High-Energy Lasers: A Promising Solution for Modern Anti-Drone Defense Systems
Published on: 2026-02-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Are lasers the future of anti-drone warfare
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
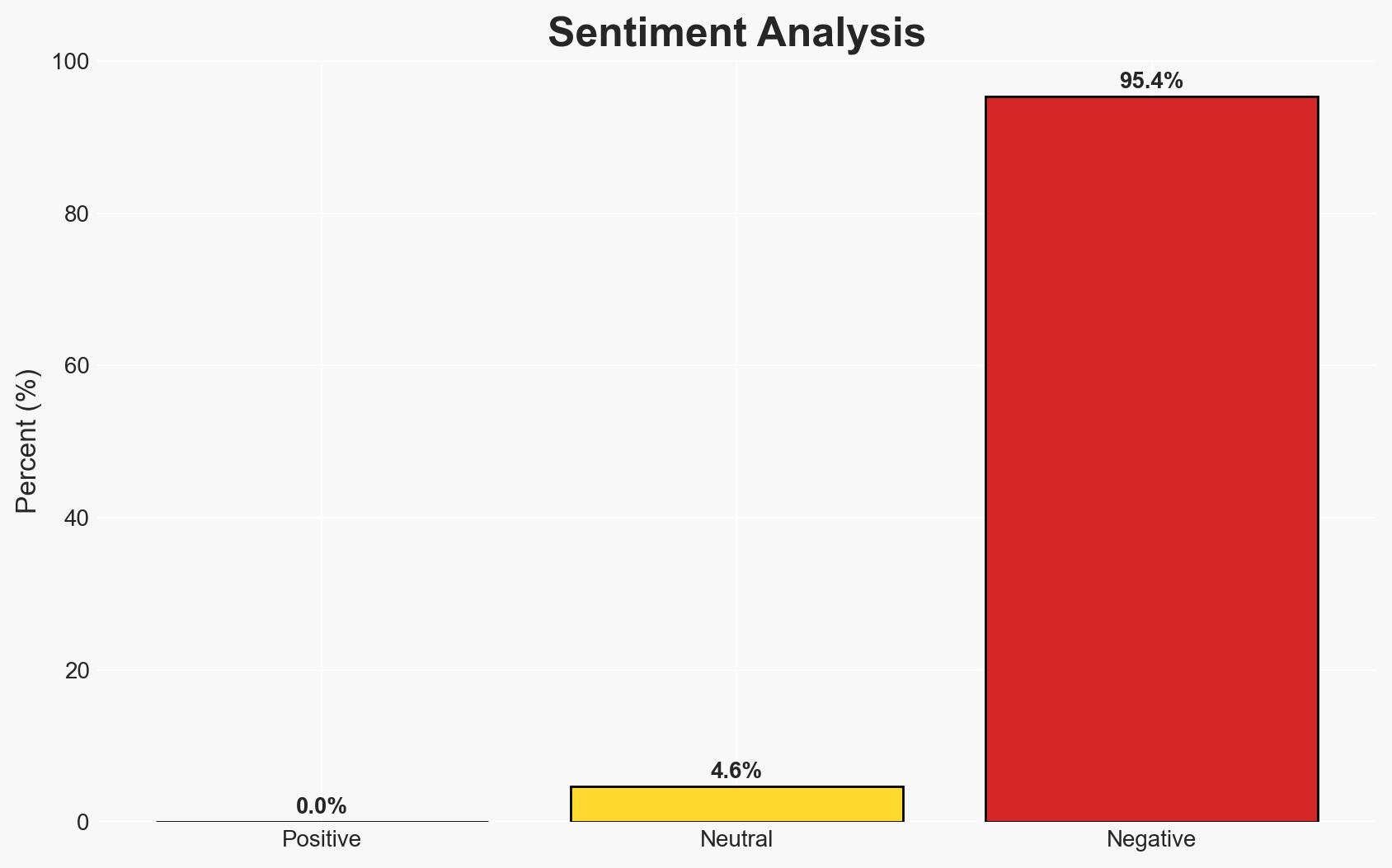
The deployment of high-energy laser systems, such as Israel’s Iron Beam, represents a significant advancement in anti-drone warfare technology, potentially offering a cost-effective solution to counter the proliferation of inexpensive drones. This development is likely to impact military strategies globally, with moderate confidence that lasers will become a key component of air defense systems. However, the full operational capability and scalability of these systems remain uncertain.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: High-energy lasers will become the primary solution for anti-drone warfare due to their cost-effectiveness and technological advancements. Supporting evidence includes successful demonstrations and substantial defense contracts. Contradicting evidence involves potential technical limitations and scalability issues.
- Hypothesis B: Traditional kinetic and electronic warfare methods will remain dominant due to the current limitations of laser technology, such as weather dependency and power requirements. Supporting evidence includes historical challenges in laser weapon development and operational constraints.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to recent successful demonstrations and significant investment in laser technology by multiple countries. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include breakthroughs in overcoming technical limitations or failures in operational deployment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Technological advancements in laser systems will continue at the current pace; defense budgets will support ongoing laser weapon development; adversaries will not develop countermeasures rapidly.
- Information Gaps: Detailed performance data of laser systems in diverse operational environments; adversaries’ current capabilities to counter laser systems.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-optimism from defense contractors; source bias from promotional materials; possible exaggeration of capabilities by involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of laser systems into military arsenals could reshape defense strategies and provoke an arms race in laser technology. The effectiveness and reliability of these systems in real-world scenarios remain to be fully validated.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions and competition among nations investing in laser technology, potentially leading to an arms race.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capabilities to neutralize drone threats could alter the balance of power in asymmetric warfare scenarios.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for cyber-attacks targeting laser system infrastructure; information warfare to influence perceptions of laser effectiveness.
- Economic / Social: Significant investment in laser technology could divert resources from other defense priorities; potential economic benefits for defense contractors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor developments in laser technology deployments; assess adversaries’ capabilities to counter laser systems.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with countries investing in laser technology; invest in research to address technical limitations and enhance system resilience.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful integration of laser systems, reducing drone threats significantly.
- Worst: Technical failures and high costs limit laser deployment, leading to strategic setbacks.
- Most-Likely: Gradual adoption of laser systems with continued reliance on traditional methods until full capabilities are proven.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Israeli Ministry of Defence
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Lockheed Martin
- MBDA
- Rheinmetall
- Electro-Optical Systems (EOS)
- Andreas Schwer
- Iain Boyd
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, anti-drone warfare, laser technology, defense innovation, military strategy, arms race, asymmetric warfare, defense contracts
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us