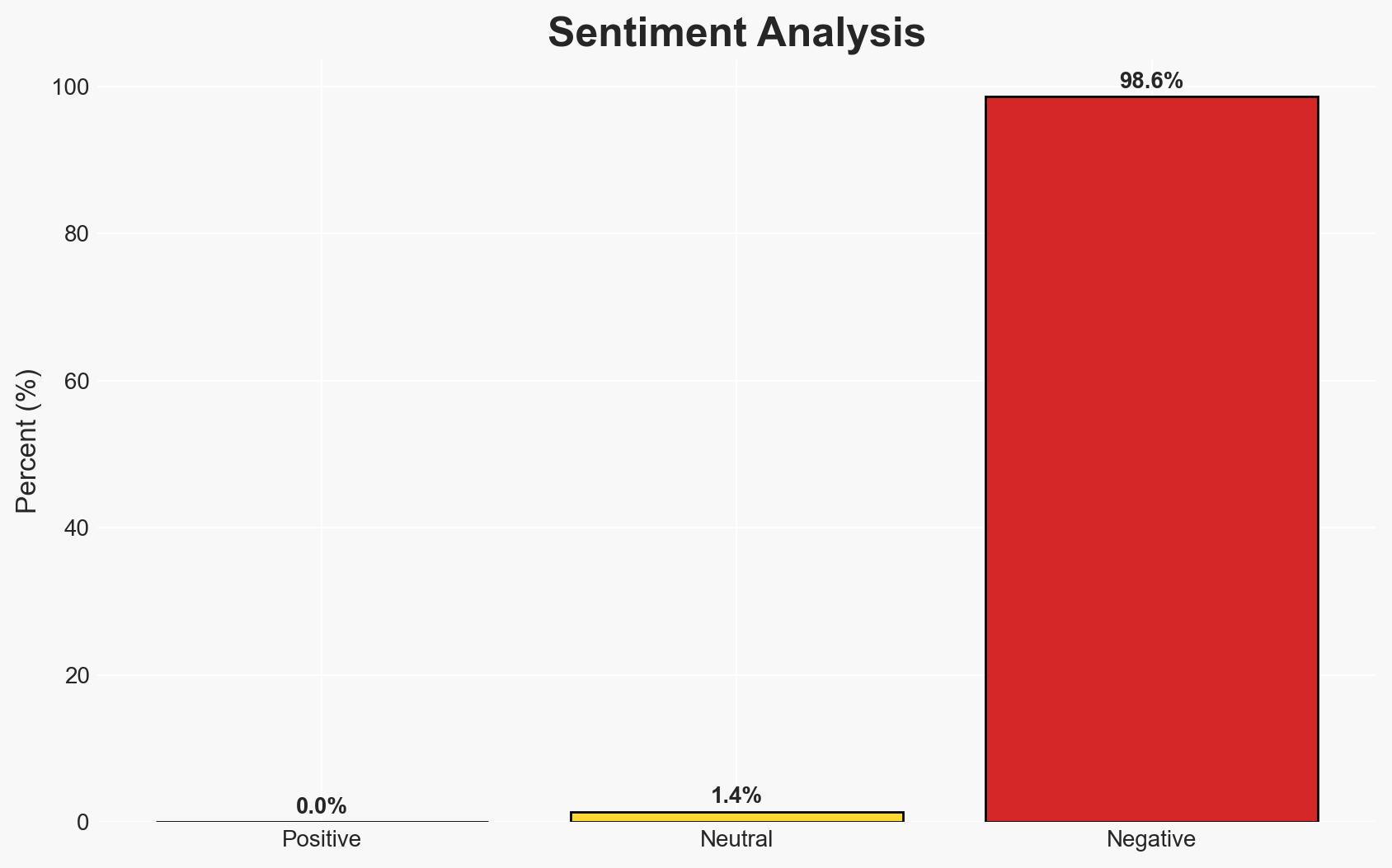
The explosion in Bandar Abbas, coinciding with heightened tensions and military activities in the Strait of Hormuz, raises concerns about potential sabotage or internal security issues. The most likely hypothesis is an accidental gas leak, but the involvement of security personnel and lack of detailed reporting suggest alternative possibilities. This incident could impact regional stability and U.S.-Iran relations, with moderate confidence in the assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
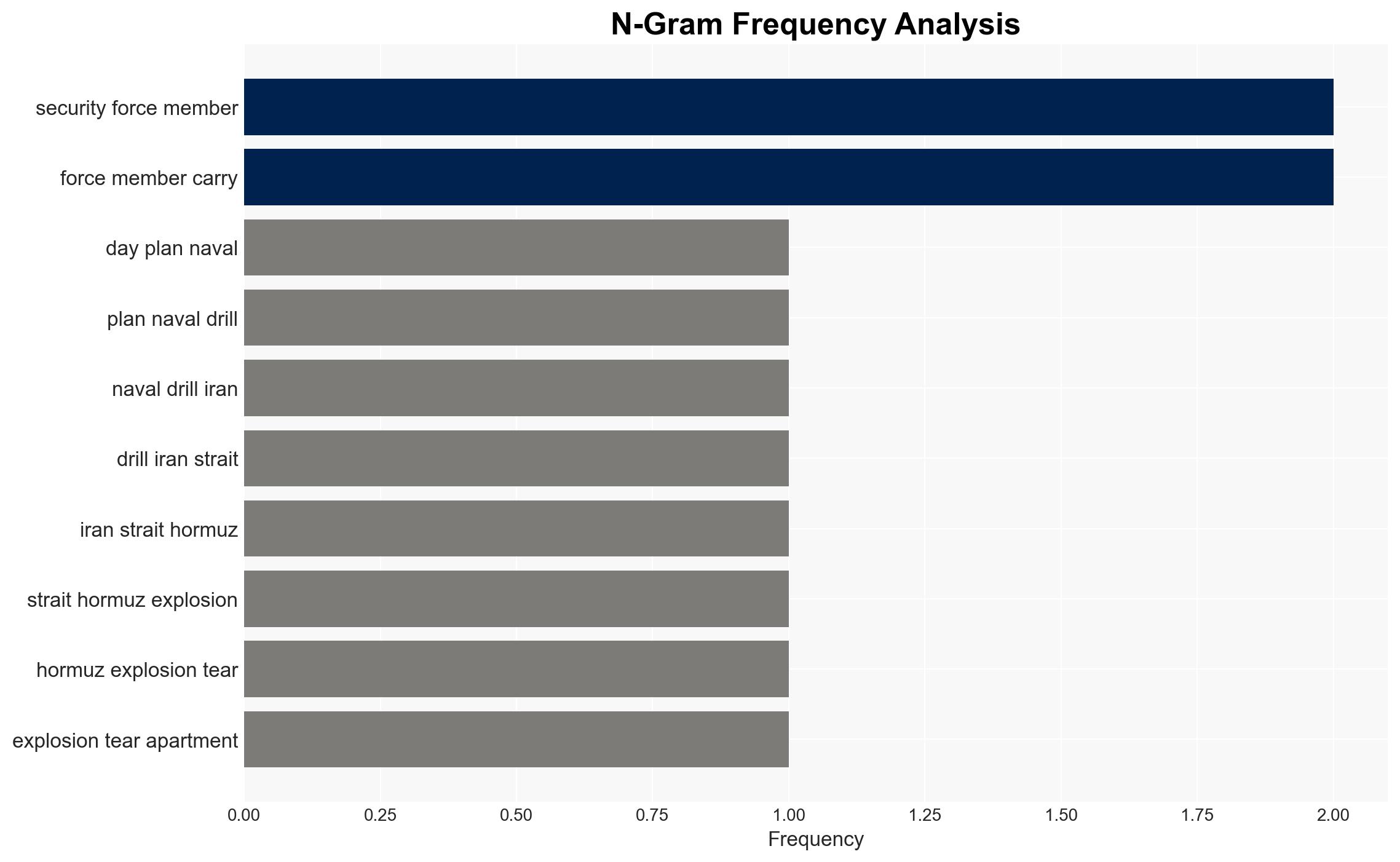
- Hypothesis A: The explosion was an accidental gas leak, as reported by local fire officials. Supporting evidence includes the official statement and the commonality of such incidents in the region. However, the presence of a security force member and the timing raise uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The explosion was a deliberate act of sabotage or an internal security incident. This is supported by the involvement of a security force member and the strategic timing before naval drills. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of claims of responsibility and official denial of military involvement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to official statements and lack of direct evidence of sabotage. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include credible claims of responsibility or further security incidents.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The official report of a gas leak is accurate; the presence of a security force member is coincidental; there is no immediate external threat linked to the explosion.
- Information Gaps: Details on the security force member’s role and the exact cause of the explosion; any intelligence on potential sabotage plans.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Iranian state media reporting; risk of information manipulation by involved parties to downplay security threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate existing tensions in the region, particularly in the context of U.S.-Iran relations and ongoing military posturing.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic strain between Iran and Western powers, particularly the U.S., if the incident is perceived as a security threat.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alertness in the region could lead to increased military presence and readiness, impacting local and regional security dynamics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for misinformation campaigns or cyber operations targeting perceptions of security in the region.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in the Strait of Hormuz could affect global oil markets; local social unrest may arise if the incident is linked to broader security issues.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on regional security incidents; engage in diplomatic channels to de-escalate potential tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional partnerships to enhance maritime security; develop contingency plans for potential disruptions in the Strait of Hormuz.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Incident confirmed as accidental, leading to de-escalation and resumption of normal activities.
- Worst: Confirmation of sabotage leading to military confrontation or broader regional conflict.
- Most-Likely: Incident remains unresolved but contained, with ongoing diplomatic and military vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Ali Larijani (Iranian security official)
- U.S. military forces in the region
- Iran’s paramilitary Revolutionary Guard
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for others involved
7. Thematic Tags
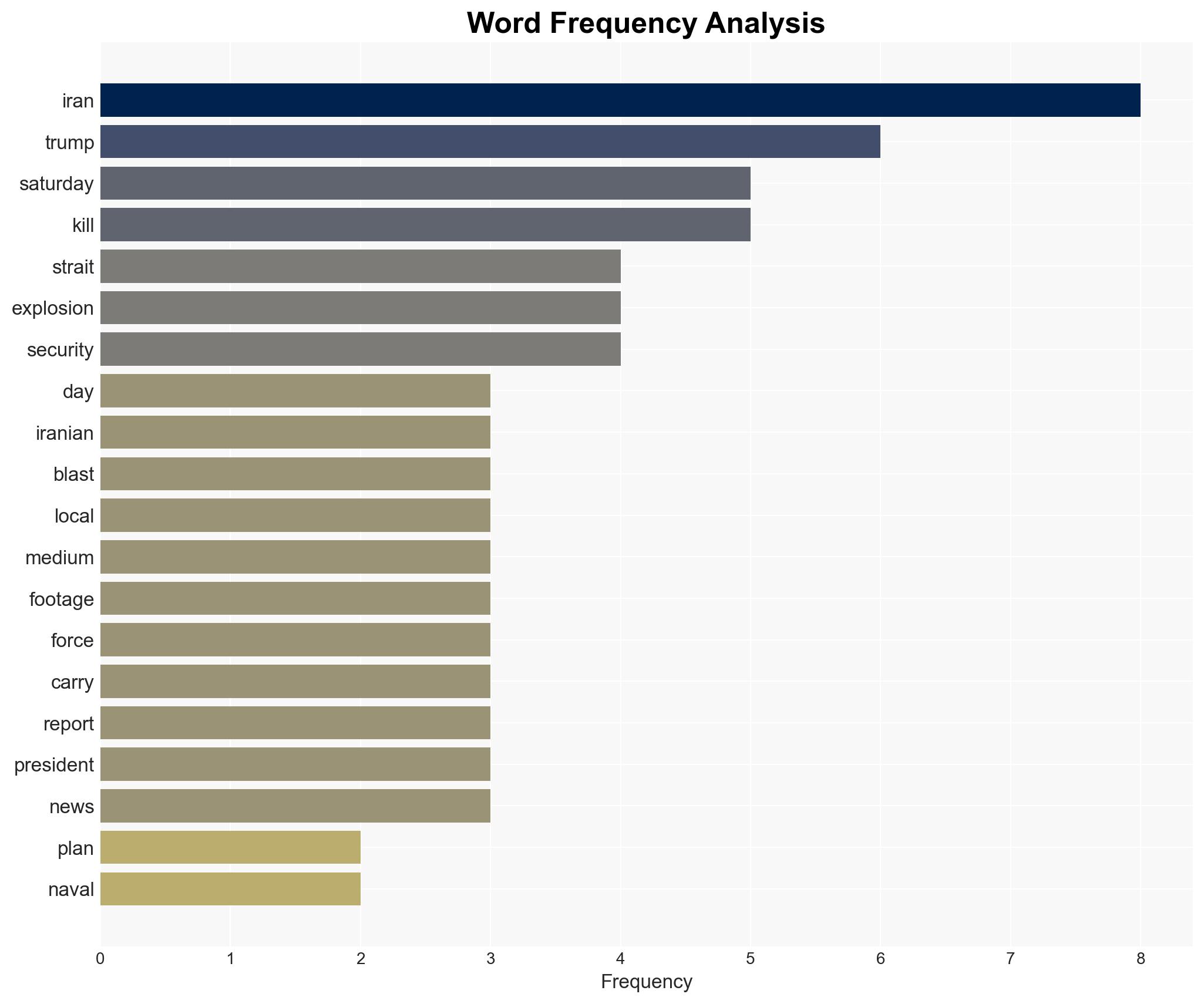
regional conflicts, regional security, Iran-U.S. relations, Strait of Hormuz, naval operations, geopolitical tensions, energy security, information operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us