Holding U.S. Arms Manufacturers Responsible is Crucial to Ending the Ongoing Violence in Gaza and the West Ba…
Published on: 2025-12-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: To End the Genocide We Must Hold Weapons Manufacturers Accountable or Shut Them Down
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The ongoing conflict involving Israel and Palestinians, particularly in Gaza and the West Bank, is significantly influenced by U.S. weapons manufacturers. The most likely hypothesis is that U.S. military aid and weapons sales are enabling continued hostilities, with moderate confidence. This situation affects geopolitical stability, economic interests, and humanitarian conditions in the region.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: U.S. military aid and weapons sales are directly enabling Israel’s military actions against Palestinians, contributing to ongoing conflict. Supporting evidence includes the significant volume of U.S. weapons supplied to Israel and the financial profits of the U.S. defense industry. Contradicting evidence is limited, but there is uncertainty regarding the full scope of U.S. influence on Israeli military decisions.
- Hypothesis B: Israel’s military actions are primarily driven by its own strategic objectives, with U.S. weapons playing a secondary role. This hypothesis is supported by Israel’s historical military policies and strategic imperatives. However, the scale of U.S. weaponry involved suggests a significant enabling role, challenging this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented volume of U.S. weapons and aid contributing to Israel’s military capacity. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in U.S. foreign policy or Israeli military strategy.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. will continue its current level of military support to Israel; Israeli military actions are heavily dependent on U.S. weapons; public and political pressure in the U.S. will not significantly alter defense policies.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the decision-making processes within the U.S. government regarding military aid to Israel; comprehensive analysis of Israeli strategic objectives independent of U.S. influence.
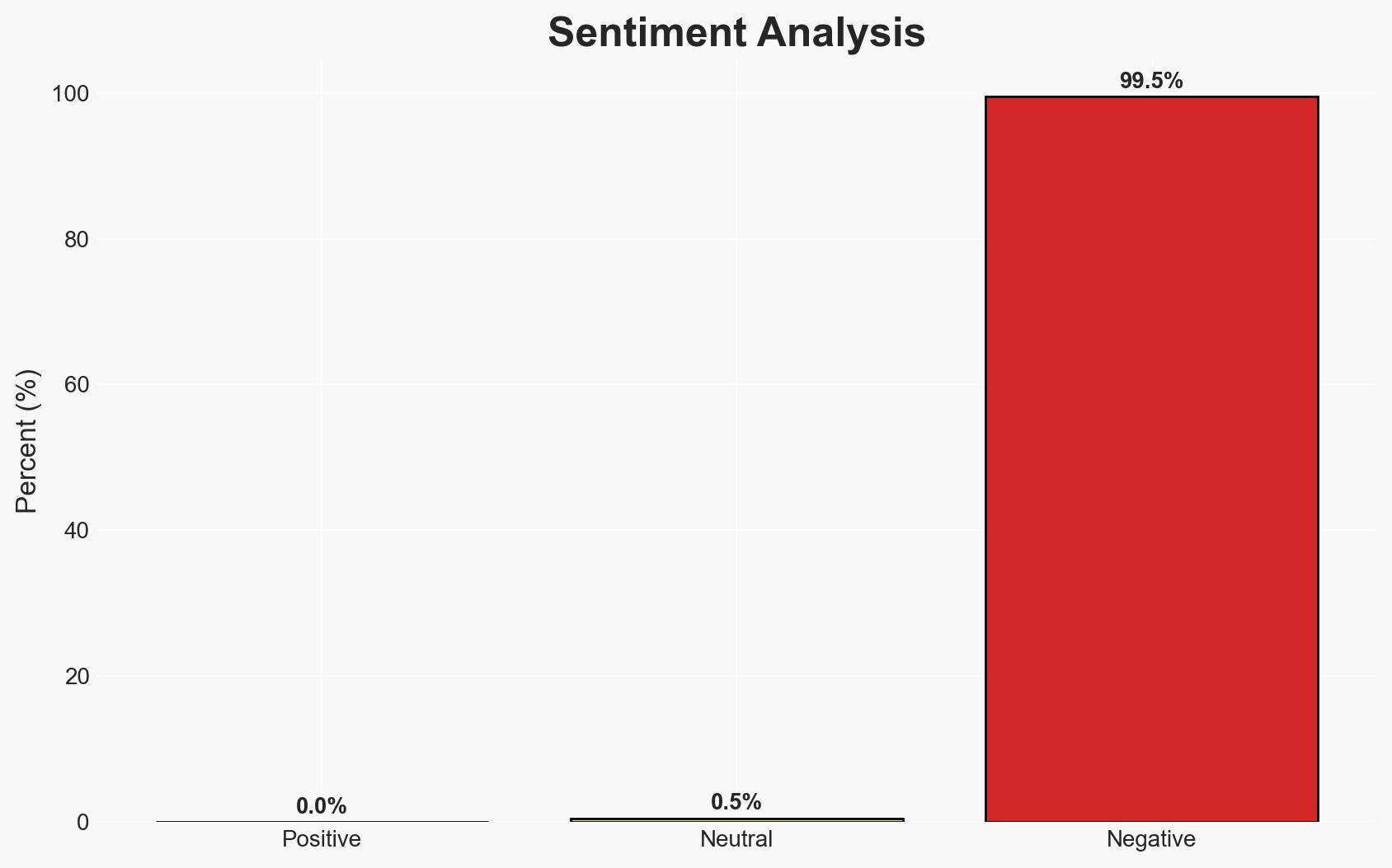
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in sources advocating for Palestinian rights; risk of manipulation in reported casualty figures and military actions; U.S. government and defense industry narratives may downplay complicity.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continuation of U.S. weapons sales to Israel could exacerbate regional tensions and undermine international diplomatic efforts. This development may influence U.S. relations with other Middle Eastern countries and impact global perceptions of U.S. foreign policy.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic isolation of the U.S.; heightened tensions with countries opposing Israeli actions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Escalation of violence could lead to increased radicalization and recruitment by extremist groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for cyber operations targeting U.S. defense contractors or governmental entities by adversaries or hacktivists.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic repercussions from international sanctions or boycotts; domestic social unrest driven by advocacy groups.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of U.S. weapons transfers to Israel; engage with diplomatic partners to assess potential shifts in policy; enhance security measures for defense contractors.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential economic impacts; strengthen partnerships with Middle Eastern allies to mitigate geopolitical risks; invest in counter-radicalization programs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: U.S. policy shift leads to reduced military aid, easing regional tensions.
- Worst: Continued escalation results in broader regional conflict and international backlash.
- Most-Likely: Status quo persists with ongoing conflict and limited diplomatic progress.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
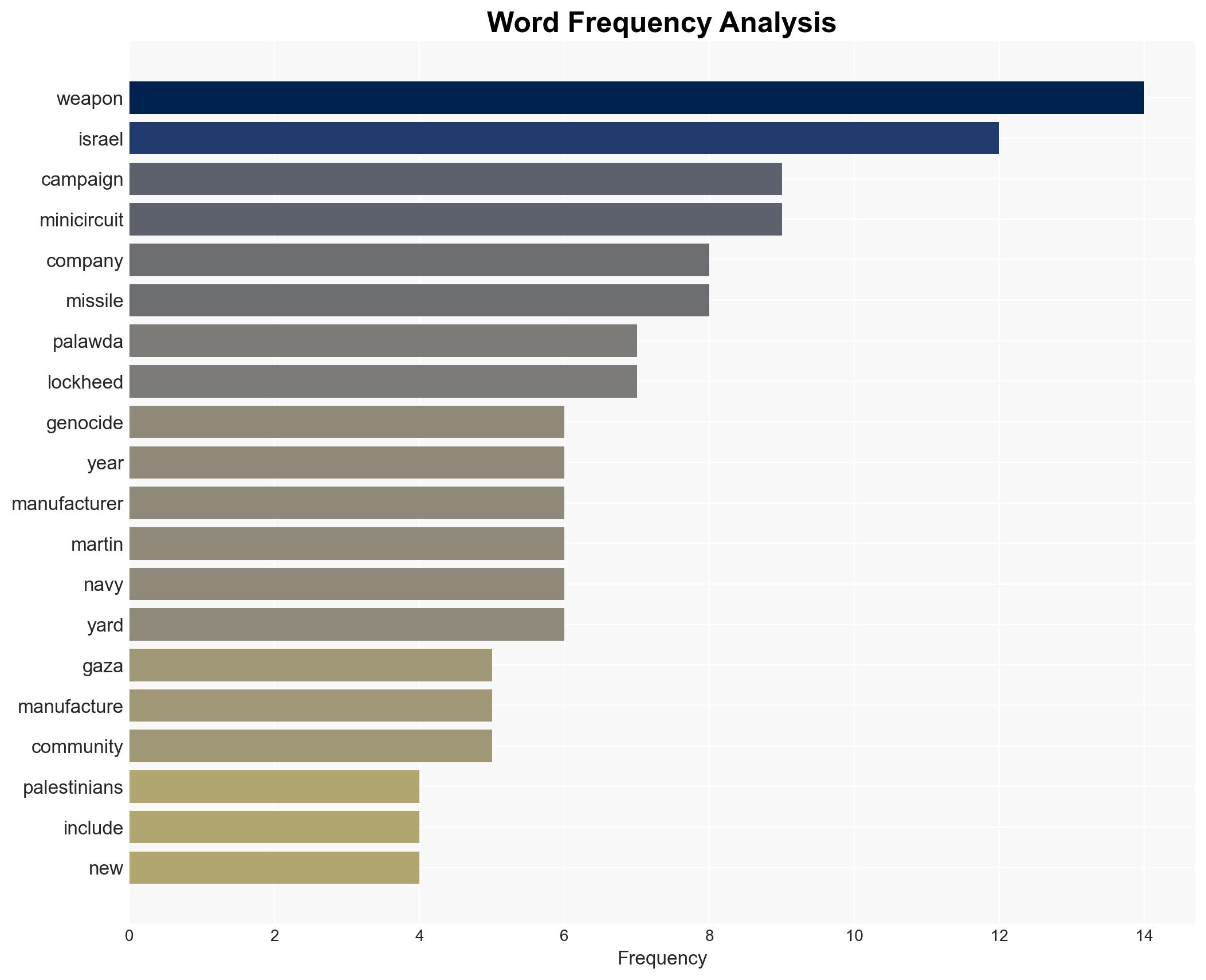
- Mini-Circuits
- Lockheed Martin
- Omar Barghouti
- PAL-Awda
- U.S. Government (Defense Department)
- Israeli Government
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, military aid, arms trade, Middle East conflict, geopolitical stability, defense industry, humanitarian crisis, U.S. foreign policy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us