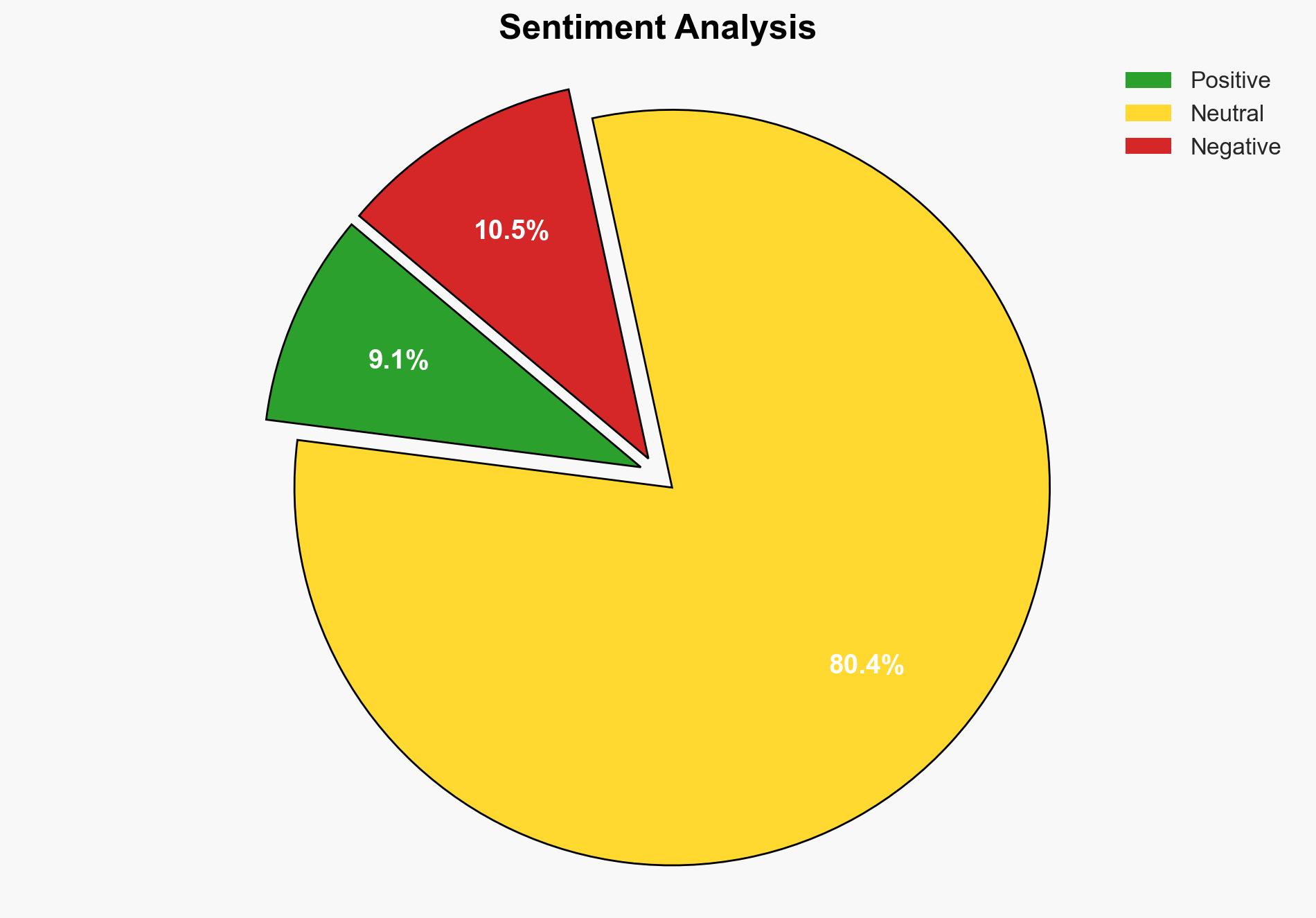
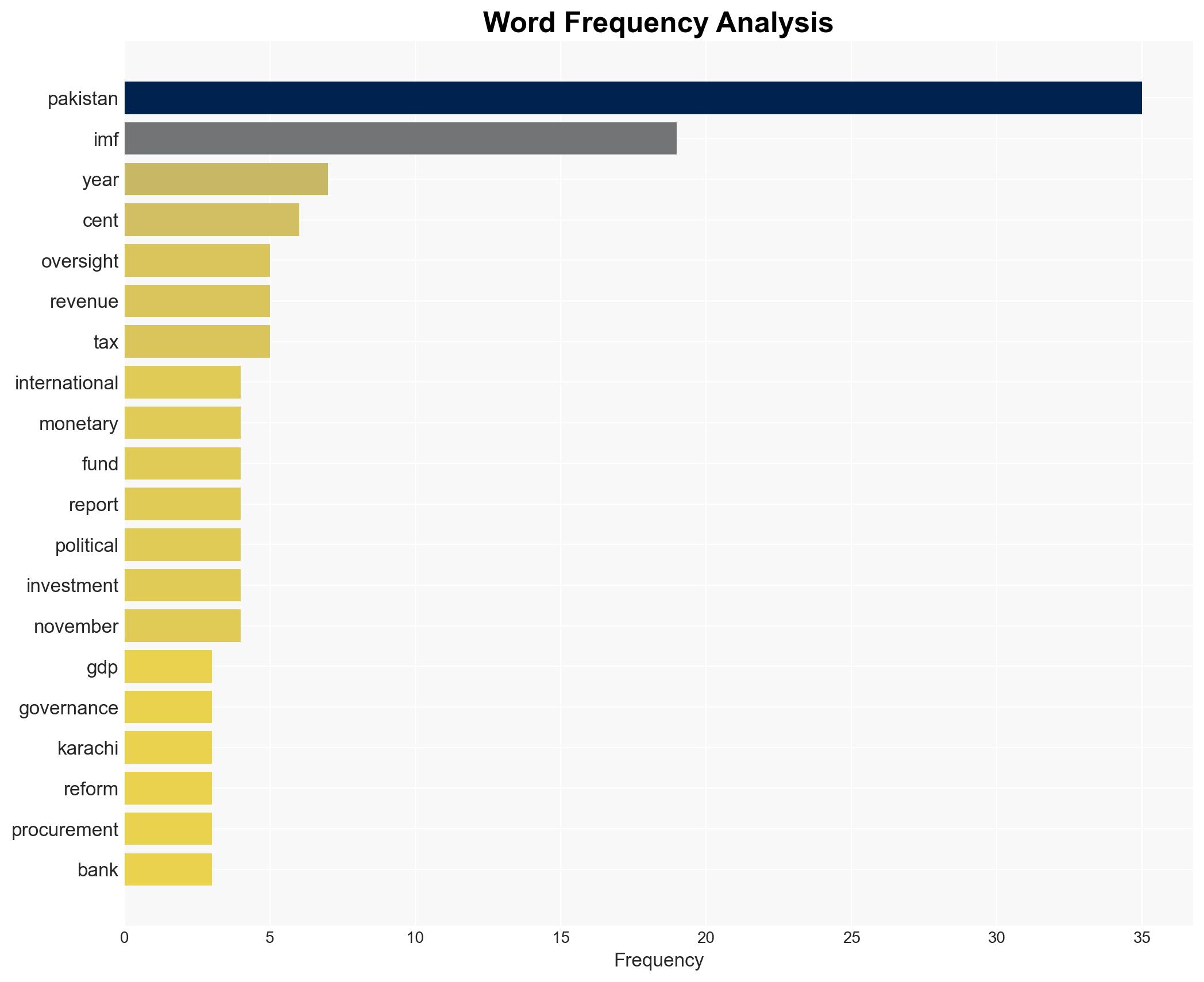
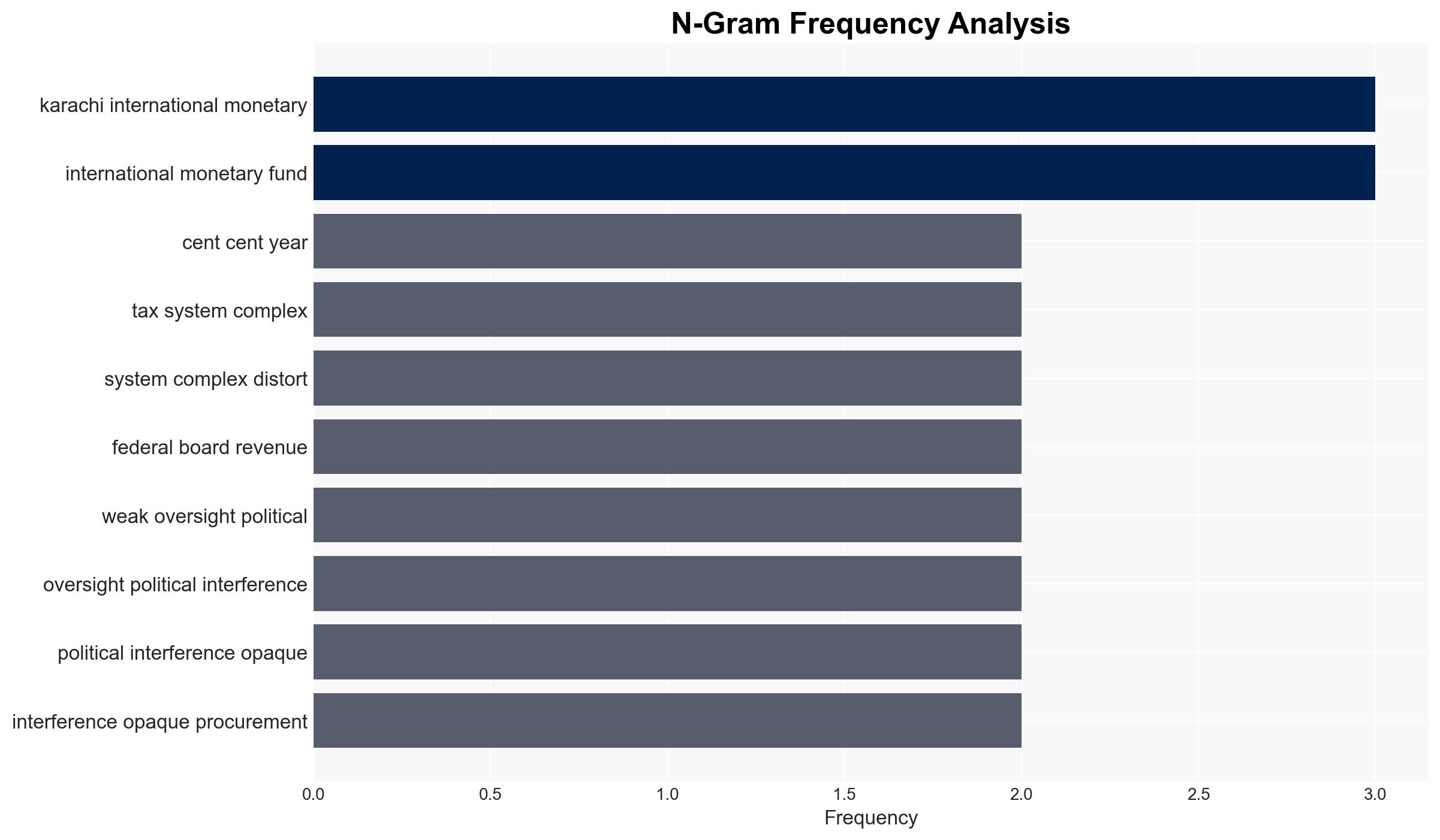
IMF sees 65 GDP upside if Pakistan fixes corruption governance – CNA
Published on: 2025-11-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Strategic Analysis of IMF’s GDP Projection for Pakistan
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that Pakistan’s GDP could significantly improve if comprehensive governance and anti-corruption reforms are implemented. However, the complexity of these reforms and political resistance may hinder progress. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes prioritizing tax system simplification and enhancing transparency in state-owned enterprises.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Pakistan will achieve a GDP growth of 5-6.5% over five years if it successfully implements the IMF-recommended reforms, focusing on reducing corruption and improving governance.
Hypothesis 2: Despite the IMF’s recommendations, Pakistan will struggle to achieve significant GDP growth due to entrenched political interference, complex tax systems, and weak institutional oversight.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the potential for economic reform to unlock growth, but Hypothesis 2 remains plausible due to historical challenges in governance and reform implementation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: The IMF’s projections assume political will and capacity to implement reforms. It also assumes that external economic conditions remain stable.
Red Flags: Political resistance to reform, especially from entities benefiting from the status quo, and potential backlash from vested interests.
Deception Indicators: Over-optimistic projections without addressing underlying political and bureaucratic inertia.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Failure to implement reforms could lead to continued economic stagnation, increased debt burden, and potential social unrest. Successful reform could enhance economic stability, increase foreign investment, and reduce dependency on international financial assistance.
Political risks include potential destabilization from reform opposition, while economic risks involve the possibility of reform fatigue and insufficient capacity to implement changes.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Prioritize tax system digitization and simplification, enhance transparency in state-owned enterprises, and strengthen judicial processes to expedite corruption cases.
- Best Scenario: Successful reform implementation leads to sustained GDP growth and improved economic resilience.
- Worst Scenario: Reform efforts stall, leading to economic decline and increased social unrest.
- Most-likely Scenario: Partial reform implementation results in moderate GDP growth with ongoing challenges in governance and corruption.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
IMF, Pakistan’s Finance Ministry, Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), Special Investment Facilitation Council (SIFC).
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Regional Focus: South Asia, Economic Reform, Governance, Anti-Corruption
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us