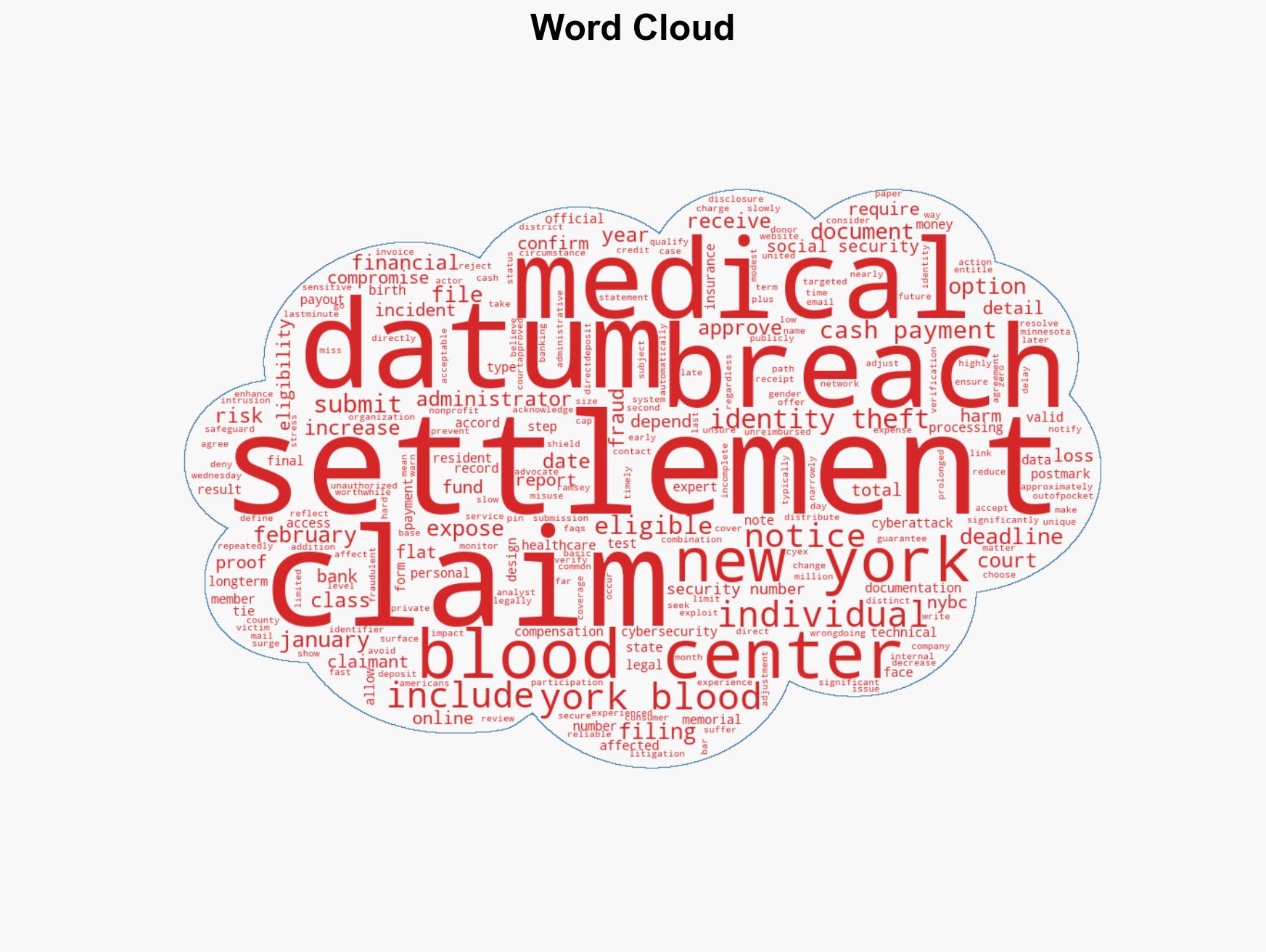
Final Day to Apply for Up to $2,500 from New York Blood Center Data Breach Settlement Eligibility
Published on: 2026-02-10
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Just 1 day left to claim up to 2500 from the New York Blood Center data breach settlement check if you qualify
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
A significant data breach at the New York Blood Center (NYBC) affected approximately 194,000 individuals, exposing sensitive personal and medical information. The breach poses long-term identity theft risks, and a settlement has been reached to compensate affected individuals. The most likely hypothesis is that the breach was financially motivated, with moderate confidence due to the nature of the data accessed.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was financially motivated, targeting sensitive data for identity theft and financial fraud. Supporting evidence includes the access to Social Security numbers and banking information. Contradicting evidence is limited but includes the possibility of non-financial motives.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was conducted for non-financial motives, such as political or ideological reasons. This is less supported due to the lack of evidence indicating such motives and the nature of the data accessed.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the type of data accessed, which is typically used for financial fraud. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of data misuse for non-financial purposes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The breach was executed by an external actor; the primary motive was financial gain; the data will be used for identity theft.
- Information Gaps: Details on the identity of the perpetrators and their specific methods; full scope of data misuse.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in assuming financial motives without direct evidence; risk of underestimating non-financial motives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This breach could lead to increased scrutiny on nonprofit healthcare organizations’ cybersecurity practices and potential regulatory changes. Long-term identity theft risks may persist, affecting victims’ financial stability and trust in healthcare institutions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory oversight and policy changes in data protection.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: No immediate impact on counter-terrorism, but highlights vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Raises awareness of the need for robust cybersecurity measures in healthcare sectors.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial strain on affected individuals; erosion of trust in healthcare data management.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for signs of data misuse; ensure affected individuals are aware of compensation and protection options.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen cybersecurity frameworks in healthcare; foster public-private partnerships for improved data protection.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Enhanced data security and no significant misuse of data. Worst: Widespread identity theft and financial fraud. Most-Likely: Some cases of identity theft, leading to moderate regulatory changes.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- New York Blood Center (NYBC)
- Memorial Blood Centers
- Settlement Administrator (not specifically named)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, identity theft, healthcare, financial fraud, regulatory oversight, data protection
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us