F-16 Pilot Receives Silver Star for Leading Successful SEAD Mission Amidst Intense Fire in Yemen
Published on: 2025-12-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US F-16 Pilot Who Led SEAD Mission Under Heavy Fire in Yemen Awarded With Silver Star
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The awarding of the Silver Star to Lt. Col. William “Skate” Parks highlights the intensity and strategic importance of U.S. air operations against Houthi forces in Yemen. This incident underscores the ongoing complexity of the conflict and the high-risk environment for U.S. forces. The mission’s success in neutralizing ballistic missile facilities suggests a significant tactical gain. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited details on broader operational impacts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The mission was a targeted operation to degrade Houthi missile capabilities, directly supporting broader U.S. strategic objectives in the region. This is supported by the mission’s focus on ballistic missile production facilities and the high-level recognition of Parks’ actions. However, the lack of specific operational details limits full validation.
- Hypothesis B: The mission was primarily a defensive action to protect U.S. naval assets and personnel, with the offensive strike as a secondary objective. This is supported by the mention of Parks’ role in defending against missile threats to the USS Harry S. Truman. Contradictory evidence includes the primary focus on missile infrastructure.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the explicit targeting of missile production facilities and the strategic implications of such a strike. Indicators that could shift this judgment include further details on the mission’s planning and objectives.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The mission’s primary goal was the degradation of Houthi missile capabilities; U.S. forces have reliable intelligence on Houthi missile infrastructure; the risk to U.S. personnel was deemed acceptable given the mission’s strategic importance.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the mission’s broader strategic context and follow-up operations; confirmation of the mission’s impact on Houthi missile capabilities.
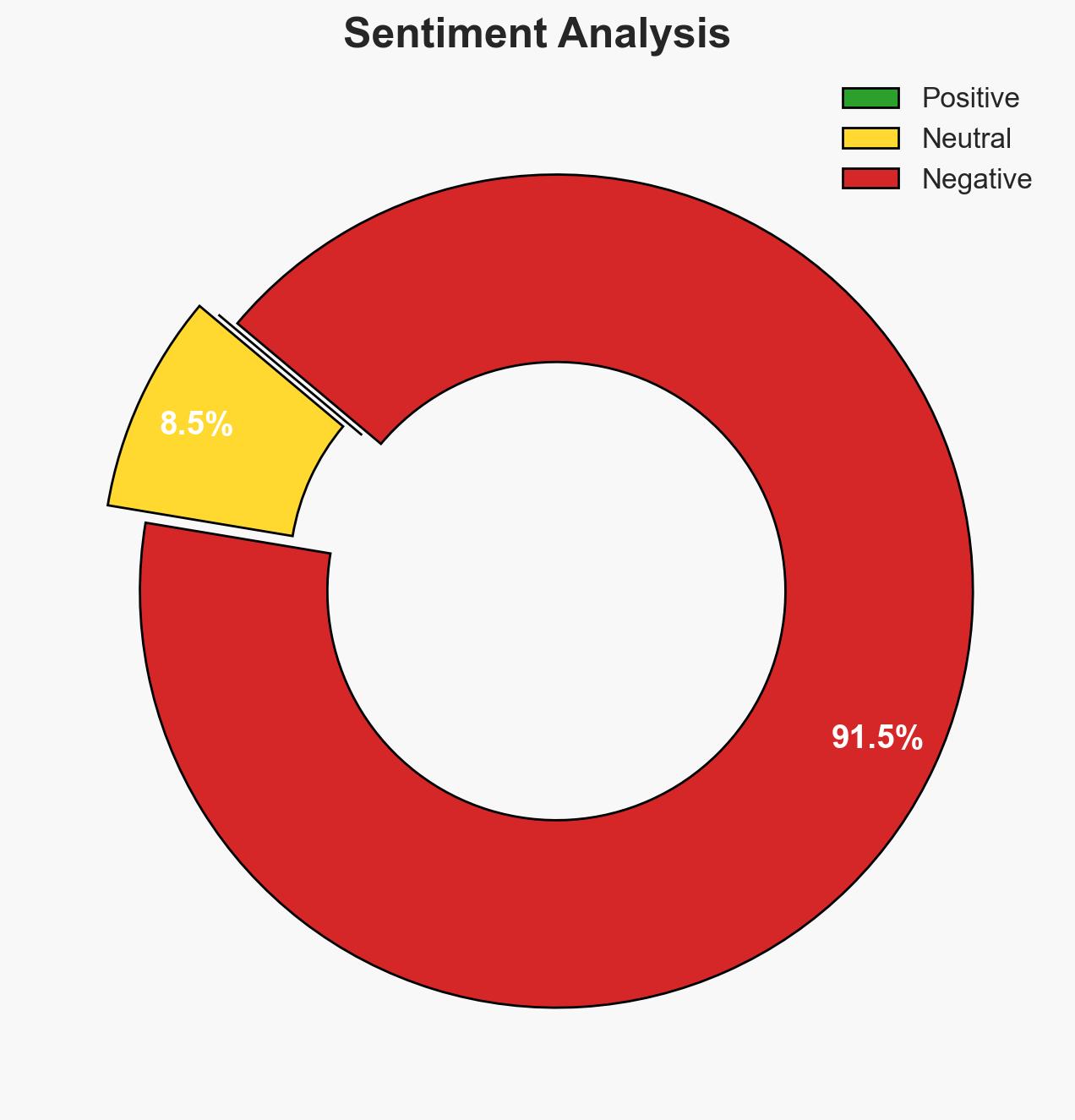
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in U.S. military reporting to emphasize mission success; possible underreporting of collateral damage or operational challenges.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could influence regional power dynamics and the operational calculus of Houthi forces. It may also impact U.S. relations with regional allies and adversaries.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation of conflict with Houthi forces; increased pressure on regional allies to support U.S. operations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment for U.S. forces; possible retaliation by Houthi forces or their allies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting U.S. assets in response to the strike.
- Economic / Social: Limited immediate economic impact; potential for increased humanitarian concerns if conflict escalates.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence gathering on Houthi capabilities; enhance defensive measures for U.S. assets in the region.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with regional allies; invest in counter-missile technologies and training.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Degradation of Houthi capabilities leads to reduced conflict intensity.
- Worst Case: Retaliatory actions by Houthi forces escalate regional tensions.
- Most Likely: Continued sporadic engagements with incremental degradation of Houthi missile capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Lt. Col. William “Skate” Parks, former commander of the 480th Expeditionary Fighter Squadron
- U.S. Air Force Chief of Staff Gen. Kenneth Wilsbach
- Houthi forces (targeted entity)
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, air operations, military strategy, Middle East conflict, missile defense, U.S. military awards
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us