Google Cloud KMS Launches Post-Quantum KEM Support to Combat Harvest Now Decrypt Later Threat – InfoQ.com
Published on: 2025-10-26
Intelligence Report: Google Cloud KMS Launches Post-Quantum KEM Support to Combat Harvest Now Decrypt Later Threat – InfoQ.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
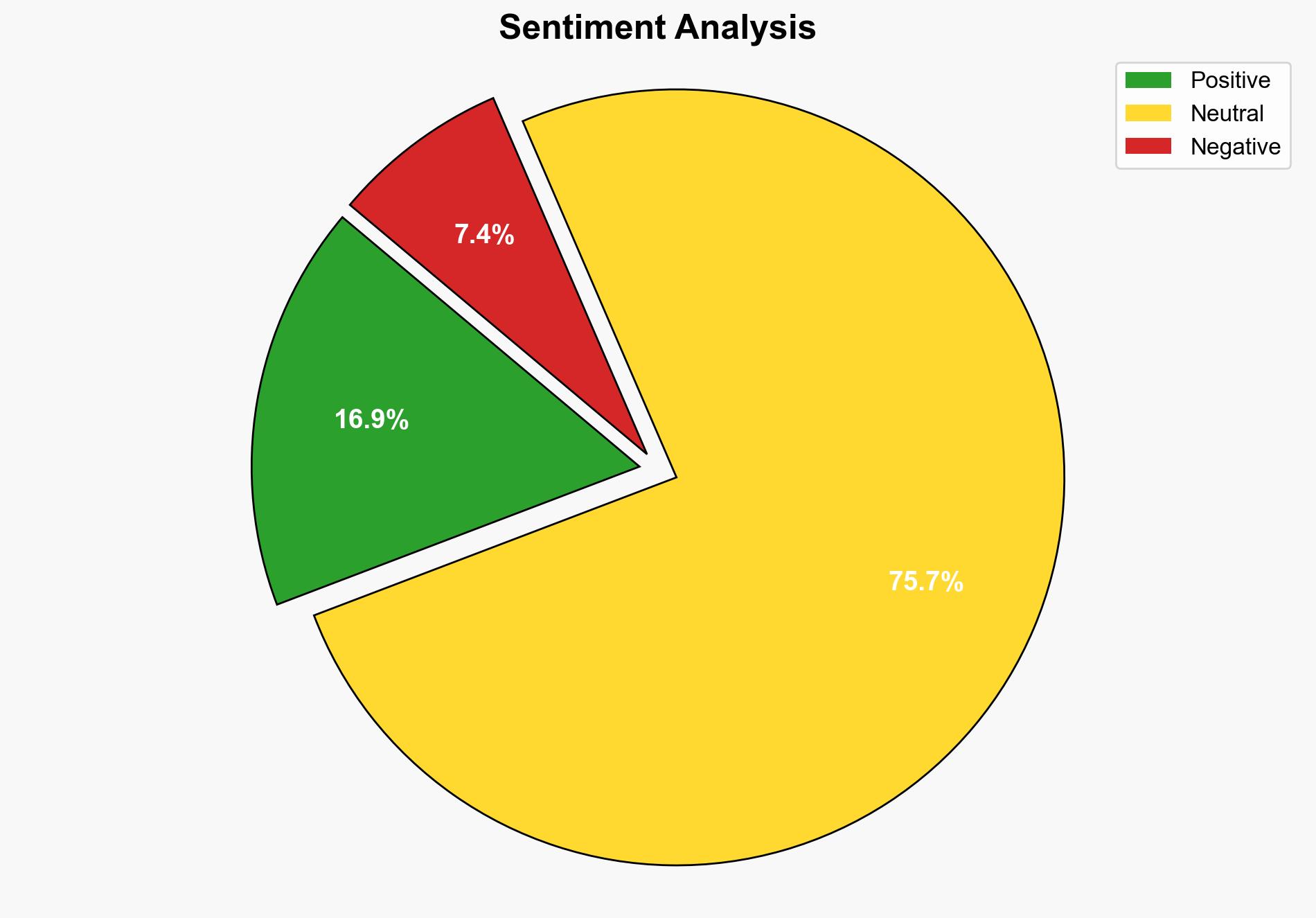
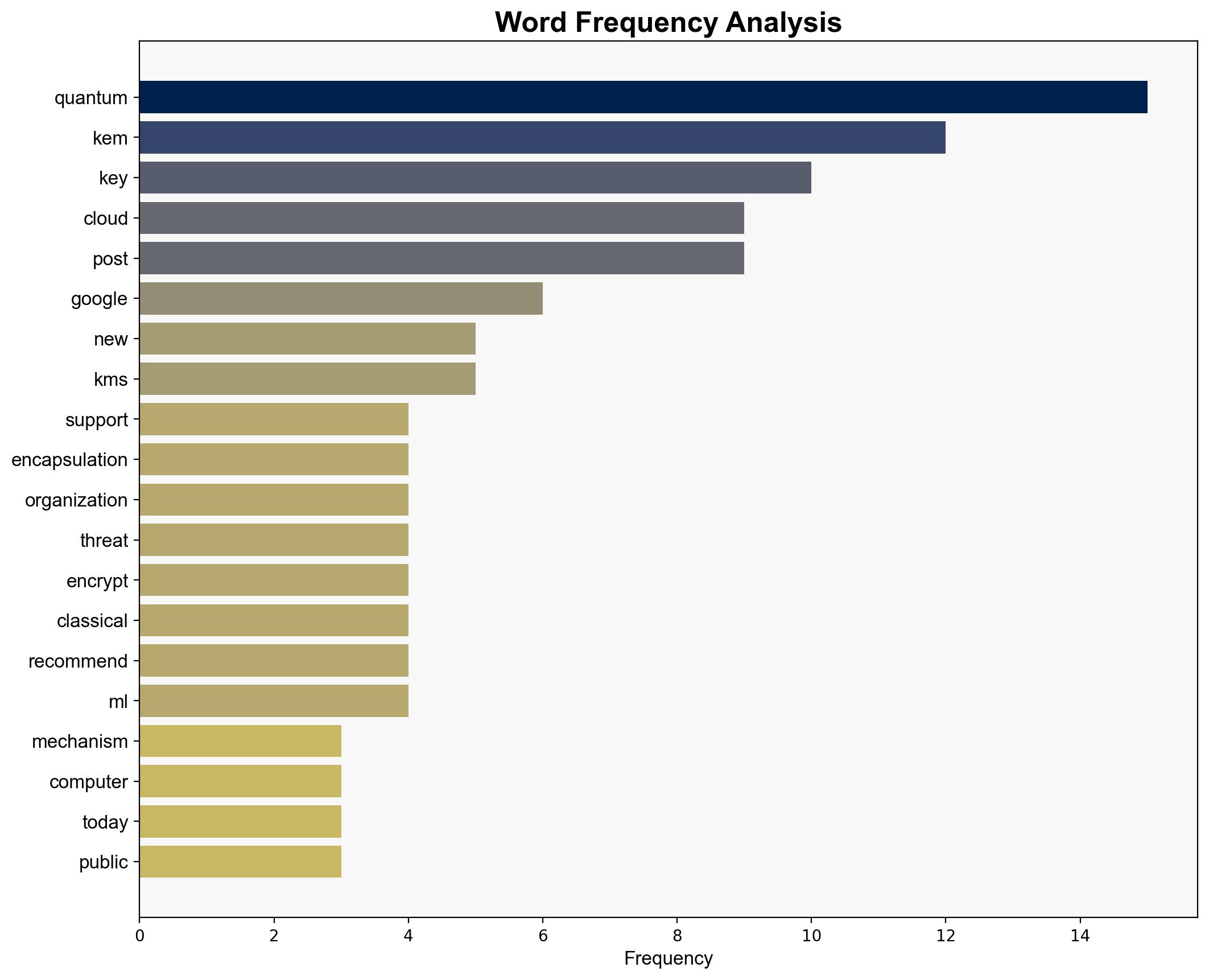
Google Cloud’s introduction of post-quantum Key Encapsulation Mechanism (KEM) support in its Key Management Service (KMS) is a proactive measure against future quantum computing threats. The most supported hypothesis is that this move positions Google Cloud as a leader in quantum-safe technology, potentially setting a new industry standard. Confidence level: High. Recommended action: Organizations should begin integrating post-quantum cryptographic solutions to safeguard long-term data confidentiality.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis 1**: Google Cloud’s KEM support is primarily a strategic move to establish itself as a leader in quantum-safe technology, influencing industry standards and gaining a competitive edge.
2. **Hypothesis 2**: The launch is a defensive measure in response to increasing awareness and pressure from stakeholders about the potential threats posed by quantum computing, aiming to mitigate future risks and liabilities.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) method, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to Google’s proactive development of open-source cryptographic libraries and its emphasis on hybrid encryption approaches, indicating a strategic vision beyond immediate defensive needs.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that quantum computing will become a viable threat within the next decade, necessitating immediate action. Another assumption is that current cryptographic methods will be insufficient against future quantum capabilities.
– **Red Flags**: The actual timeline for quantum computing threats remains uncertain, and there may be overestimation of immediate risks. Additionally, the complexity of integrating new cryptographic methods could pose unforeseen challenges.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The introduction of post-quantum KEM could accelerate the industry’s transition to quantum-safe technologies, impacting economic and cybersecurity landscapes. Organizations lagging in adoption may face increased vulnerability. Geopolitically, nations investing in quantum computing could gain strategic advantages, potentially leading to an arms race in quantum technology.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Organizations should assess their current cryptographic infrastructure and begin planning for the integration of post-quantum solutions.
- Best-case scenario: Early adopters gain a competitive advantage and enhanced security posture.
- Worst-case scenario: Delayed adoption results in increased vulnerability to quantum threats.
- Most likely scenario: Gradual industry-wide shift towards post-quantum cryptography, driven by leading tech companies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Brent Muir
– Swamynathan Arunachalam
– Toyosi Kuteyi
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, quantum computing, cryptography, technology innovation