Hamas-Linked Ashen Lepus Group Deploys AshTag Malware Against Middle Eastern Diplomatic Targets
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hamas Linked Hackers Using AshTag Malware Against Diplomatic Offices
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
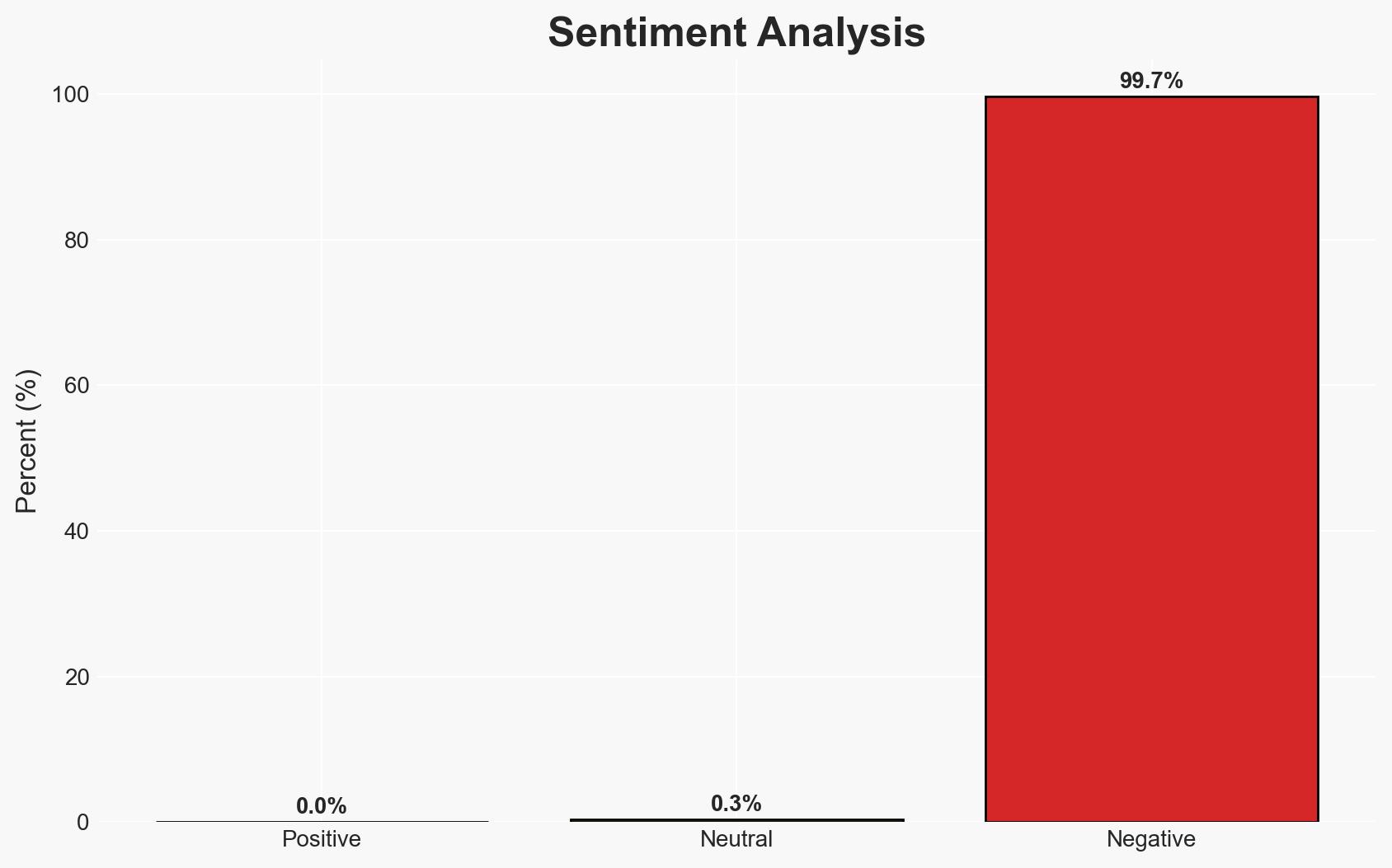
The cyber-espionage group Ashen Lepus, linked to Hamas, is actively using AshTag malware to target diplomatic offices in the Middle East, with recent expansions into Oman and Morocco. This campaign represents a persistent threat, utilizing sophisticated techniques to evade detection. The most likely hypothesis is that Ashen Lepus aims to gather intelligence on Middle Eastern geopolitical affairs, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to limited direct attribution evidence.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Ashen Lepus is conducting intelligence-gathering operations to support Hamas’s strategic objectives in the Middle East. This is supported by their persistent activity and focus on regional diplomatic targets. However, the lack of direct evidence linking specific intelligence gains to Hamas’s operational decisions presents uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: Ashen Lepus is acting independently or on behalf of another state actor interested in Middle Eastern geopolitical dynamics. The expansion of targets to include Oman and Morocco could indicate broader espionage goals. Contradicting this is the group’s known association with Hamas and its historical focus on Palestinian-related issues.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the group’s established links to Hamas and their focus on regional diplomatic targets. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of collaboration with other state actors or changes in targeting patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Ashen Lepus is primarily motivated by geopolitical intelligence collection; Hamas has the capability to utilize such intelligence; the malware’s sophistication indicates significant resource backing.
- Information Gaps: Direct evidence linking intelligence gathered to specific Hamas operations; detailed understanding of Ashen Lepus’s command structure and external affiliations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing activities to Hamas due to historical associations; risk of deception by Ashen Lepus in masking their true affiliations or objectives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions in the Middle East, particularly if diplomatic communications are compromised. The group’s activities may prompt regional governments to enhance cybersecurity measures, potentially leading to a cyber arms race.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation in regional tensions if intelligence is used to influence political decisions or negotiations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment for diplomatic missions; potential for retaliatory cyber operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication in cyber-espionage tactics; potential spread of similar techniques to other groups.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on regional stability and economic relations if diplomatic communications are compromised.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of diplomatic communications; deploy advanced threat detection tools; increase awareness among potential targets.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop regional cybersecurity partnerships; invest in training for cyber defense capabilities; establish protocols for information sharing among affected nations.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation of AshTag malware with no significant intelligence losses.
- Worst: Major diplomatic fallout due to leaked sensitive communications.
- Most-Likely: Continued espionage activities with incremental improvements in defensive measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, Middle East, diplomatic security, Hamas, malware, intelligence gathering
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us