France imposes €42 million fine on Free Mobile for 2024 data breach affecting 23 million customers
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: France fines Free Mobile 42 million over 2024 data breach incident
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
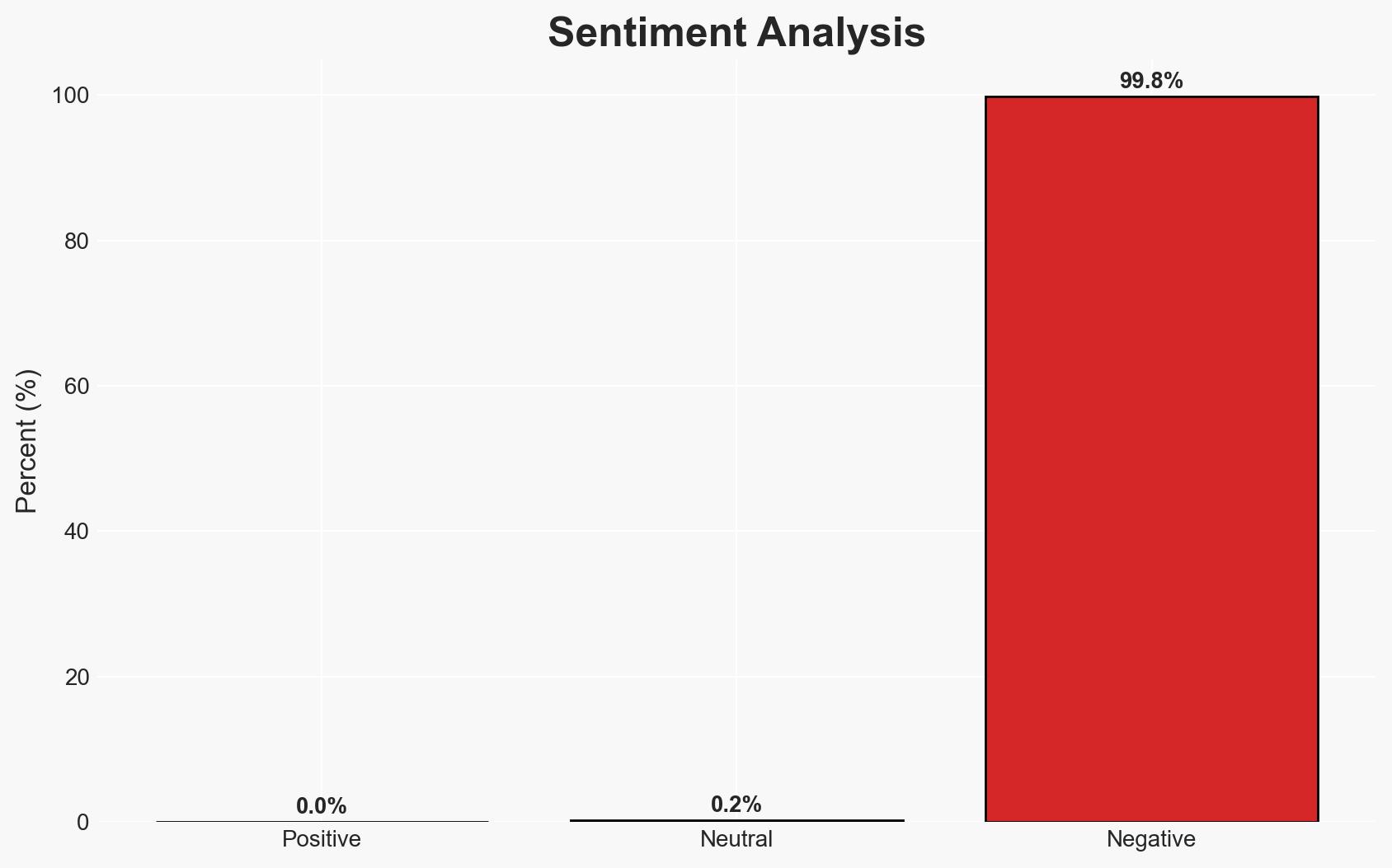
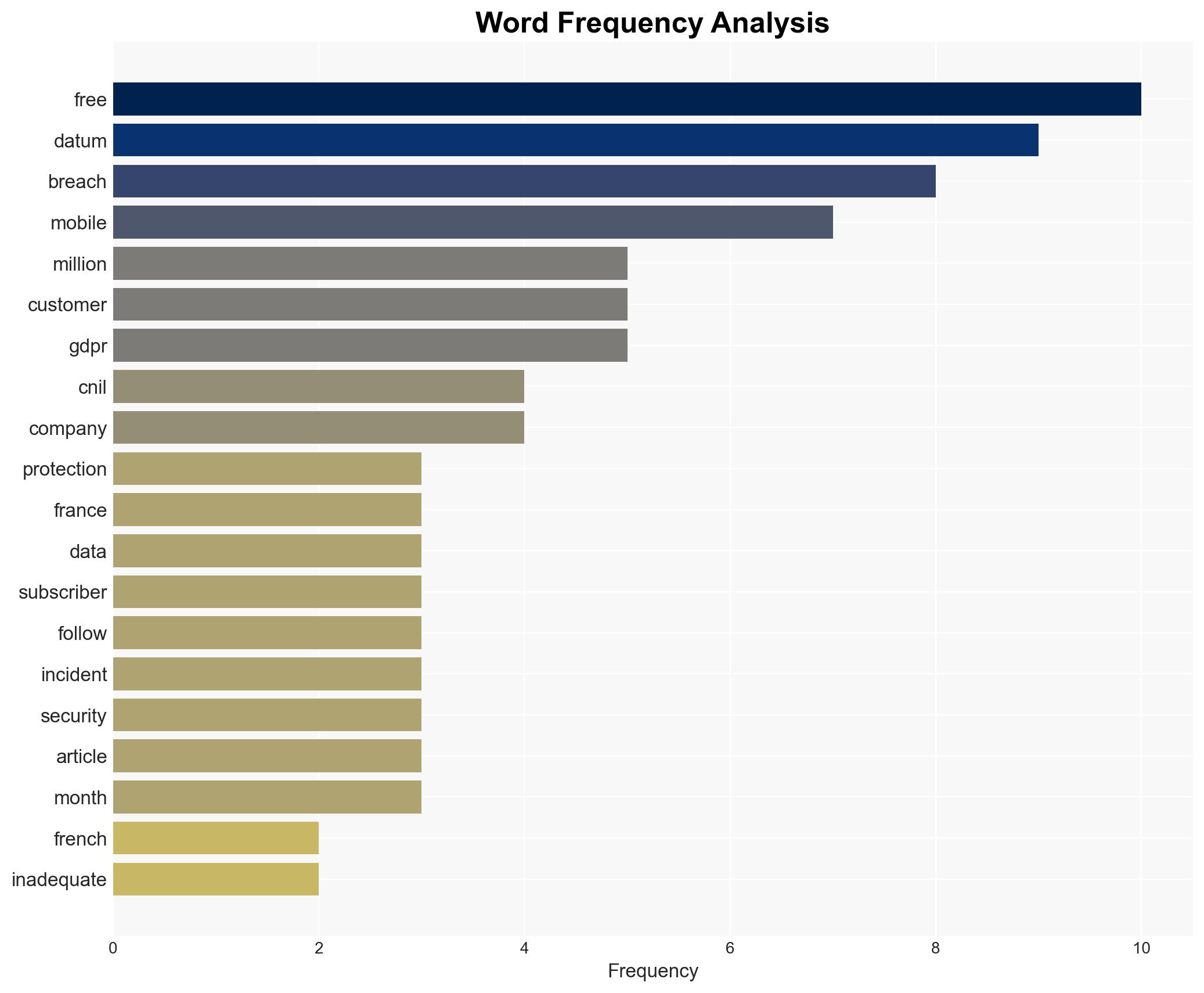
The French data protection authority fined Free Mobile €42 million for inadequate data protection leading to a significant breach affecting nearly 23 million subscribers. The breach highlights systemic cybersecurity weaknesses within major French telecommunications firms. The most likely hypothesis is that the breach resulted from insufficient cybersecurity measures rather than a targeted attack. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was primarily due to inadequate cybersecurity measures at Free Mobile, as evidenced by weak VPN authentication and poor detection of abnormal activity. However, the exact sophistication of the attack remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was a targeted attack by a sophisticated threat actor exploiting systemic vulnerabilities across the telecommunications sector, as indicated by subsequent breaches at other major providers. Evidence for this is less direct and relies on broader sector trends.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to specific findings of inadequate security practices at Free Mobile. Indicators such as improved cybersecurity measures post-breach could shift this judgment if they reveal more about the attack’s sophistication.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Free Mobile’s cybersecurity improvements are genuine and comprehensive; the breach was not state-sponsored; CNIL’s findings are accurate and unbiased.
- Information Gaps: Details on the hackers’ identity and methods; specific vulnerabilities exploited; comprehensive data on sector-wide cybersecurity practices.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in CNIL’s reporting; possible underreporting or misrepresentation by Free Mobile; deception by the hacker community regarding the breach’s scope.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The breach could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and pressure on telecommunications firms to enhance cybersecurity. This may drive sector-wide improvements but also increase operational costs.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased EU-wide regulatory actions on data protection and cybersecurity.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of similar breaches being exploited for malicious purposes, including espionage or sabotage.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased hacker activity targeting perceived vulnerabilities in telecommunications; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting breach data.
- Economic / Social: Loss of consumer trust in telecommunications providers; potential financial losses from fines and increased security expenditures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough review of cybersecurity protocols across the telecommunications sector; enhance monitoring for similar breach attempts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop sector-wide cybersecurity resilience measures; foster partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Comprehensive cybersecurity reforms prevent further breaches.
- Worst: Continued breaches lead to significant economic and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity with occasional breaches due to evolving threat landscape.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Free Mobile
- CNIL (French data protection authority)
- Orange France
- Bouygues Telecom
- ‘drussellx’ (hacker forum account)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, telecommunications, GDPR, regulatory compliance, hacker activity, France
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us