How Rapid AI Adoption Is Creating an Exposure Gap – Tenable.com
Published on: 2025-11-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How Rapid AI Adoption Is Creating an Exposure Gap – Tenable.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
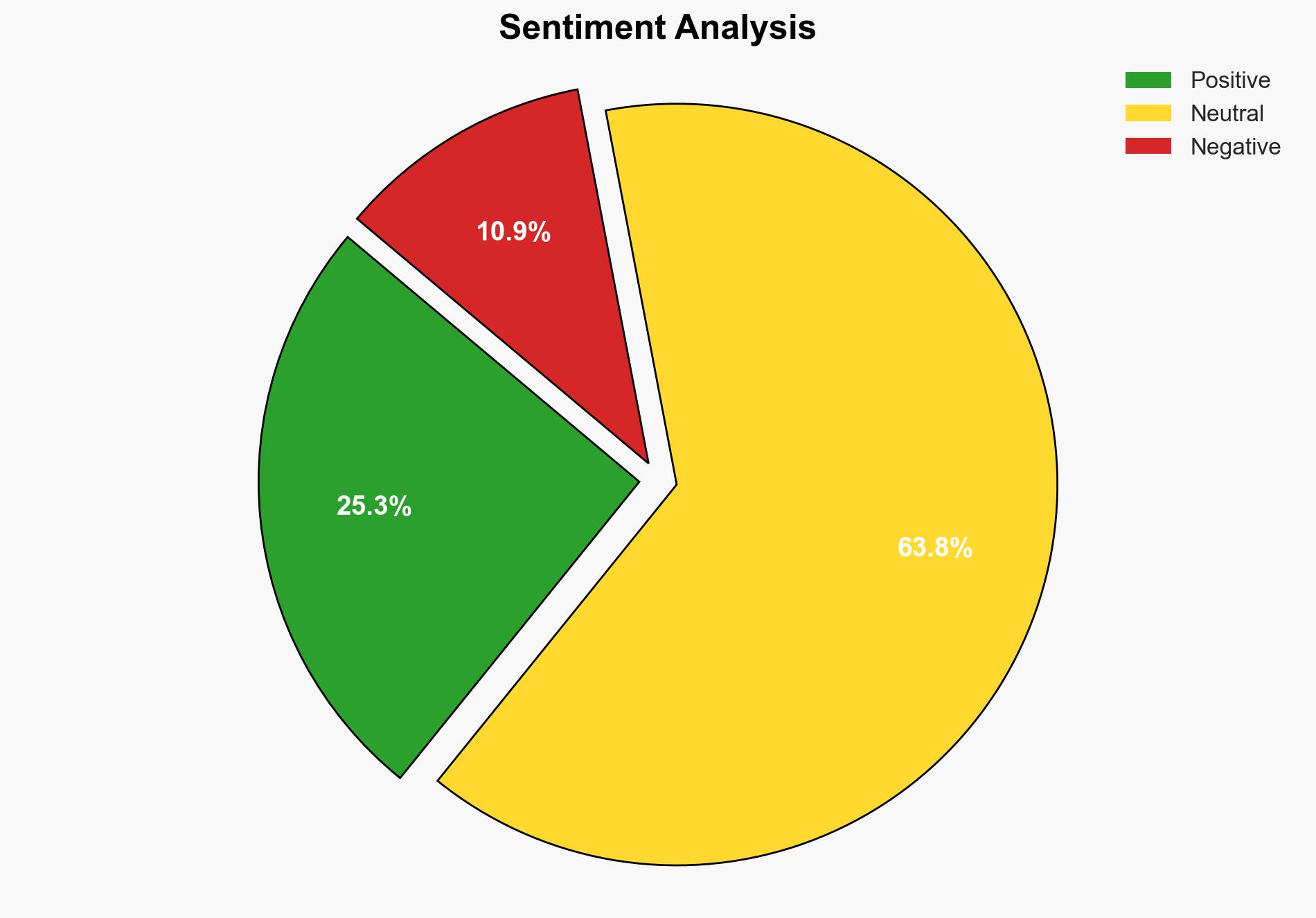
With a moderate confidence level, it is assessed that the rapid adoption of AI technologies is outpacing the implementation of adequate security measures, creating a significant exposure gap. Organizations should prioritize integrating AI-specific security frameworks and proactive risk management strategies to mitigate vulnerabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
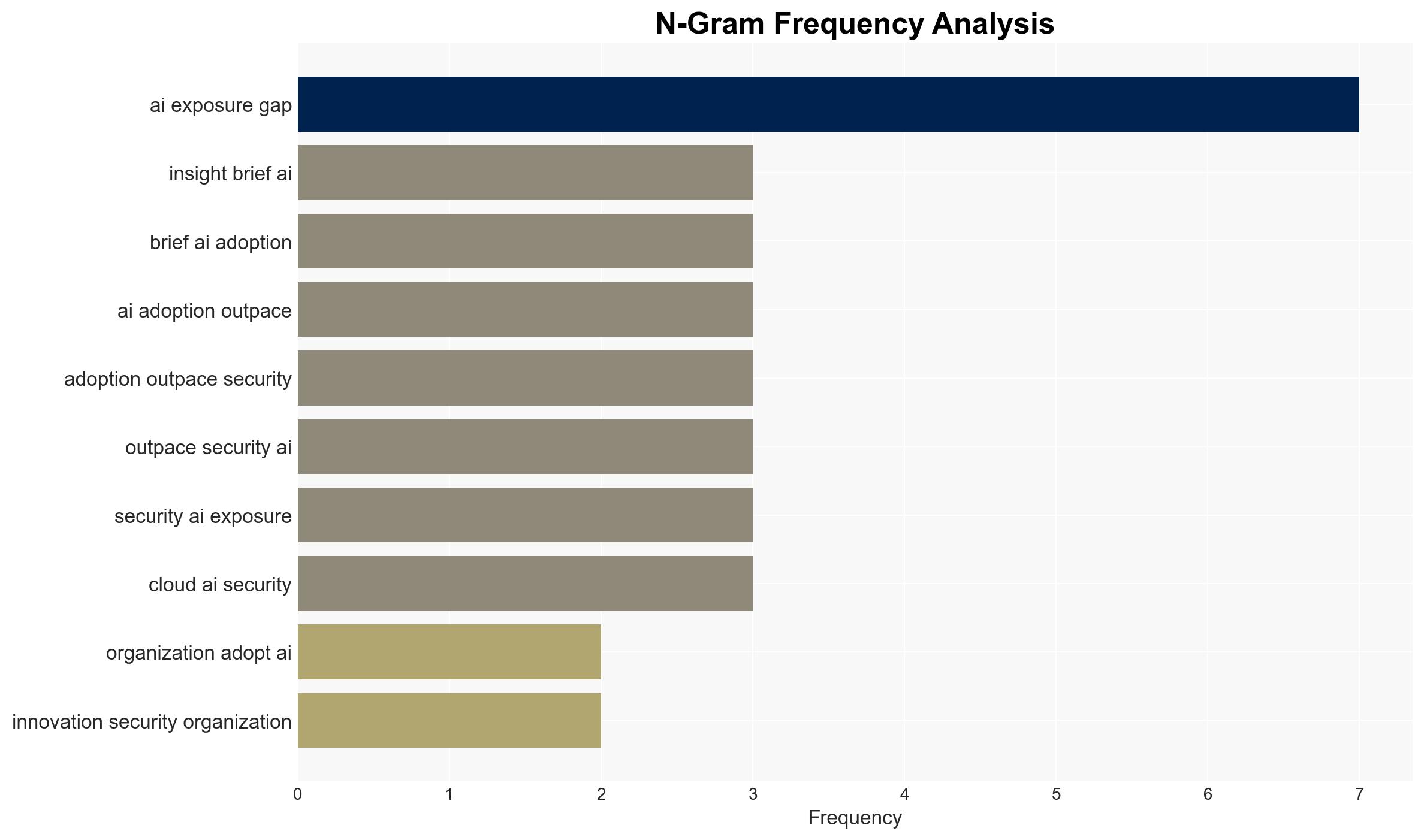
Hypothesis 1: The rapid adoption of AI is inherently creating an exposure gap because security measures are not keeping pace with technological advancements.
Hypothesis 2: The exposure gap is exaggerated, and organizations are effectively managing AI security risks through existing cybersecurity frameworks and practices.
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to evidence that organizations are struggling with AI-specific vulnerabilities, as indicated by the prevalence of AI-related breaches and the challenges in aligning with frameworks like the EU AI Act and NIST AI RMF. The rapid integration of AI into business operations without parallel security enhancements supports this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that AI technologies are being adopted faster than security measures can be implemented. There is also an assumption that existing cybersecurity frameworks are insufficient for AI-specific threats.
Red Flags: Potential bias in reporting from Tenable.com, a cybersecurity firm, which may emphasize risks to promote their services. Lack of independent corroboration of the scale of the exposure gap could indicate a need for further verification.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary implication is an increased risk of cyberattacks exploiting AI vulnerabilities, potentially leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Politically, this could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and pressure on organizations to comply with evolving AI security standards. Economically, failure to secure AI systems could deter investment in AI innovations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Organizations should adopt AI-specific security frameworks, conduct regular security audits, and implement AI-specific identity and access controls. Continuous monitoring and anomaly detection should be prioritized.
- Best Case Scenario: Organizations successfully integrate AI security measures, reducing exposure gaps and enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
- Worst Case Scenario: Persistent exposure gaps lead to significant breaches, regulatory penalties, and loss of stakeholder trust.
- Most Likely Scenario: Organizations will gradually improve AI security measures, but exposure gaps will persist in the short term due to the rapid pace of AI adoption.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are identified in the source text. Key entities include organizations adopting AI technologies, cybersecurity firms like Tenable.com, and regulatory bodies such as the EU and NIST.
7. Thematic Tags
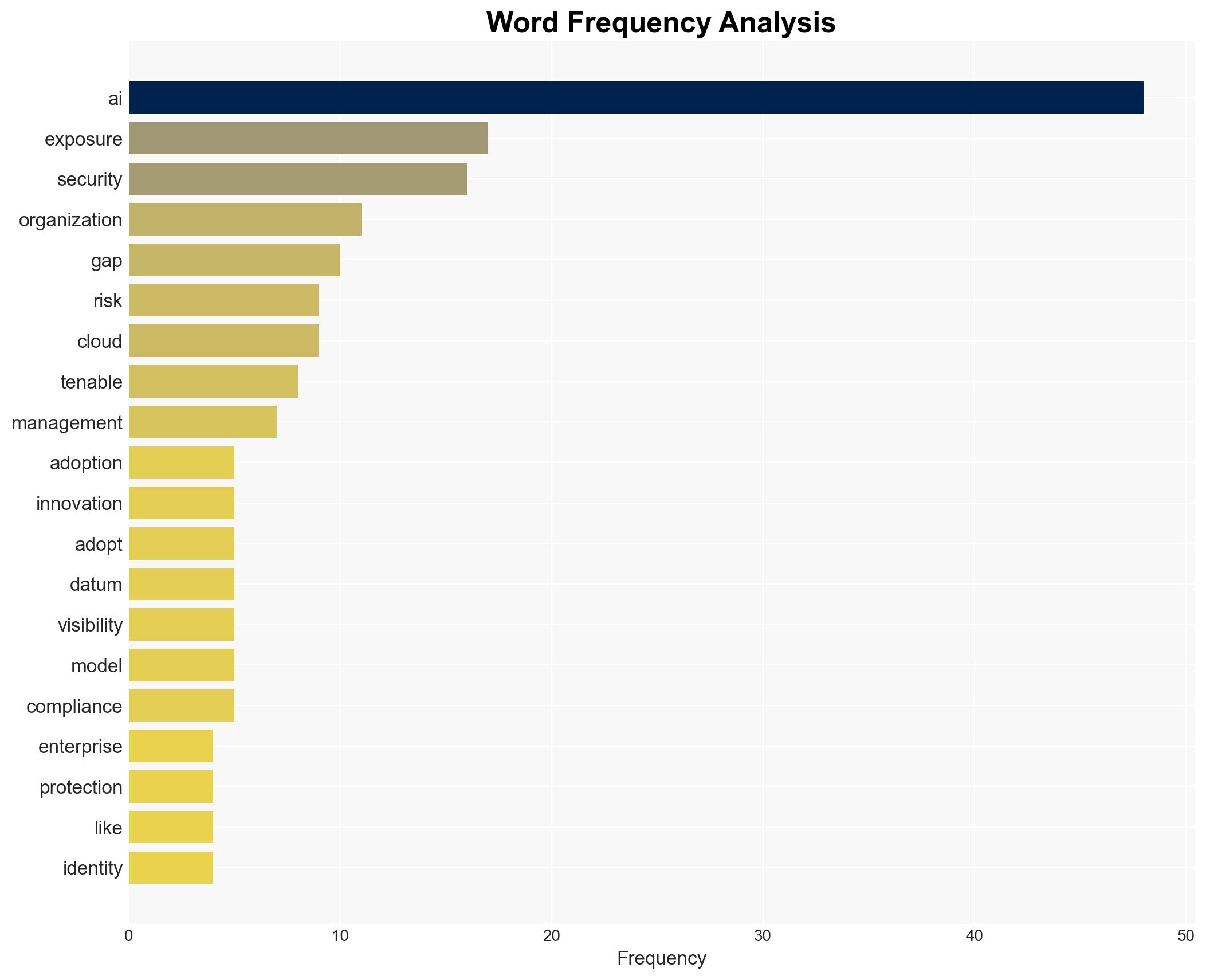
Cybersecurity, AI Adoption, Risk Management, Regulatory Compliance
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology