Humanitarian laws face unprecedented challenges amid escalating global conflicts, report reveals
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Global conflicts pushing humanitarian law to breaking point report warns
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
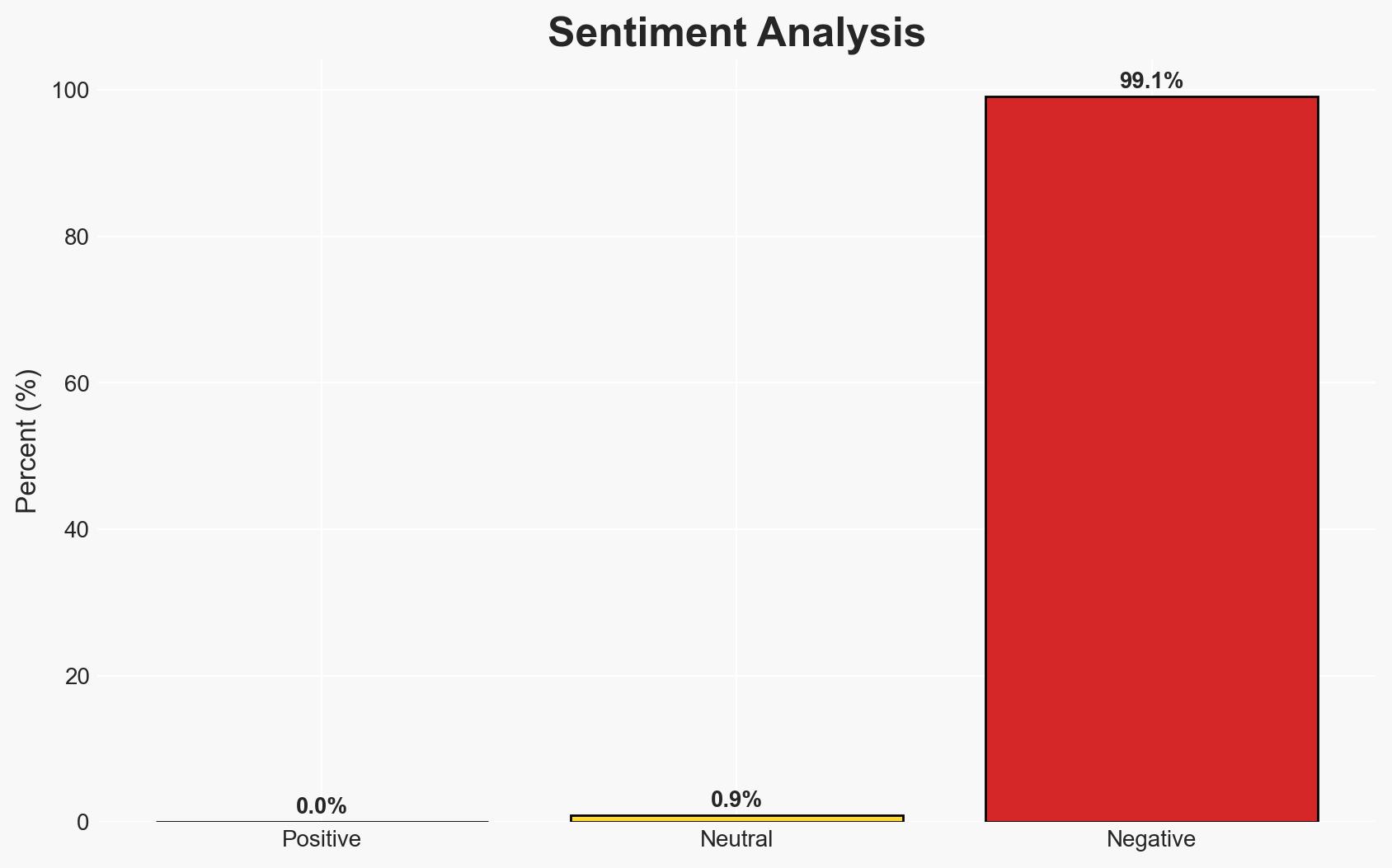
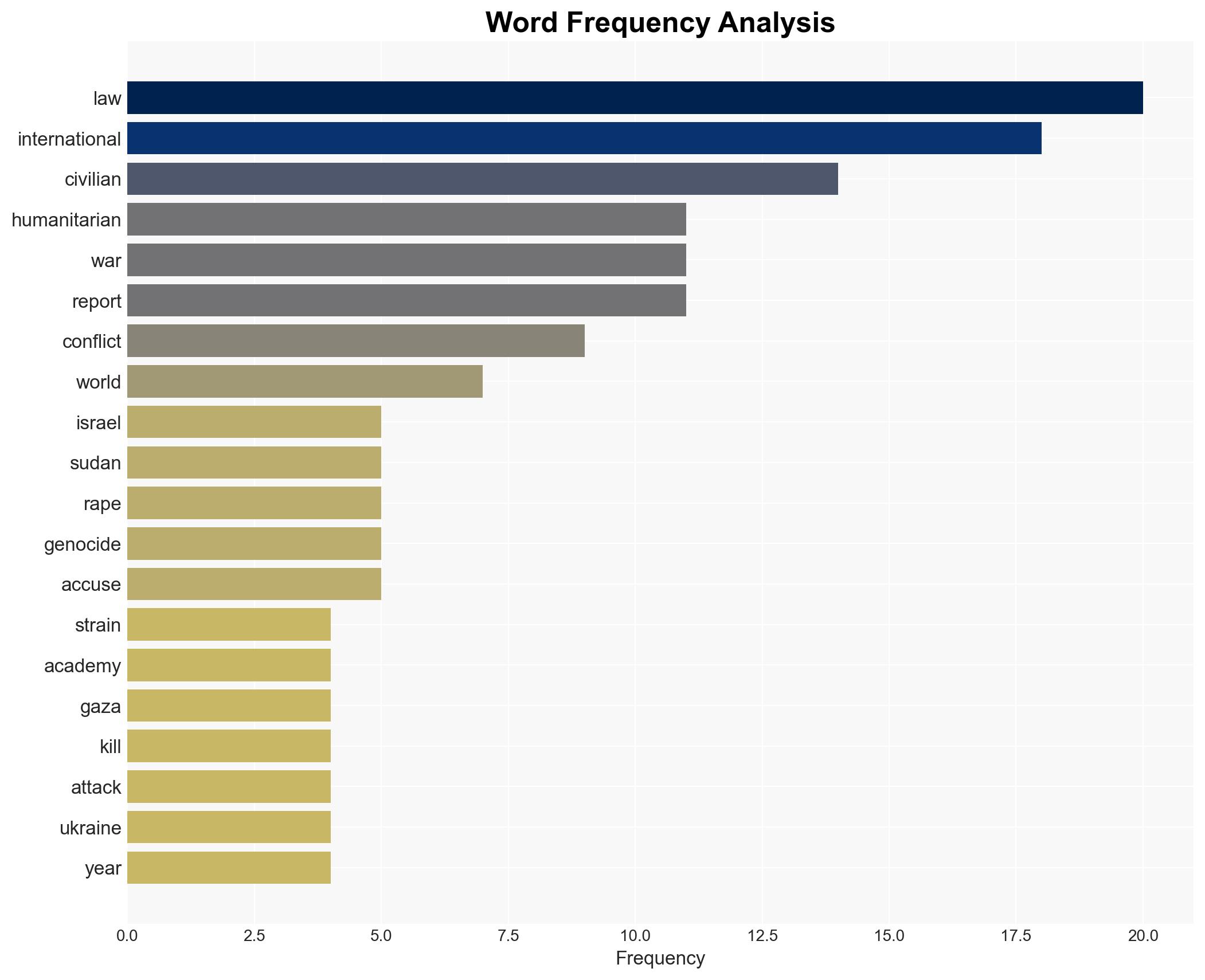
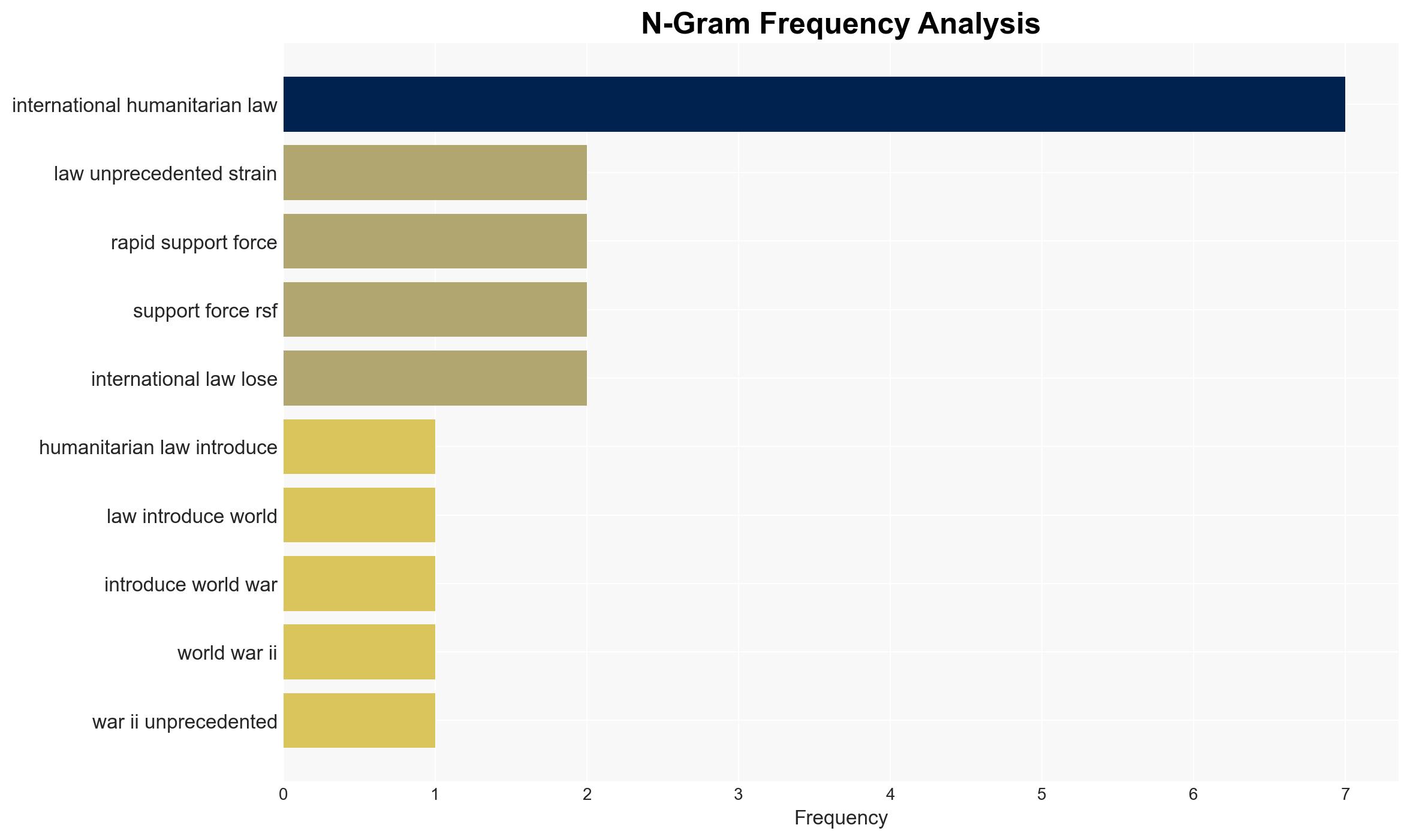
The Geneva Academy report highlights severe breaches of international humanitarian law across multiple global conflicts, with Israel’s actions in Gaza and Sudan’s ongoing violence being particularly noted. The strain on these laws is exacerbated by the perceived retreat of the United States from its traditional role in upholding them. This situation poses significant risks to global stability and civilian safety. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the potential for bias in source reporting and incomplete data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The strain on international humanitarian law is primarily due to the increased frequency and intensity of conflicts globally, coupled with a decline in international enforcement mechanisms. Supporting evidence includes the widespread reports of civilian atrocities and the lack of effective international intervention. Key uncertainties include the reliability of conflict reporting and the actual capacity for international enforcement.
- Hypothesis B: The perceived breakdown of humanitarian law is exaggerated, with media and advocacy groups amplifying certain conflicts while underreporting others. This hypothesis is supported by potential biases in media coverage and the selective focus of international bodies. Contradicting evidence includes consistent reports from multiple credible organizations about widespread violations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the breadth of documented violations across diverse conflicts and the noted lack of effective international response. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new data on enforcement actions or changes in international diplomatic engagement.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The reported data accurately reflects the scale of violations; international bodies have the capacity but lack the will to enforce laws; media reports are unbiased and comprehensive.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of international interventions and the internal decision-making processes of key states involved in conflicts.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential biases in media reporting and advocacy group agendas; possible manipulation of conflict data by involved parties to influence international opinion.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing strain on international humanitarian law could lead to further destabilization in conflict regions, with potential spillover effects into neighboring areas. The erosion of legal norms may embolden state and non-state actors to commit further violations without fear of repercussion.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased geopolitical tensions as states may exploit weakened legal frameworks to pursue aggressive policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as non-state actors may gain influence in lawless regions, potentially increasing terrorism risks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting humanitarian organizations and misinformation campaigns to shape narratives.
- Economic / Social: Economic destabilization in affected regions, leading to increased migration and social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of conflict zones through satellite and cyber intelligence; engage with international partners to reaffirm commitments to humanitarian law.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for affected regions, including humanitarian aid and capacity-building for local governance; strengthen international coalitions to address enforcement gaps.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Renewed international commitment leads to effective enforcement and reduced violations.
- Worst: Continued erosion of legal norms results in widespread conflict and humanitarian crises.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in some regions, but overall strain on humanitarian law persists.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, international humanitarian law, global conflicts, civilian protection, geopolitical tensions, media bias, enforcement mechanisms, humanitarian crises
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us