Healthcare Data Breaches Surge in 2025, Yet Patient Records Compromised Decline Significantly
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 2025 Double the breaches but less patient data compromised
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
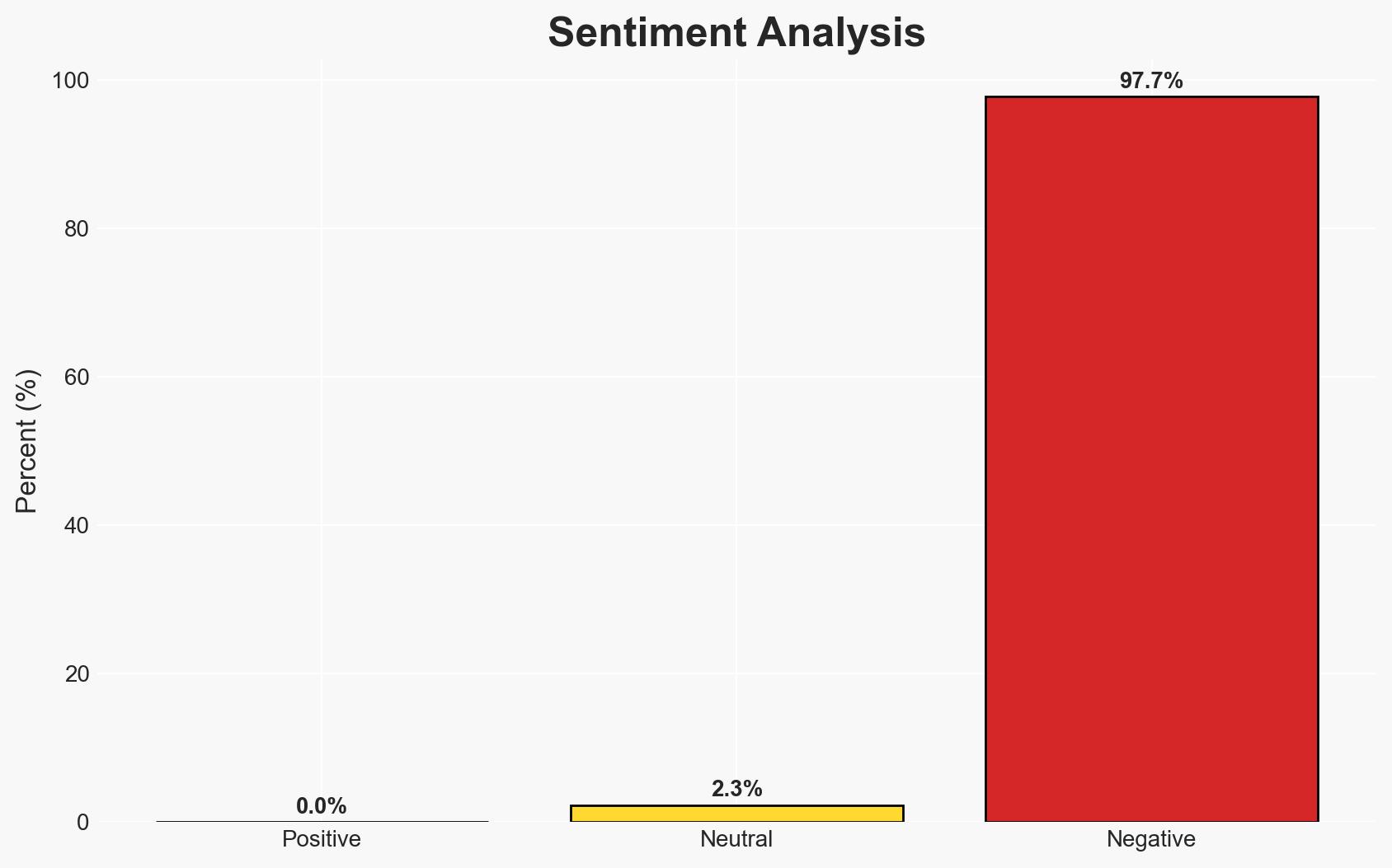
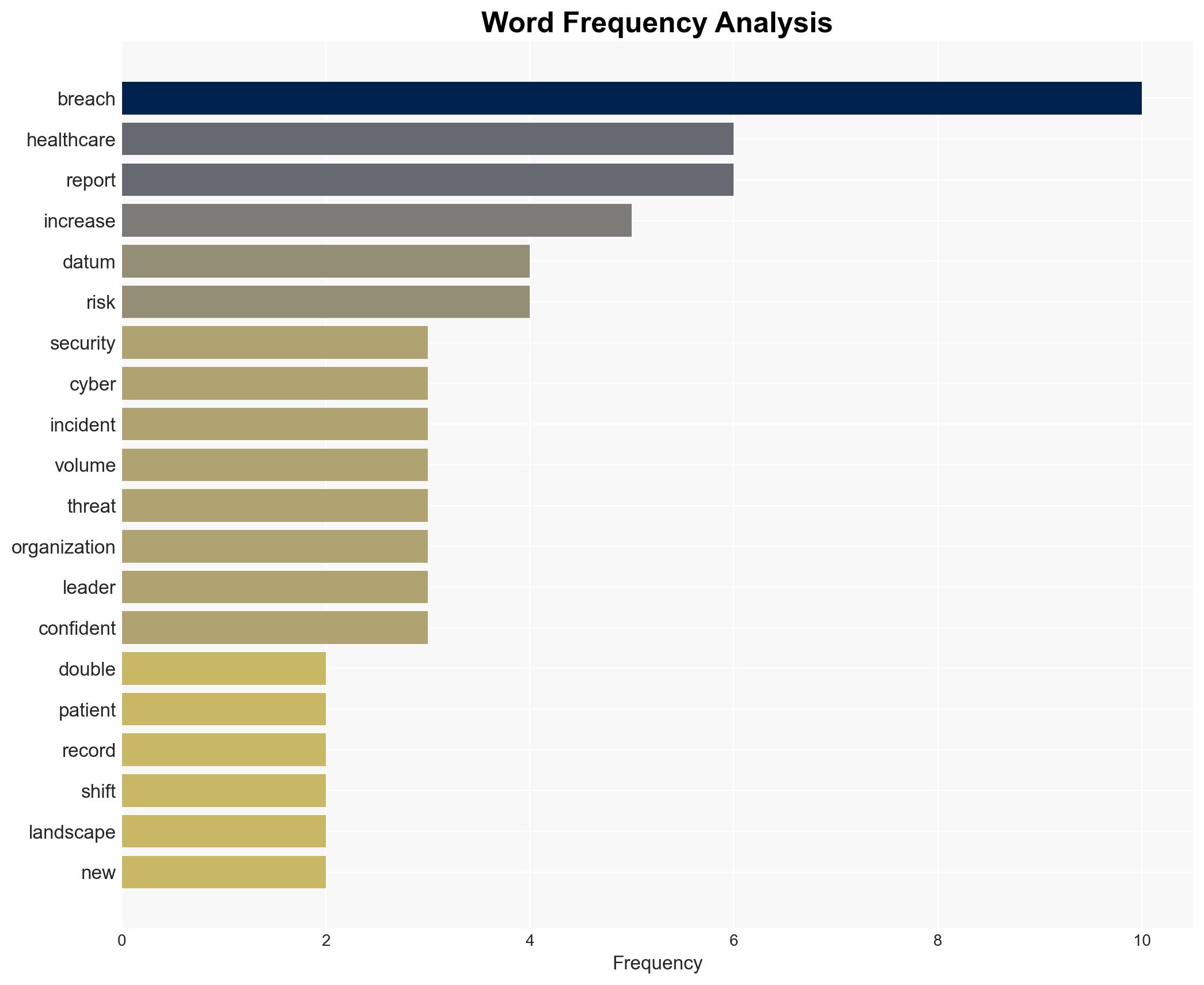
In 2025, healthcare data breaches more than doubled, yet fewer patient records were compromised, suggesting a shift towards smaller-scale but more frequent attacks. This trend highlights the increasing importance of operational resilience and response capacity in healthcare cybersecurity. The most likely hypothesis is that attackers are focusing on operational disruption rather than data theft. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps and potential biases in the data sources.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cyber attackers are primarily targeting healthcare systems for operational disruption rather than data theft, as indicated by the increased frequency of breaches with fewer records compromised. This is supported by the rise in ransomware and identity compromise incidents. However, the lack of detailed attribution data introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The decrease in compromised patient records is due to improved data protection measures within healthcare organizations, despite the increased breach frequency. This is contradicted by the low confidence levels among healthcare leaders in their cybersecurity defenses and third-party risk assessments.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of breach characteristics with operational disruption tactics. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of significant data exfiltration or improved cybersecurity measures leading to reduced breach frequency.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Healthcare organizations have not significantly improved data protection; attackers are motivated by disruption rather than theft; reported data accurately reflects the broader trend.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of cyber incidents; comprehensive data on the effectiveness of new cybersecurity measures; insights into attacker motivations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in self-reported data from healthcare organizations; reliance on limited data sources could skew analysis; possible underreporting of data exfiltration incidents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift towards more frequent, smaller-scale cyberattacks in healthcare could lead to increased operational costs and resource strain, impacting service delivery and patient care. This trend may also influence regulatory and policy responses in the cybersecurity domain.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny and international collaboration on healthcare cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened focus on protecting critical healthcare infrastructure from cyber threats, with possible implications for national security.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased emphasis on developing robust incident response and recovery capabilities within the healthcare sector.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial strain on healthcare providers due to repeated cyber incidents, affecting overall healthcare delivery and public trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of healthcare cyber threats; conduct rapid assessments of third-party risks; initiate targeted staff retraining on cybersecurity practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for cross-industry cybersecurity collaboration; invest in AI-driven threat detection and response technologies; strengthen regulatory frameworks for healthcare cybersecurity.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Significant reduction in breach frequency due to improved defenses and collaboration.
- Worst: Continued rise in breach frequency with major operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Steady increase in breach frequency with incremental improvements in resilience and response.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortified Health Security
- HHS Office for Civil Rights
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, healthcare, data breaches, operational resilience, ransomware, third-party risk, shadow AI
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us