Global Encryption Defense: 2025 Insights on Legislative Challenges and Resilience
Published on: 2025-12-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Defending Encryption in the US and Abroad 2025 in Review
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
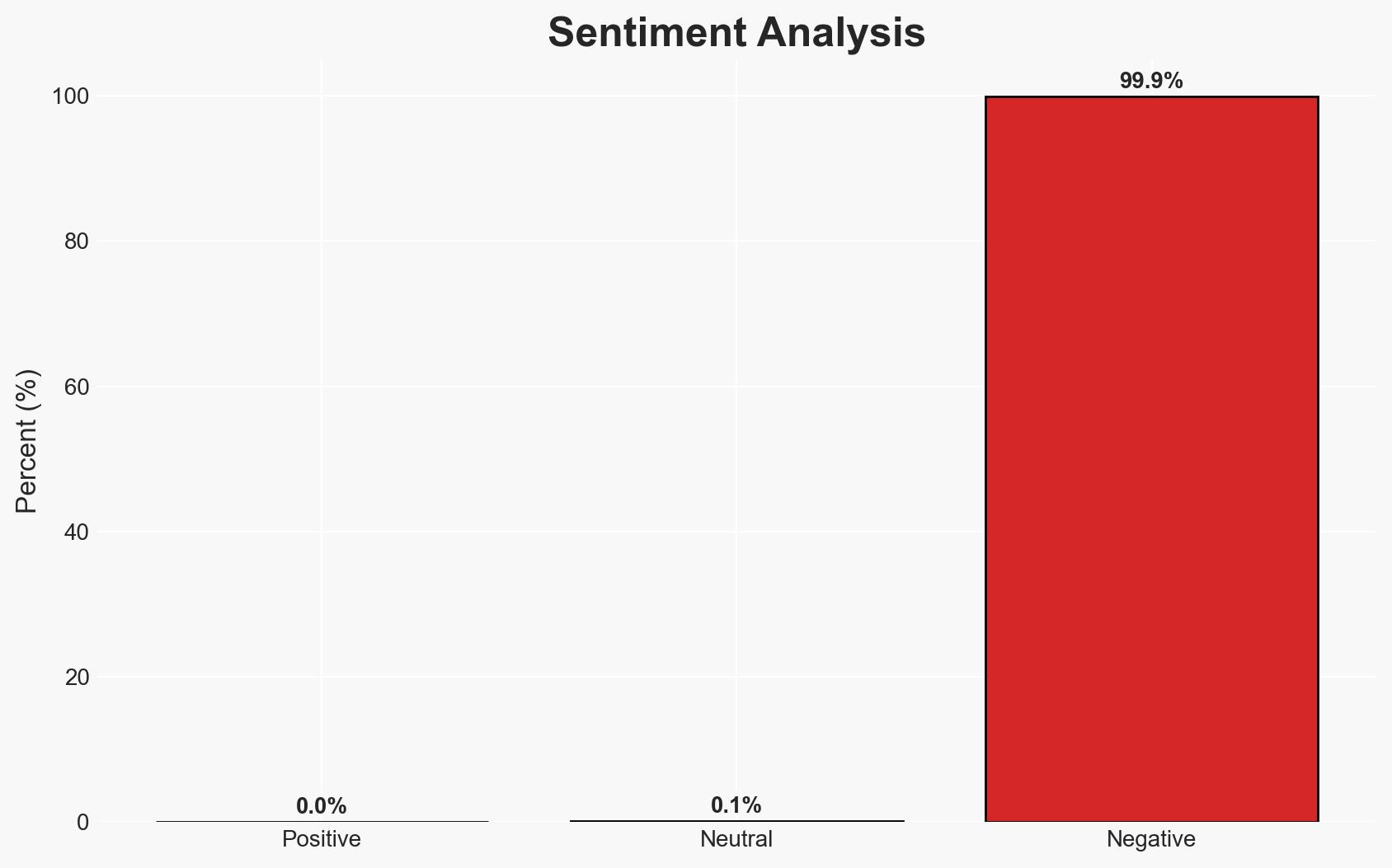
Efforts to undermine encryption continue globally, with significant legislative challenges in the EU, UK, and US. The most likely hypothesis is that these efforts will persist, driven by national security concerns, despite strong opposition from privacy advocates. This situation affects technology companies, law enforcement, and users of encrypted services. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Governments will continue to push for encryption-breaking measures due to national security imperatives. This is supported by ongoing legislative attempts in the EU and UK. However, repeated failures to pass such measures indicate significant resistance and uncertainty about future success.
- Hypothesis B: Privacy advocates and technology companies will successfully defend encryption, preventing significant legislative changes. Evidence includes the rejection of proposals in France and the EU, but the UK’s actions against Apple suggest this outcome is not guaranteed.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the persistent nature of government efforts and the partial successes in the UK. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in public opinion or significant technological advancements in encryption.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Governments prioritize national security over privacy; technology companies will resist encryption-breaking measures; public opinion favors privacy rights.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the EU’s “Technology Roadmap on Encryption” and the UK’s revised demands to Apple are lacking.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from privacy advocacy groups and technology companies; possible government manipulation of national security narratives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing debate over encryption could lead to increased tensions between governments and technology companies, affecting international relations and digital privacy standards.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic friction between countries with differing encryption policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Encryption-breaking measures could enhance law enforcement capabilities but also risk misuse or overreach.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased vulnerability to cyber threats if encryption is weakened; potential chilling effects on digital communication.
- Economic / Social: Impact on technology sector innovation and consumer trust; possible public backlash against perceived privacy infringements.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor legislative developments in the EU, UK, and US; engage with stakeholders to assess potential impacts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience strategies for technology companies; foster international dialogue on encryption standards.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Strengthened encryption standards globally. Worst: Widespread adoption of encryption-breaking laws. Most-Likely: Continued legislative battles with incremental changes.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
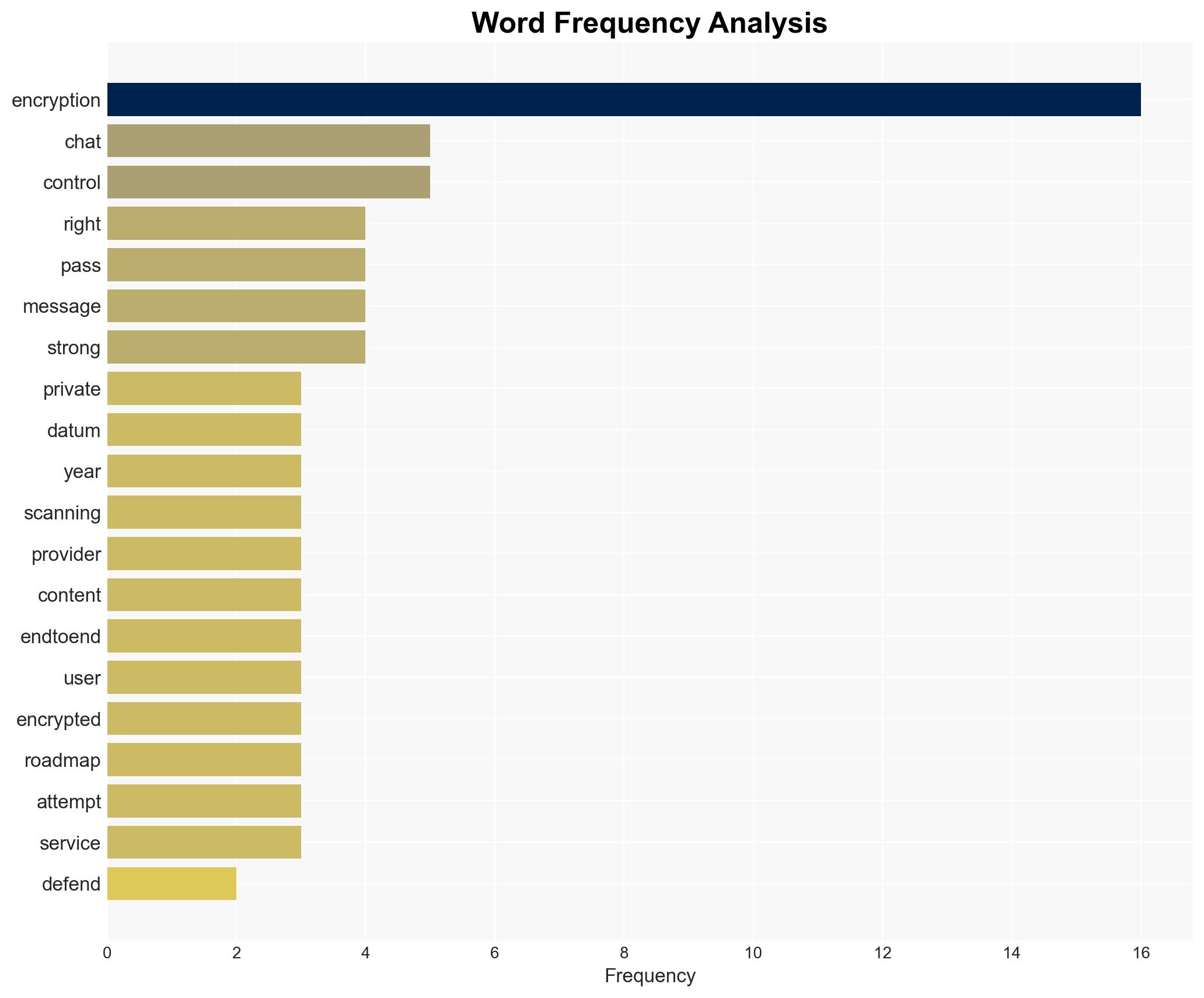
cybersecurity, encryption, privacy rights, national security, legislation, technology policy, cyber security, international relations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us