Hackers exploit OpenAI’s team invitation feature to launch sophisticated phishing attacks on businesses
Published on: 2026-01-25
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Beware hackers have hijacked OpenAIs ‘invite your team’ feature to break into your business
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
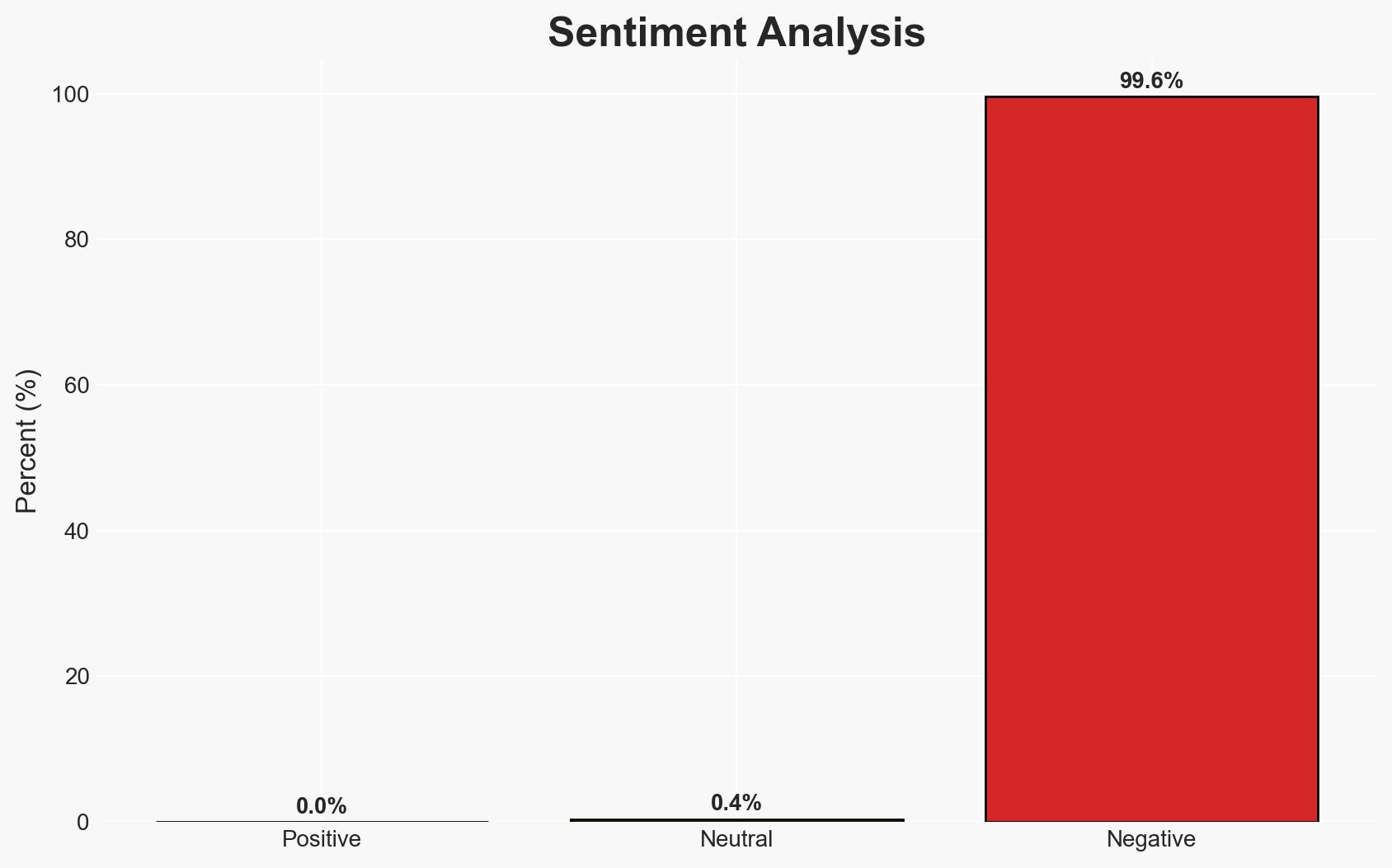
Cybercriminals are exploiting OpenAI’s team invitation feature to conduct phishing attacks, posing significant risks to businesses by using legitimate-looking emails to deceive recipients. The most likely hypothesis is that these attacks are primarily financially motivated, targeting multiple employees simultaneously. Overall, there is moderate confidence in this assessment due to the sophistication of the attack method and the potential for widespread impact.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The primary goal of these attacks is financial gain through phishing schemes. This is supported by the use of deceptive links and fraudulent offers, such as fake subscription renewals and adult services. However, the exact scale of financial losses remains unclear.
- Hypothesis B: The attacks are part of a broader campaign to gather intelligence or disrupt operations by exploiting trusted platforms. While plausible, there is limited evidence of direct intelligence-gathering or operational disruption beyond financial theft.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the consistent use of financial deception tactics. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of data exfiltration or targeting of specific industries for strategic purposes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Attackers have the technical capability to exploit OpenAI’s features; businesses lack adequate phishing defenses; financial gain is the primary motive.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the number of affected organizations and the total financial impact of the scams.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating the strategic motives behind the attacks; deception indicators include the use of legitimate-looking emails to bypass filters.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of collaboration platforms and their security features. Over time, similar tactics may be adopted by other threat actors, increasing the overall threat landscape.
- Political / Geopolitical: Heightened tensions if state actors are suspected of involvement, leading to diplomatic strains.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased pressure on cybersecurity frameworks to adapt to evolving phishing tactics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread adoption of similar tactics across other platforms, challenging existing cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for businesses, potential erosion of trust in digital collaboration tools.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance phishing detection systems, conduct employee training on identifying phishing attempts, and report suspicious activities to OpenAI and relevant authorities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing, and invest in advanced endpoint protection solutions.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Strengthened defenses reduce attack success rates; Worst: Widespread adoption of similar tactics leads to significant financial and data losses; Most-Likely: Continued but controlled threat with periodic successful breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Anna Lazaricheva, senior spam analyst at Kaspersky
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, phishing, financial fraud, OpenAI, social engineering, cyber defense, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us