Financial Implications of Security Breaches on SaaS Investment Strategies
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The Budget Effect of a Security Incident
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The shift towards proactive SaaS security investment is reducing the frequency of post-incident budget surges, as organizations increasingly recognize the cost-effectiveness of preventive measures. This trend affects SaaS vendors and customers, with moderate confidence that proactive security strategies will continue to gain traction. However, the evolving threat landscape and the integration of agentic AI present ongoing challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Organizations are increasingly adopting proactive security measures, reducing the need for emergency budget increases post-incident. This is supported by the decline in organizations increasing emergency investments after breaches, as reported by IBM. Key uncertainties include the actual effectiveness of these proactive measures against emerging threats.
- Hypothesis B: Despite the trend towards proactive investment, many organizations remain reactive, leading to significant budget reallocations following incidents. This is contradicted by the reported decrease in emergency spending, but supported by ongoing challenges in SaaS security expertise and resource allocation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the reported decrease in emergency spending and the proactive stance of organizations. Indicators such as the frequency of breaches and the integration of new technologies could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations have the capacity to implement effective proactive security measures; SaaS vendors and customers are aligned in their security priorities; the threat landscape will not outpace current security advancements.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of proactive measures and specific threat vectors targeting SaaS environments.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in vendor-reported security effectiveness; reliance on self-reported data from organizations may understate actual reactive spending.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The trend towards proactive security investment could stabilize organizational security postures, but the rapid evolution of threats, particularly with agentic AI, may outpace current measures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased global collaboration on cybersecurity standards may emerge as a response to shared threats.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security postures could deter cyber-terrorism efforts targeting SaaS platforms.
- Cyber / Information Space: Proactive measures may reduce the impact of cyber incidents, but the sophistication of attacks could increase.
- Economic / Social: Organizations investing in security may gain competitive advantages, influencing market dynamics and potentially leading to increased consumer trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage organizations to conduct comprehensive security audits and enhance collaboration between SaaS admins and InfoSec teams.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for shared threat intelligence and invest in training programs to bridge the SaaS security expertise gap.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Proactive measures significantly reduce breach incidents. Worst: New attack vectors overwhelm current defenses. Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security posture with periodic adjustments to address emerging threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
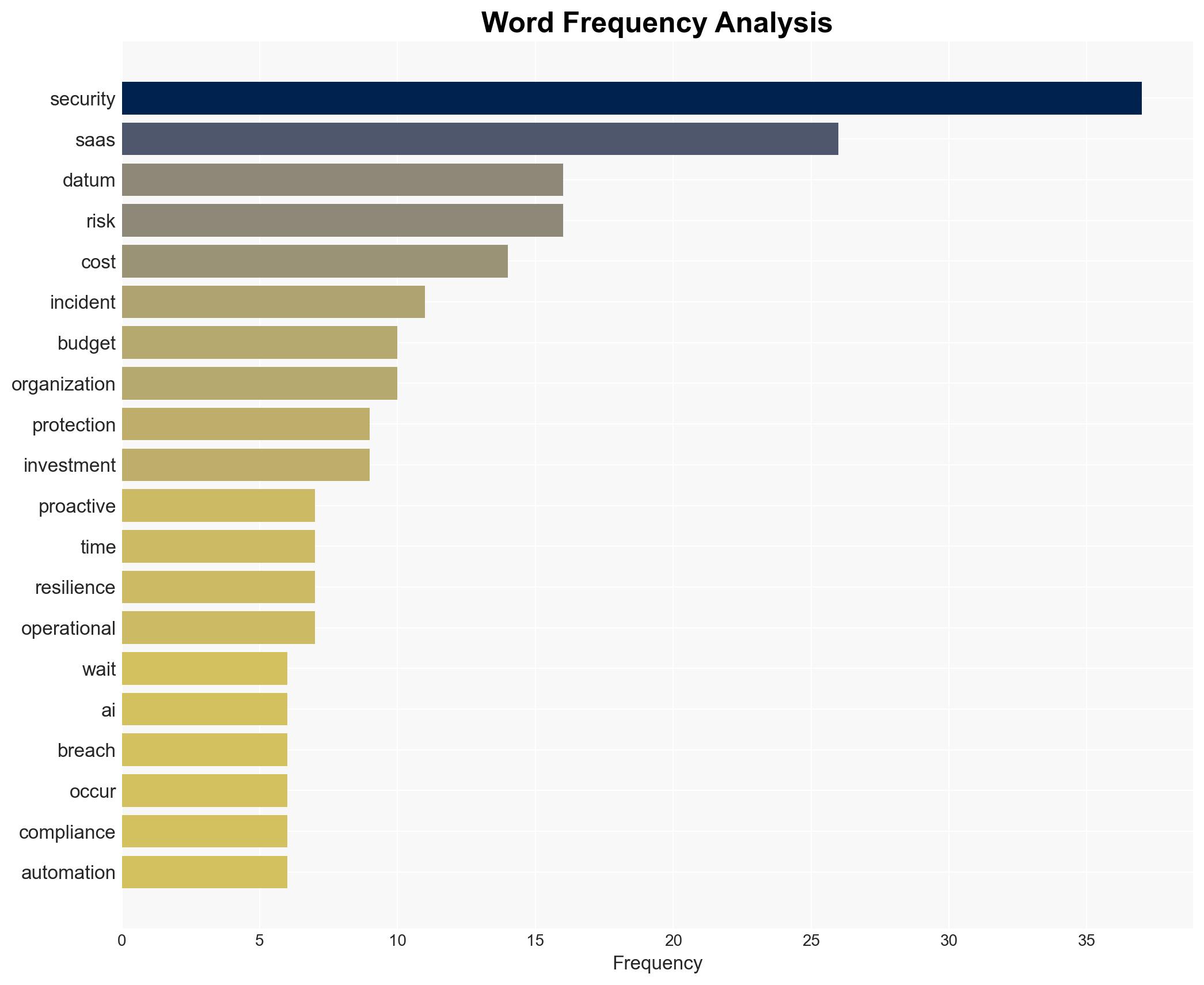
cybersecurity, SaaS security, proactive investment, data protection, agentic AI, threat landscape, budget allocation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us