FortiGate firewalls compromised by automated attacks exploiting SSO vulnerabilities for configuration theft
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: FortiGate firewalls hit by silent SSO intrusions and config theft
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
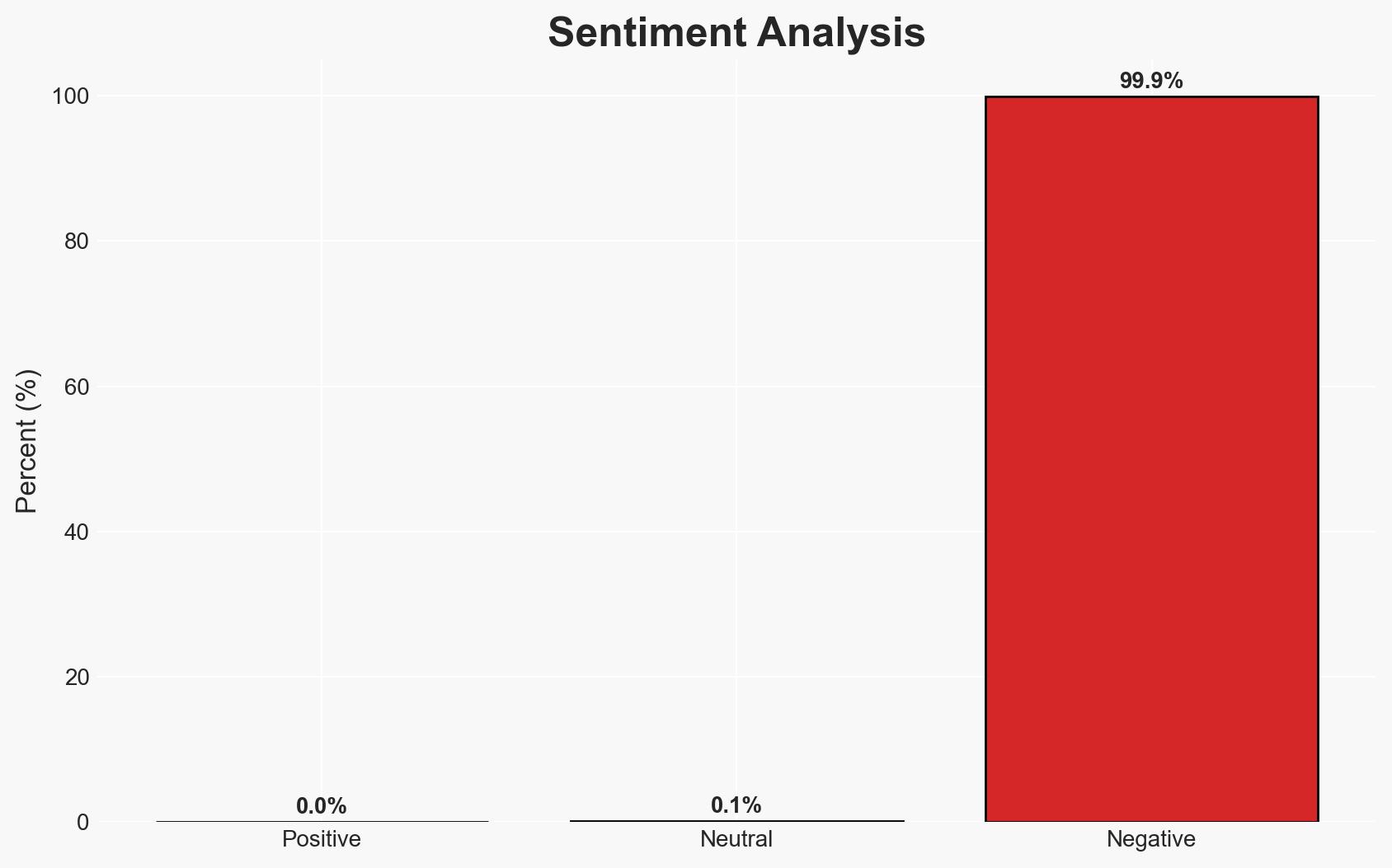
FortiGate firewalls are being compromised through a bypass of SSO protections, leading to unauthorized configuration changes and data exfiltration. This activity is likely facilitated by exploiting known vulnerabilities in Fortinet’s systems. The affected entities include organizations using FortiGate appliances. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The intrusions are due to exploitation of a patch bypass for CVE-2025-59718, which attackers are using to compromise systems believed to be secure. Supporting evidence includes reports from administrators and Arctic Wolf’s observations. However, the exact method of bypass remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The intrusions result from a new, undisclosed vulnerability in FortiGate systems that attackers have discovered. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of confirmation of a new vulnerability and the alignment of activity with known exploits.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of observed activity with known vulnerabilities and the lack of evidence for a new vulnerability. Indicators that could shift this judgment include discovery of a new exploit or confirmation of a patch bypass.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The reported vulnerabilities are the primary method of attack; Fortinet’s forthcoming patches will address the issue; organizations are following recommended security practices.
- Information Gaps: Specific technical details on how the patch bypass is being executed; confirmation of whether a new vulnerability exists.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from affected administrators; risk of deception by attackers to mislead about the method of intrusion.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny on Fortinet’s security practices and potential loss of trust among its user base. If not addressed, it could result in broader network compromises.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of network breaches and data theft across affected organizations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber threat activity targeting Fortinet users; potential for information operations exploiting the breach.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected companies and reputational damage to Fortinet.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Audit FortiGate admin accounts, review recent configuration changes, rotate credentials, and monitor SSO activity closely.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced monitoring and response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful patching and mitigation of vulnerabilities; Worst: Discovery of additional vulnerabilities leading to widespread breaches; Most-Likely: Continued exploitation attempts until effective patches are deployed.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortinet
- Arctic Wolf
- Administrators of affected systems
- Attackers using IP address 104.28.244.114
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability exploitation, network security, Fortinet, SSO bypass, cyber threat, data exfiltration
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us