Implications of Quantum Computing Advances on Cybersecurity Strategies
Published on: 2026-01-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: What the post-quantum shift means for your security strategy
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
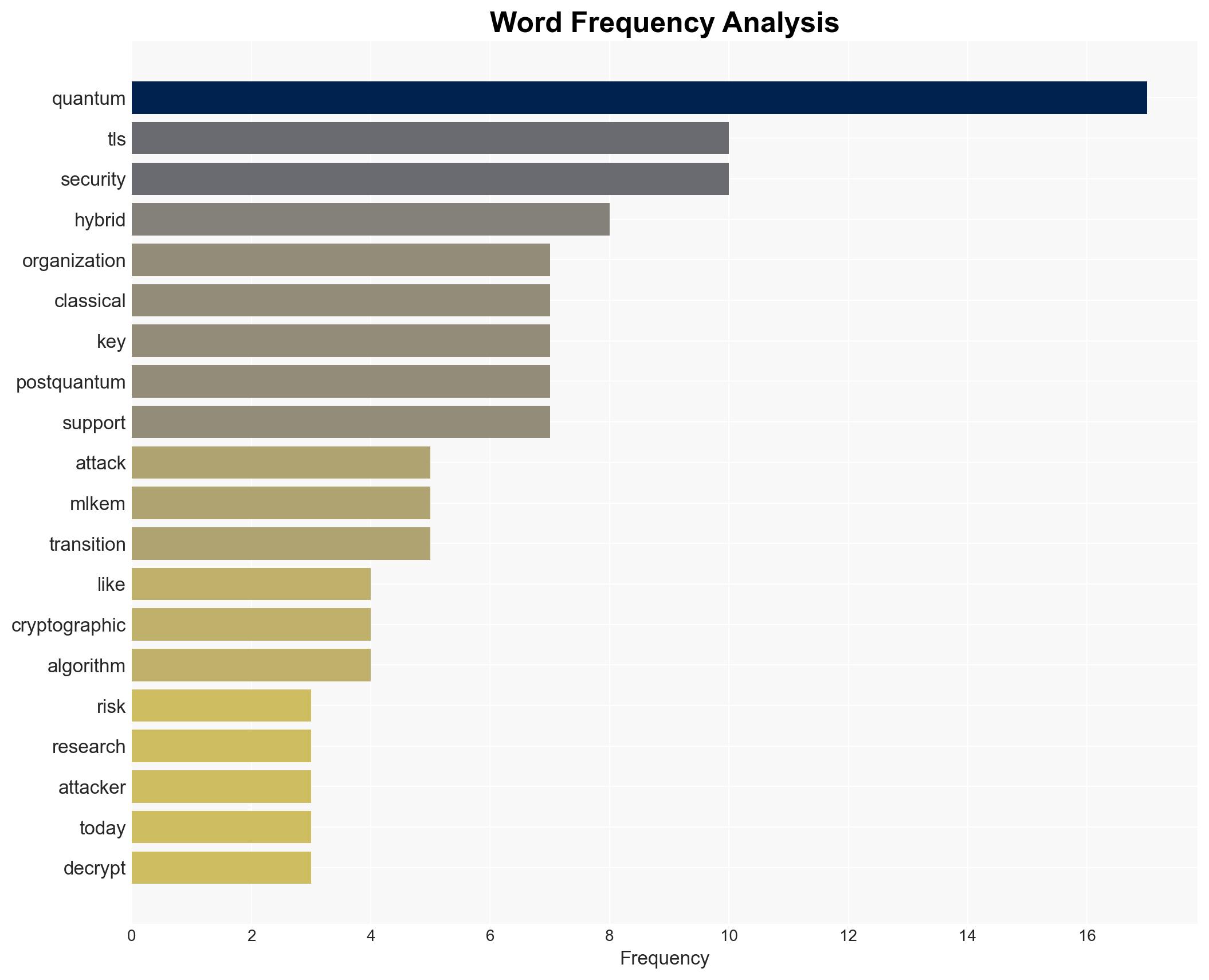
The rapid advancement in quantum computing poses a significant threat to current cybersecurity protocols, particularly TLS, due to its vulnerability to quantum cryptanalysis. Organizations handling sensitive data are at heightened risk from the “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” tactic. The transition to post-quantum cryptographic standards is crucial. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the ongoing developments in quantum research and cryptographic responses.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Quantum computing will soon render current cryptographic protocols obsolete, necessitating immediate transition to post-quantum cryptography. This is supported by rapid advancements in quantum research and the vulnerability of current protocols like TLS to quantum attacks. However, the timeline for when quantum computers will be capable of such attacks remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Quantum computing will not achieve the capability to break current cryptographic standards in the near future, allowing more time for transition. This is supported by the current technical challenges in scaling quantum computers. However, ongoing investments and breakthroughs suggest this could change rapidly.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the significant investments and progress in quantum computing, alongside the proactive development of post-quantum cryptographic standards. Indicators such as breakthroughs in qubit stability and error correction could further support this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Quantum computing will continue to advance at its current pace; current cryptographic protocols are vulnerable to quantum attacks; post-quantum cryptography will be effective against quantum threats.
- Information Gaps: Precise timeline for quantum computers achieving cryptanalysis capability; effectiveness of post-quantum cryptographic algorithms in real-world applications.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Over-reliance on optimistic projections of quantum advancements; potential underestimation of adversaries’ capabilities and intentions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of quantum computing could significantly alter the cybersecurity landscape, impacting various domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Nations may accelerate quantum research to gain strategic advantages, potentially leading to an arms race in quantum technology.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and espionage as encrypted communications become vulnerable.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread cyber disruption if quantum attacks are deployed against critical infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Businesses may face increased costs to upgrade security systems; public trust in digital transactions could be undermined.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Initiate audits of cryptographic systems to assess vulnerability to quantum attacks; begin planning for transition to post-quantum cryptography.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cryptographic research institutions; invest in training for post-quantum cryptographic implementation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful transition to post-quantum cryptography with minimal disruption.
- Worst: Quantum breakthroughs outpace cryptographic defenses, leading to widespread data breaches.
- Most-Likely: Gradual transition with intermittent vulnerabilities as quantum capabilities develop.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- IBM
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, quantum computing, cryptography, TLS, data security, national security, cyber threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us