Google security chief warns of imminent AI-driven cyberattack tools for criminals
Published on: 2026-01-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: AI-powered cyberattack kits are ‘just a matter of time’ warns Google exec
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
AI-powered cyberattack kits are likely to emerge within the next six to 18 months, posing significant risks to cybersecurity due to their potential for automation and scale. This development will primarily affect organizations’ security postures globally, with moderate confidence in this assessment. The democratization of these tools could lead to widespread exploitation by both state and non-state actors.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI-powered cyberattack kits will become widely available and lead to a significant increase in automated cyberattacks. This hypothesis is supported by current trends in AI usage for small-scale cybercriminal activities and the historical precedent of exploit kits like Metasploit. However, the timeline for full development remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: AI-powered cyberattack kits will not significantly alter the current threat landscape due to effective countermeasures and the complexity of integrating AI into full-scale attack frameworks. This is contradicted by the ongoing experimentation with AI by cybercriminals and state actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the observable trend of AI integration into cybercriminal activities and the potential for these tools to be chained together. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include advancements in defensive AI technologies and regulatory measures limiting AI misuse.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technology will continue to advance at its current pace; cybercriminals will have access to AI tools; defensive measures will not outpace offensive capabilities.
- Information Gaps: Specific timelines for the development of end-to-end AI cyberattack kits; detailed capabilities of current AI tools in use by cybercriminals.
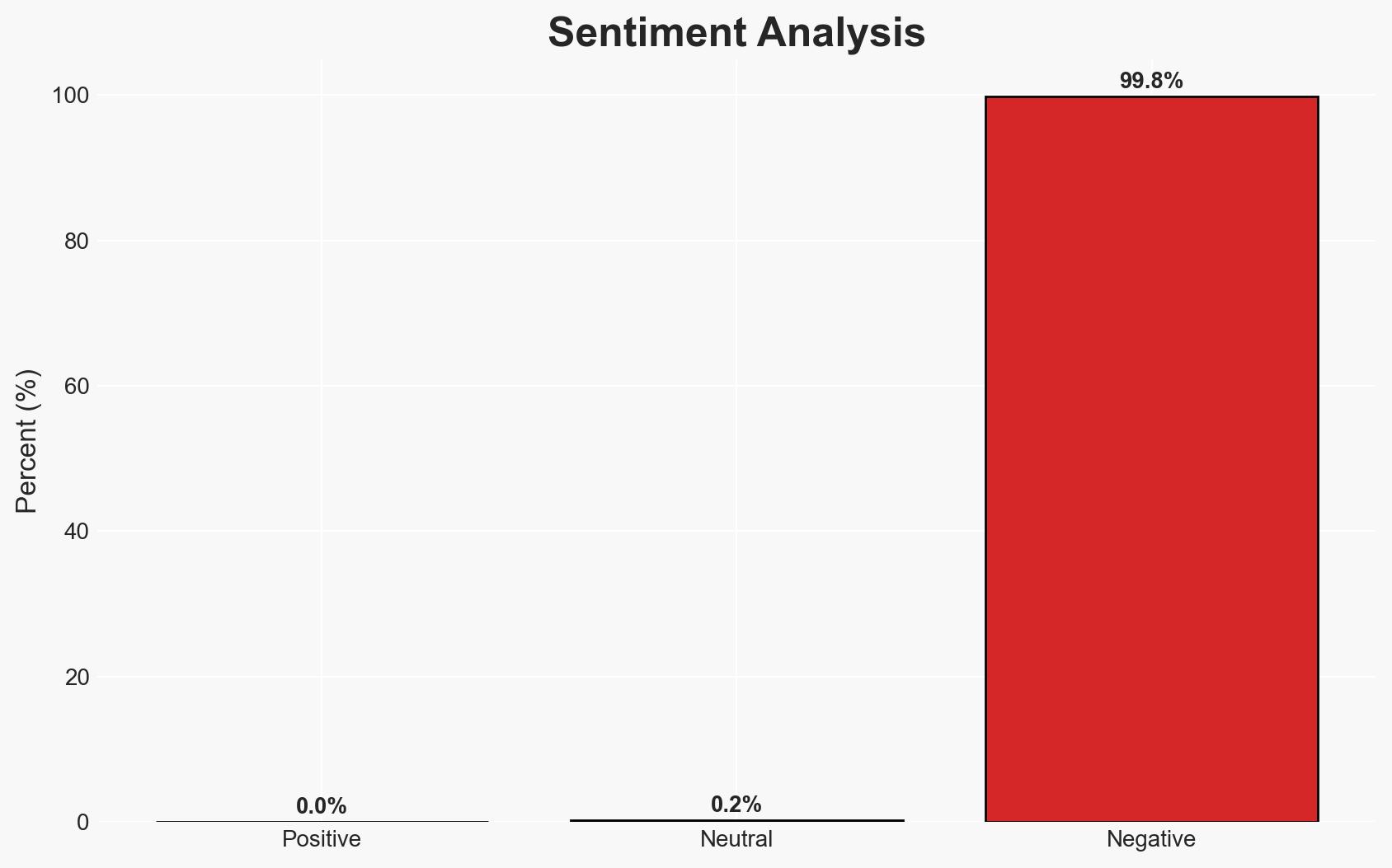
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source perspectives due to vested interests in cybersecurity solutions; risk of overestimating AI capabilities based on speculative scenarios.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of AI-powered cyberattack kits could significantly alter the cybersecurity landscape, leading to increased automation and scale of attacks. This could exacerbate existing vulnerabilities and create new challenges for defense mechanisms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation of cyber conflicts involving state actors leveraging AI tools, impacting international relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat from non-state actors and terrorist groups utilizing AI for cyber operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced capabilities for data theft, network infiltration, and misinformation campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruptions from large-scale cyberattacks, affecting business continuity and public trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of AI developments in cybercrime; enhance collaboration with tech companies for threat intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop AI-based defensive tools; invest in cybersecurity training for detecting AI-driven threats; strengthen international cyber norms.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures limit AI tool misuse, maintaining current threat levels.
- Worst: Rapid proliferation of AI attack kits leads to widespread cyber disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in AI-driven attacks with corresponding advancements in defense, maintaining a dynamic threat landscape.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Heather Adkins, VP of Security Engineering, Google
- Sandra Joyce, VP, Google Threat Intelligence Group
- Anton Chuvakin, Security Advisor, Google’s Office of the CISO
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI in cybercrime, threat intelligence, exploit kits, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us