Hundreds of Malware-Laden Apps Downloaded 41 Million Times From Google Play – Infosecurity Magazine
Published on: 2025-11-05
Intelligence Report: Hundreds of Malware-Laden Apps Downloaded 41 Million Times From Google Play – Infosecurity Magazine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
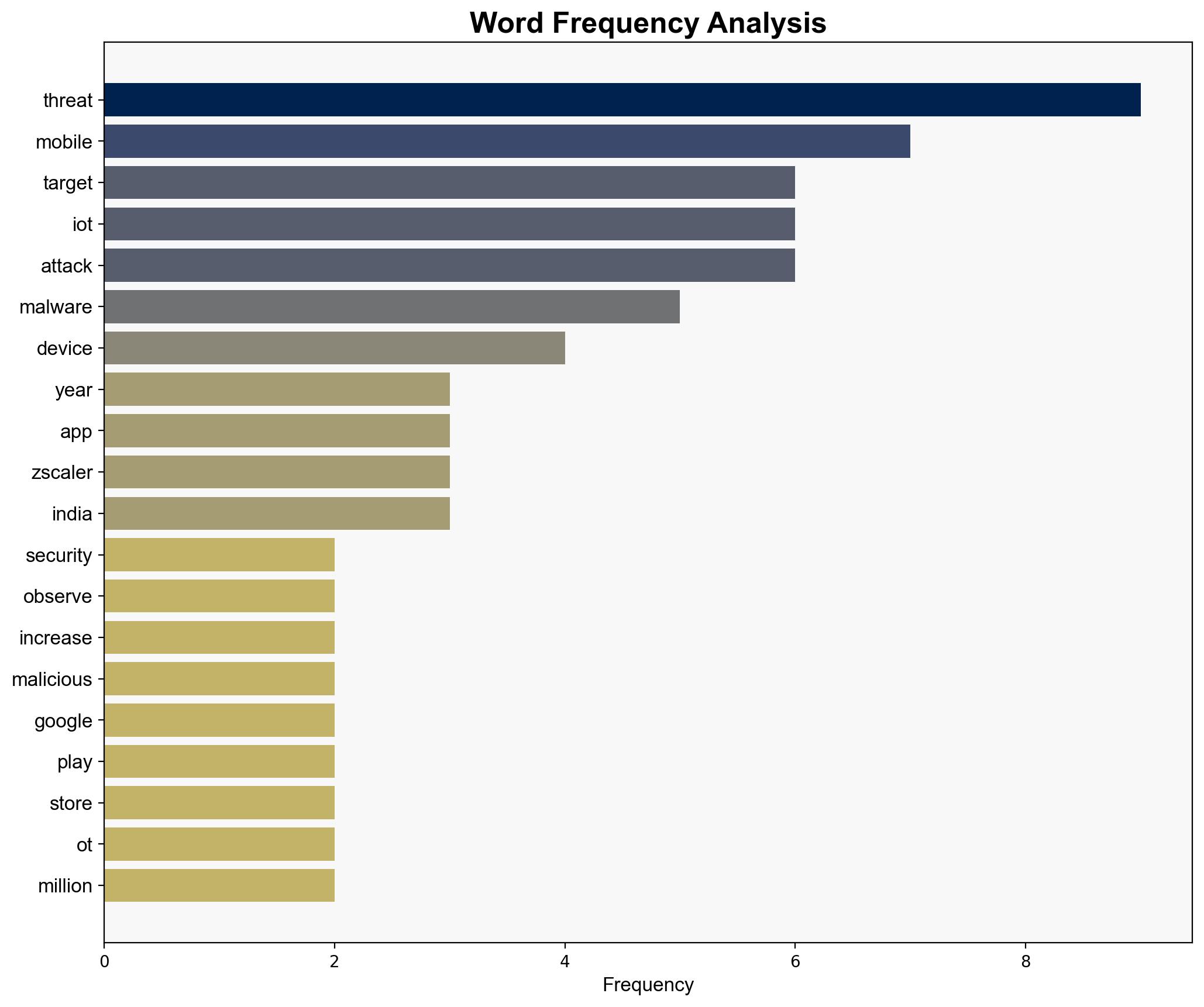
The most supported hypothesis is that threat actors are increasingly exploiting vulnerabilities in the Google Play Store to distribute malware, leveraging user trust in official platforms. This is corroborated by the significant number of downloads and the bypassing of Google’s security filters. Confidence level: High. Recommended action: Enhance security protocols for app vetting on Google Play and increase user awareness about app permissions and security.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Threat actors are exploiting vulnerabilities in the Google Play Store’s security measures, allowing malware-laden apps to bypass filters and reach users.
Hypothesis 2: The increase in malware-laden apps is primarily due to a rise in sophisticated social engineering tactics that trick users into downloading malicious apps, rather than technical failures in Google Play’s security.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to the evidence of apps bypassing security filters and the large volume of downloads. Hypothesis 2 lacks direct evidence of increased social engineering sophistication in this context.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– Assumption: Google Play’s security measures are currently insufficient to detect all malware.
– Red Flag: Lack of detailed data on the specific vulnerabilities exploited.
– Potential Bias: Confirmation bias towards technical failures over human factors.
– Missing Data: Specific methods used by malware to bypass security filters.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The proliferation of malware-laden apps poses significant risks to personal and organizational data security, potentially leading to economic losses and compromised critical infrastructure. The trend of targeting mobile devices and IoT systems suggests a strategic shift by threat actors towards more ubiquitous and less protected endpoints. This could escalate into broader cyber threats impacting national security and economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance app vetting processes on Google Play with advanced AI-driven threat detection.
- Conduct user education campaigns on app security and permissions.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Improved security measures significantly reduce malware incidents.
- Worst Case: Continued exploitation leads to widespread data breaches and infrastructure disruptions.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements in security reduce but do not eliminate threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Zscaler (ThreatLabZ)
– Google Play
– Threat actors targeting mobile and IoT devices
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus