French Interior Minister confirms breach of email servers in recent cyberattack, investigation underway.
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
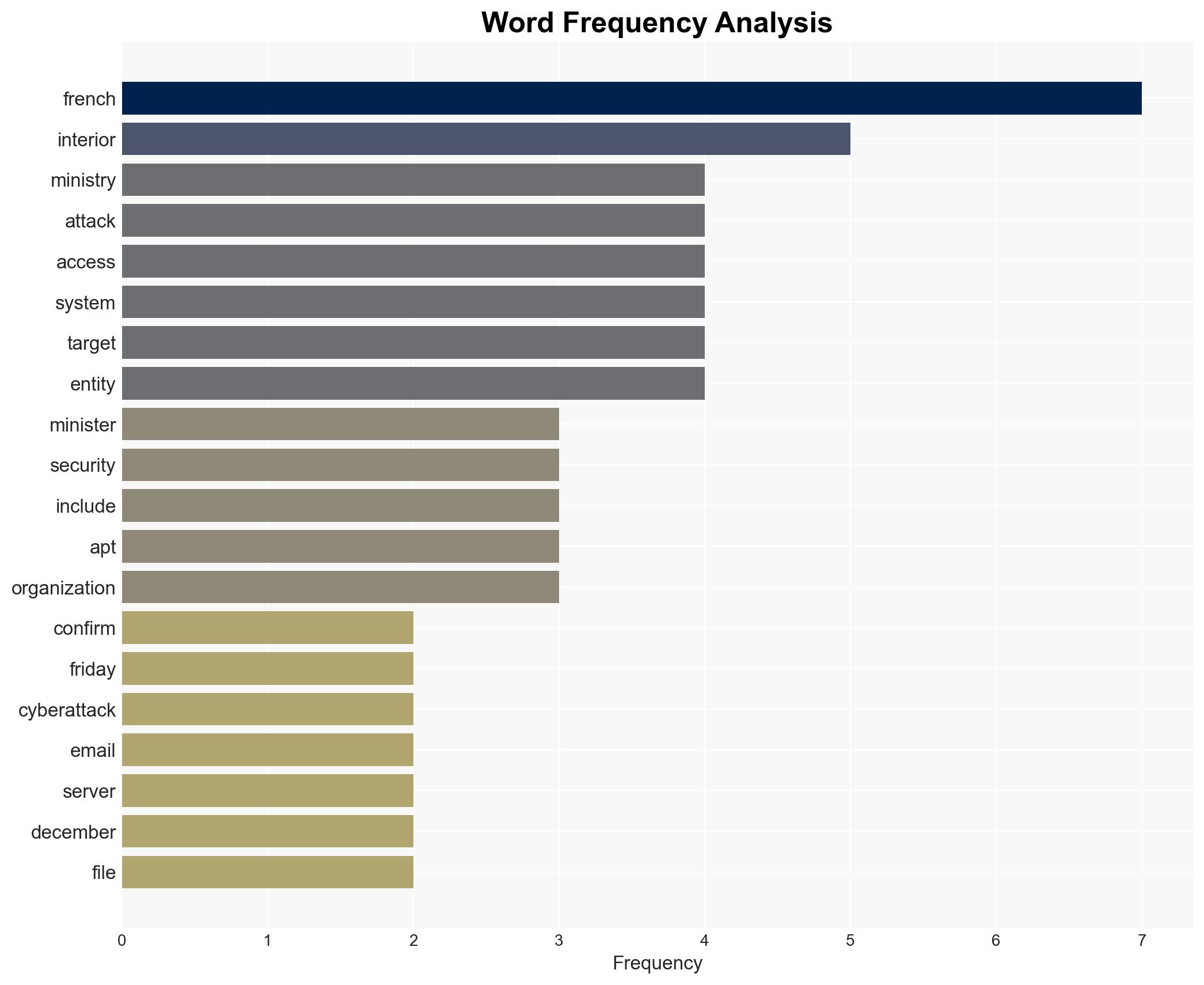
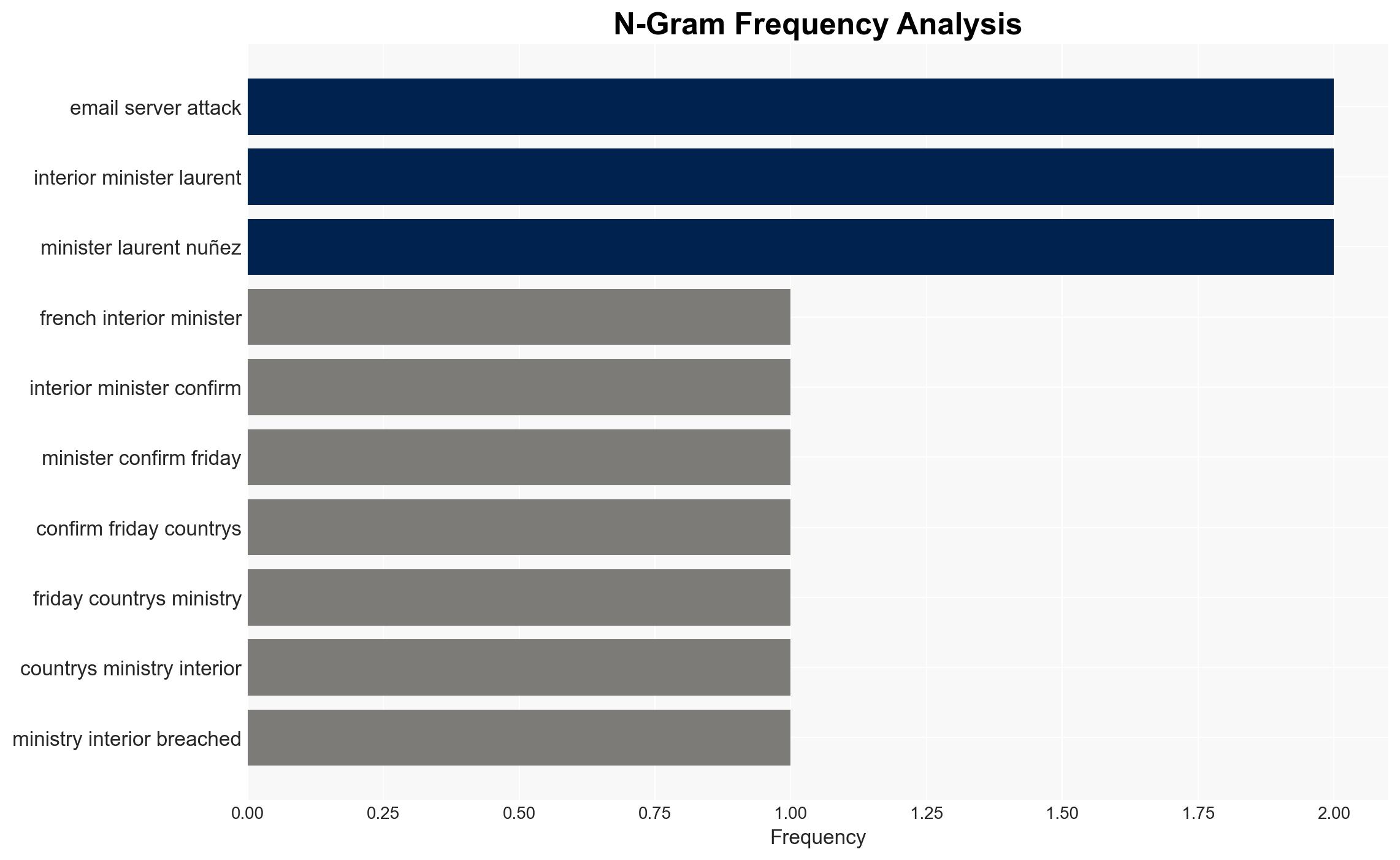
Intelligence Report: French Interior Ministry confirms cyberattack on email servers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
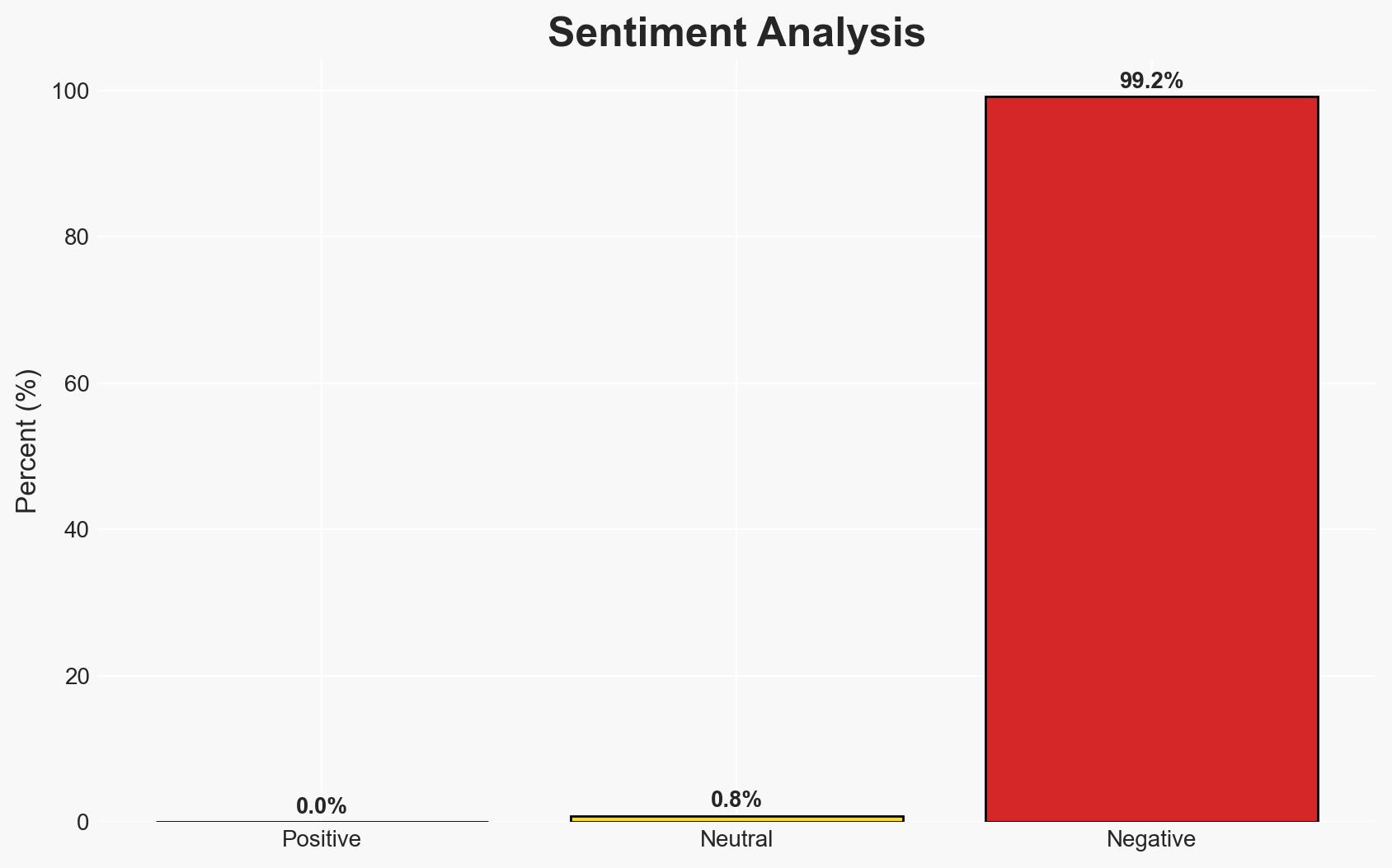
The French Interior Ministry experienced a cyberattack compromising its email servers, potentially linked to foreign interference or cybercrime. The breach underscores vulnerabilities in government systems, with a moderate confidence level in attributing the attack to state-sponsored actors, possibly linked to previous APT28 activities. The incident affects national security and internal operations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The cyberattack was conducted by a state-sponsored group, potentially APT28, aiming to gather intelligence or disrupt French governmental operations. This hypothesis is supported by the ministry’s high-value target status and APT28’s history of targeting similar entities. However, the lack of confirmed data exfiltration and attribution remains a key uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was executed by non-state actors, such as hacktivists or cybercriminals, seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for ideological reasons or financial gain. This is supported by the possibility of activists demonstrating system weaknesses, but lacks direct evidence linking specific groups.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the pattern of previous APT28 activities targeting similar entities and the strategic value of the Interior Ministry. Indicators such as confirmed data exfiltration or specific malware signatures could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The breach was sophisticated enough to suggest a well-resourced actor; the Interior Ministry’s systems were not fully secured against known threats; APT28 remains active in targeting European entities.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the methods used in the breach, confirmation of data exfiltration, and forensic analysis results are missing.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Attribution bias towards APT28 due to historical patterns; potential misinformation from threat actors to obscure true origins.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The cyberattack on the French Interior Ministry could have significant ramifications for national security and international relations, particularly if linked to state-sponsored actors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in tensions between France and suspected state actors, notably Russia, if attribution to APT28 is confirmed.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased scrutiny on internal security measures and potential reevaluation of cyber defense strategies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness of vulnerabilities in governmental systems, possibly leading to enhanced cybersecurity protocols and international cooperation.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on public trust in governmental cybersecurity capabilities and increased demand for cybersecurity investments.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive forensic investigation, enhance monitoring of critical systems, and engage with international partners for intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including regular security audits, staff training, and improved incident response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No significant data exfiltration, leading to minimal operational disruption.
- Worst: Confirmation of state-sponsored involvement, resulting in diplomatic fallout and increased cyber threats.
- Most-Likely: Identification of threat actors with moderate impact, prompting policy and security adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Laurent Nuñez, French Interior Minister
- APT28, suspected state-sponsored hacking group
- French National Agency for the Security of Information Systems (ANSSI)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, state-sponsored hacking, APT28, national security, cyber-espionage, intelligence gathering, France
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us