Fortinet Issues Security Update for Critical CVE-2026-24858 Exploiting FortiOS SSO Vulnerability
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Fortinet Patches CVE-2026-24858 After Active FortiOS SSO Exploitation Detected
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
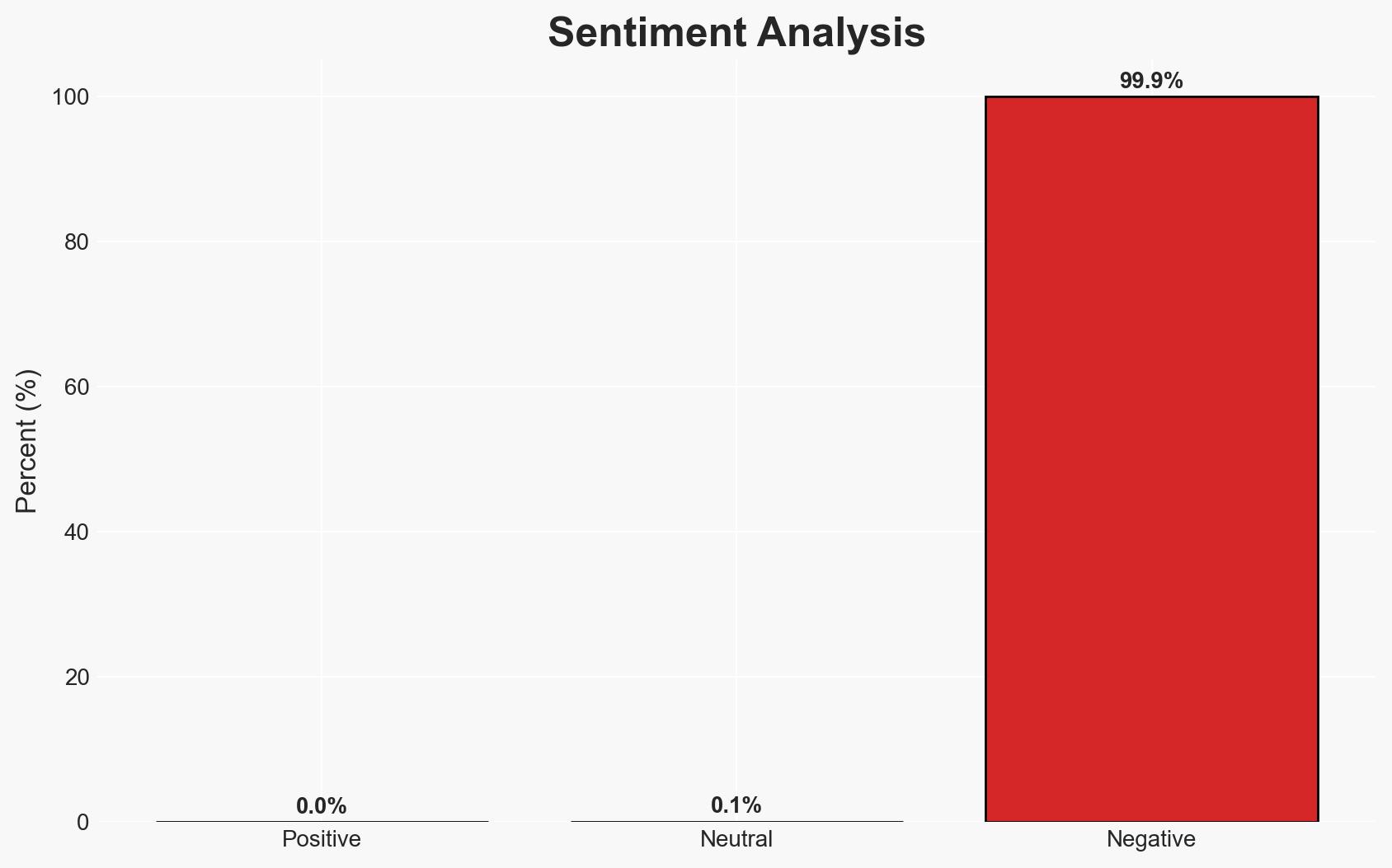
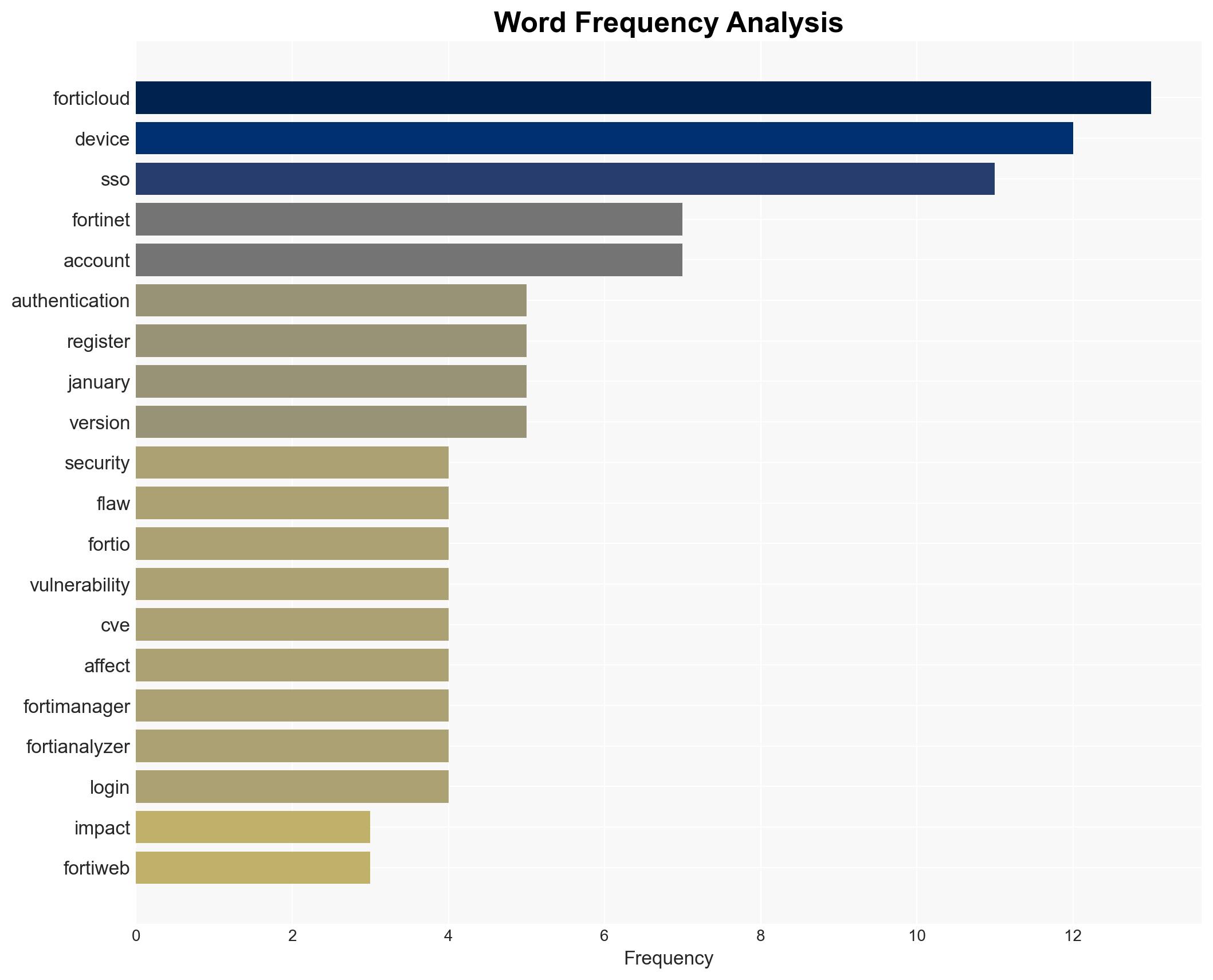
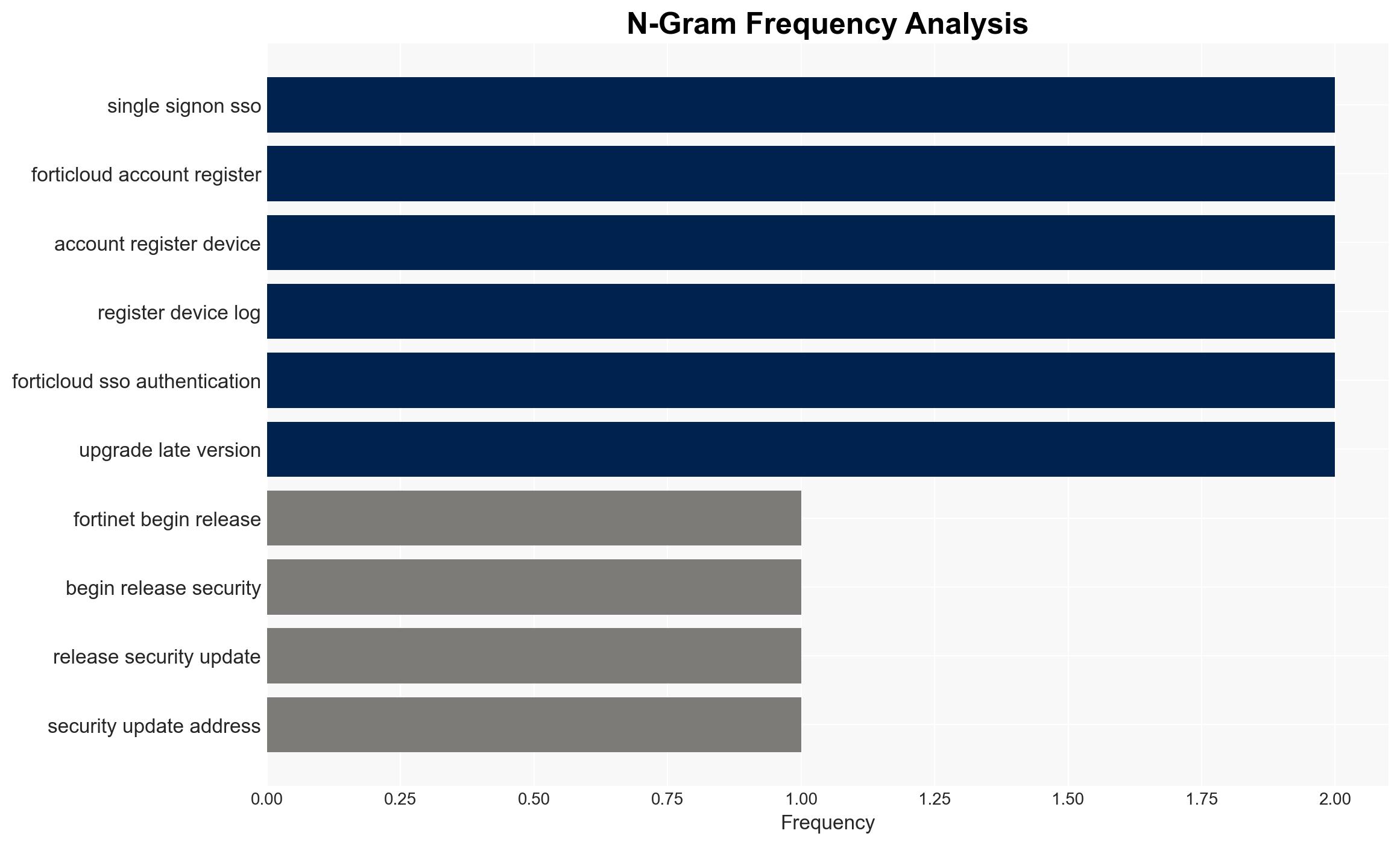
Fortinet has released patches for a critical vulnerability (CVE-2026-24858) in FortiOS, which has been actively exploited. This flaw allows unauthorized access via FortiCloud SSO, impacting FortiManager and FortiAnalyzer. The vulnerability poses significant risks to organizations using these systems. There is moderate confidence in the assessment that the exploitation is likely part of a broader campaign targeting Fortinet products.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The exploitation of CVE-2026-24858 is part of a targeted campaign by a sophisticated threat actor aiming to compromise critical infrastructure. Supporting evidence includes the active exploitation and the creation of persistent admin accounts. However, the identity and motives of the threat actors remain unclear.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation is opportunistic, conducted by multiple actors exploiting the vulnerability for various purposes, such as data theft or network disruption. This is supported by the rapid exploitation following the vulnerability’s disclosure and the involvement of multiple malicious accounts.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the coordinated nature of the attacks and the specific targeting of Fortinet’s security infrastructure. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include identification of the threat actors or evidence of widespread, indiscriminate exploitation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is not present in the default configuration; Fortinet’s patches effectively mitigate the risk; the threat actors have limited resources to exploit patched systems.
- Information Gaps: The identity and objectives of the threat actors; the full scope of affected systems; potential undisclosed vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underestimation of the threat actors’ capabilities; reliance on Fortinet’s disclosures without independent verification; possible misdirection by threat actors to obscure true targets.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of CVE-2026-24858 could lead to increased scrutiny of Fortinet’s security practices and impact trust in their products. This development may also prompt similar attacks on other security vendors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are involved; scrutiny on cybersecurity policies and vendor accountability.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for similar vulnerabilities; potential for exploitation in critical infrastructure sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased activity in cyber threat forums; potential for new attack vectors leveraging similar vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Financial impact on affected organizations; potential loss of customer trust in Fortinet and similar vendors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently apply Fortinet patches; audit systems for signs of compromise; enhance monitoring for unusual activity.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in resilience measures and incident response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patch adoption mitigates threat with minimal impact.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leads to significant breaches and financial losses.
- Most Likely: Continued targeted attacks with moderate impact, prompting increased security measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortinet
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Unidentified threat actors
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, threat actors, Fortinet, network security, cyber exploitation, incident response
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us