Hackers Exploit Google Ads to Distribute MacSync Malware through ClickFix Technique Targeting Mac Users
Published on: 2026-02-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Google Ads and Claude AI Abused to Spread MacSync Malware via ClickFix
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
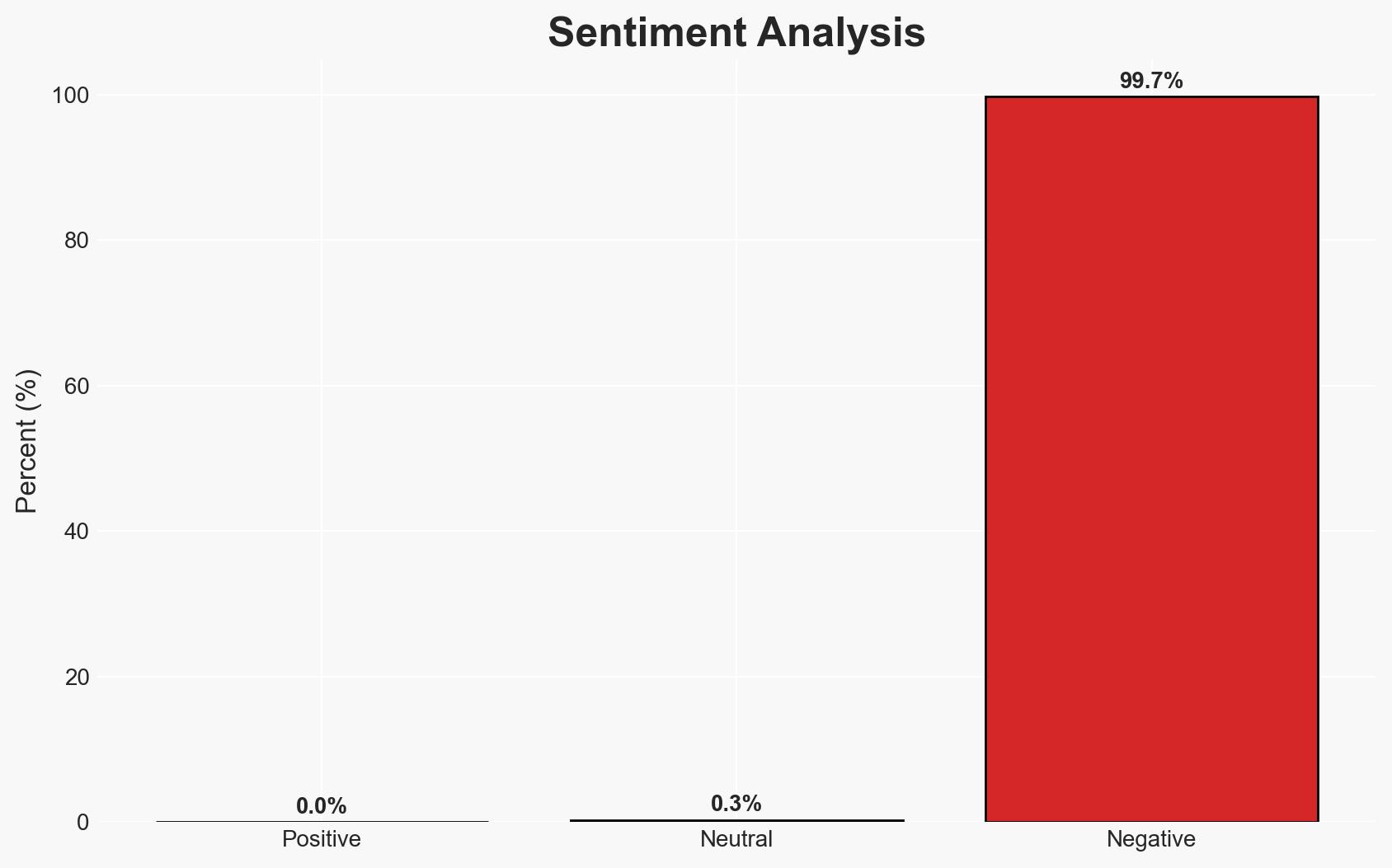
The MacSync malware campaign exploits legitimate Google Ads and AI platforms to target Mac users, leveraging social engineering to bypass traditional security measures. The campaign primarily affects users searching for technical macOS solutions. The most likely hypothesis is that a sophisticated threat actor is refining existing malware techniques to exploit trusted platforms. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate due to limited visibility into the threat actor’s identity and capabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: A coordinated cybercriminal group is systematically exploiting trusted platforms like Google Ads and Claude AI to distribute MacSync malware, utilizing advanced social engineering techniques. This is supported by the use of verified accounts and the sophisticated nature of the malware.
- Hypothesis B: Disparate individual actors are opportunistically using available tools and platforms to spread malware, without a centralized coordination. This is less supported due to the consistent use of the same C2 server and the rebranding of known malware.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the sophistication and consistency of the attack methods, indicating a coordinated effort. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of disparate actors or a lack of further coordinated attacks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The threat actor has significant technical capabilities; Google and AI platforms are not fully aware of the exploitation; Mac users are the primary targets.
- Information Gaps: Identity and motivation of the threat actor; full scope of the campaign’s impact; detailed technical analysis of the malware’s evolution.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing the attack to a single group; risk of deception in the use of legitimate platforms to mask malicious intent.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny and regulation of online advertising and AI platforms. The campaign’s success may encourage similar attacks, impacting user trust in digital platforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions if state-sponsored actors are involved or if platforms are perceived as negligent.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to cybersecurity infrastructure and potential for similar tactics in other domains.
- Cyber / Information Space: Erosion of trust in digital platforms and increased demand for robust cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for affected users and reputational damage to platforms involved.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of Google Ads and AI platforms for similar exploits; increase user awareness campaigns on safe computing practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies to improve detection and response capabilities; invest in AI-driven threat intelligence tools.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Platforms implement effective countermeasures, reducing attack success rates.
- Worst: Attack techniques evolve, leading to widespread data breaches and loss of trust.
- Most-Likely: Continued refinement of malware tactics with periodic successful attacks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Moonlock Lab (Cyber security researchers)
- MacPaw (Software developer)
- Earth Rangers (Canadian children’s charity)
- T S Q SA (Colombian watch retailer)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet (Threat actor)
7. Thematic Tags
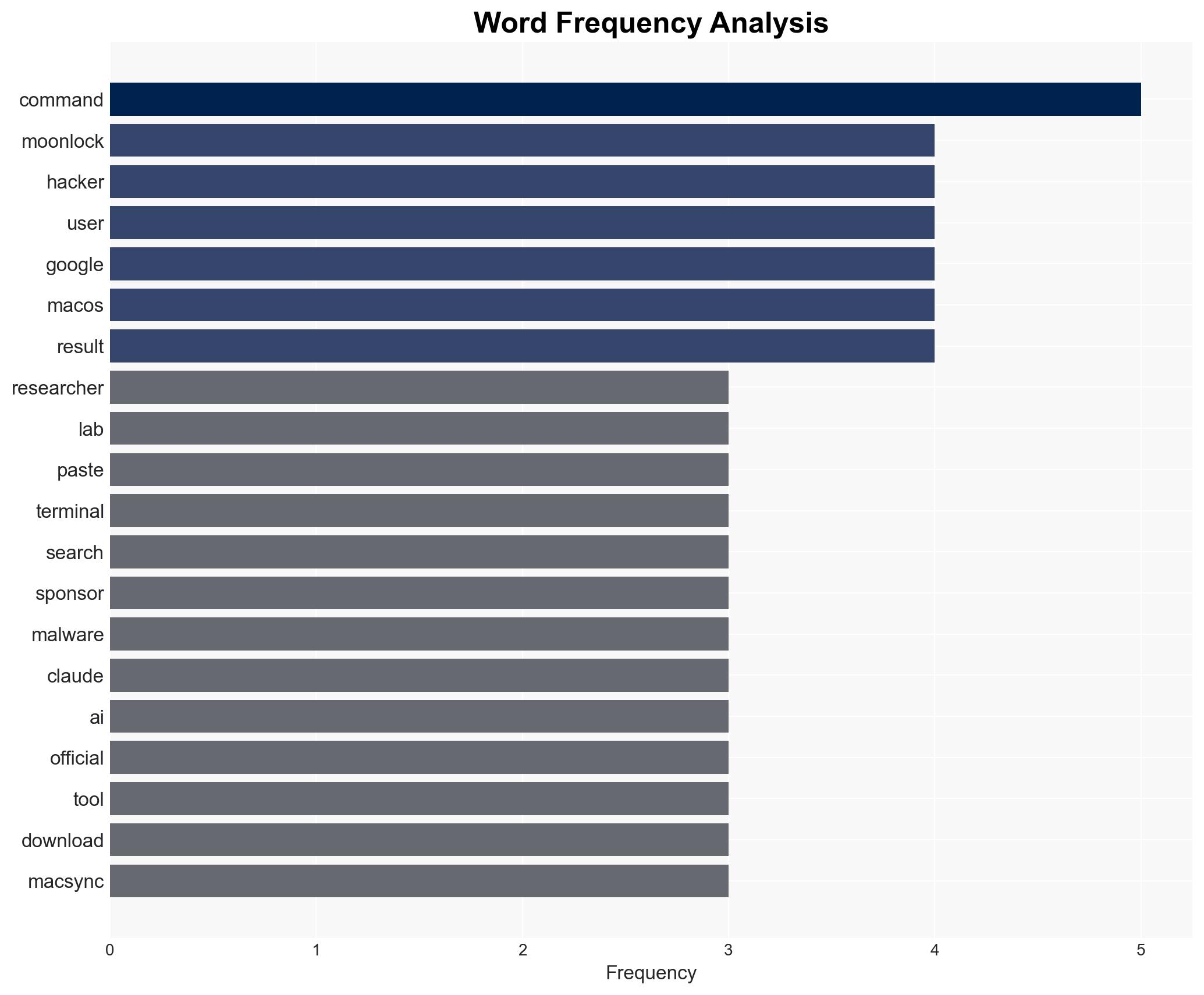
cybersecurity, malware, social engineering, AI exploitation, digital trust, platform security, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us