India Hosts Capacity Building Initiative to Combat Terror Financing in Central Asia
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: COMBAT TERRORISM THROUGH CAPACITY BUILDING PROGRAMME
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
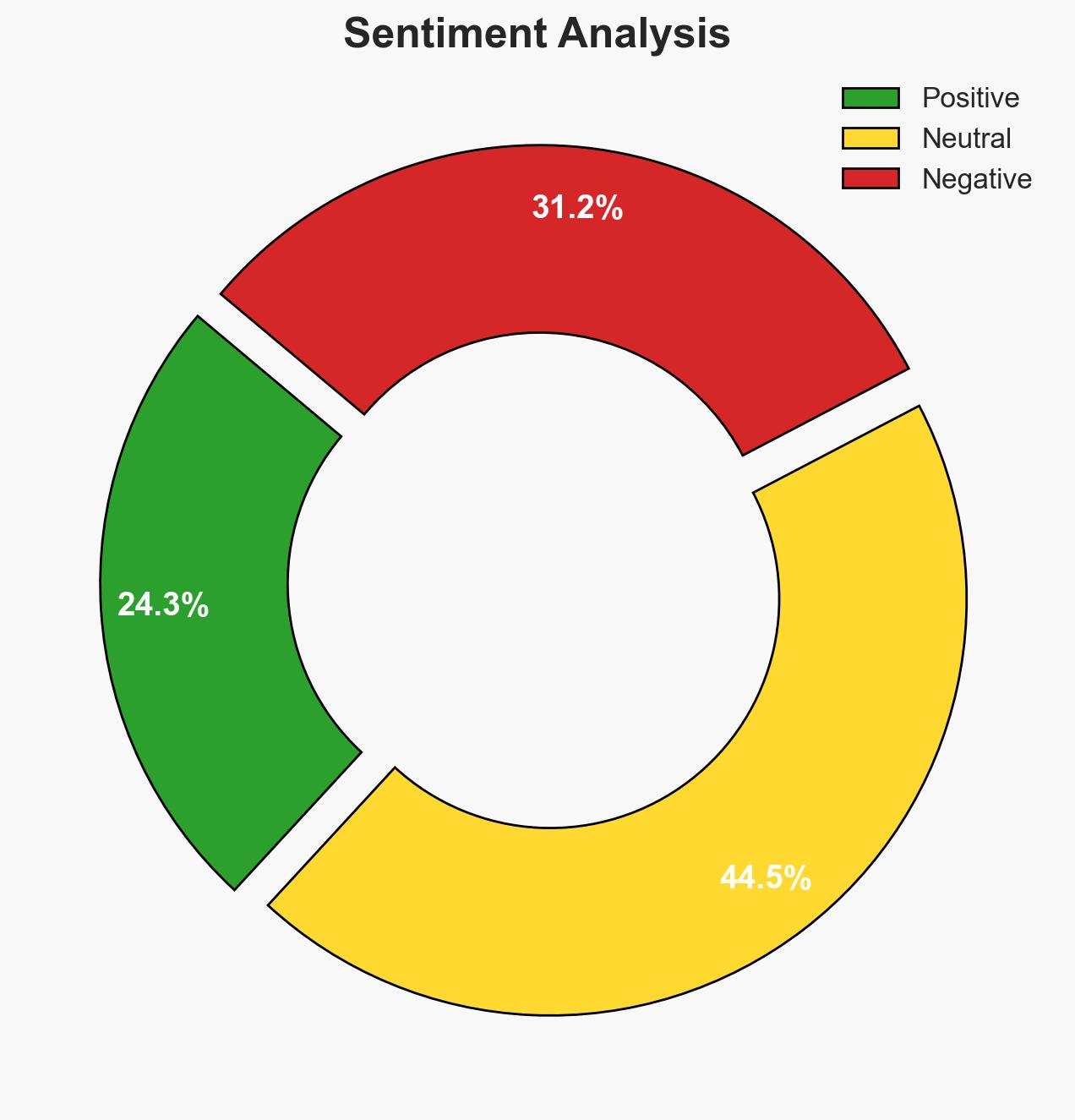
India’s initiative to conduct a Capacity Building Programme for Central Asian Republics (CARs) on countering terrorism financing through digital means reflects its strategic commitment to combating emerging threats. The program’s focus on cryptocurrencies, crowdfunding, and non-profit organizations highlights India’s proactive stance in addressing these vulnerabilities. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the limited information on post-training engagements and outcomes.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: India is effectively enhancing regional capabilities against terrorism financing by sharing technical expertise with CARs, leading to improved regional security. This is supported by the structured training and provision of customized materials. However, the lack of follow-up engagements post-training introduces uncertainty about sustained impact.
- Hypothesis B: India’s efforts may be primarily symbolic, aimed at asserting geopolitical influence rather than achieving substantial counter-terrorism outcomes. The absence of ongoing support and collaboration post-training could indicate limited commitment to long-term capacity building.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the comprehensive nature of the training and India’s active role in regional CFT groups. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of ongoing collaboration or measurable improvements in CARs’ counter-terrorism capabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: India has the technical expertise and resources to effectively train CARs; CARs are willing and able to implement learned strategies; India’s geopolitical interests align with genuine counter-terrorism goals.
- Information Gaps: Details on CARs’ post-training implementation efforts; specific metrics for evaluating the program’s success; India’s long-term engagement plans with CARs.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting India’s intentions and capabilities; risk of overestimating CARs’ capacity to implement changes; possibility of India using the program for geopolitical leverage rather than genuine capacity building.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could enhance regional security cooperation and counter-terrorism effectiveness if sustained. However, without continued engagement, the program’s impact may diminish over time.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened ties between India and CARs could shift regional power dynamics, potentially affecting relations with neighboring powers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Improved capabilities in CARs could lead to a reduction in terrorism financing, but gaps in ongoing support pose a risk to long-term effectiveness.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on digital threats may prompt adversaries to adapt tactics, necessitating continuous updates to countermeasures.
- Economic / Social: Enhanced security could foster economic stability in CARs, but failure to address root causes of radicalization may limit social cohesion benefits.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Establish communication channels for ongoing support with CARs; monitor implementation of training outcomes; assess CARs’ needs for further assistance.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with regional and international bodies to sustain capacity building; invest in technology and expertise sharing; evaluate and refine training modules based on feedback.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Sustained collaboration leads to significant reduction in terrorism financing in CARs.
- Worst: Lack of follow-up results in negligible impact, with CARs remaining vulnerable.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in CARs’ capabilities with potential for expanded cooperation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Department of Revenue, India
- Ministry of External Affairs, India
- National Security Council Secretariat, India
- Financial Intelligence Unit India (FIU IND)
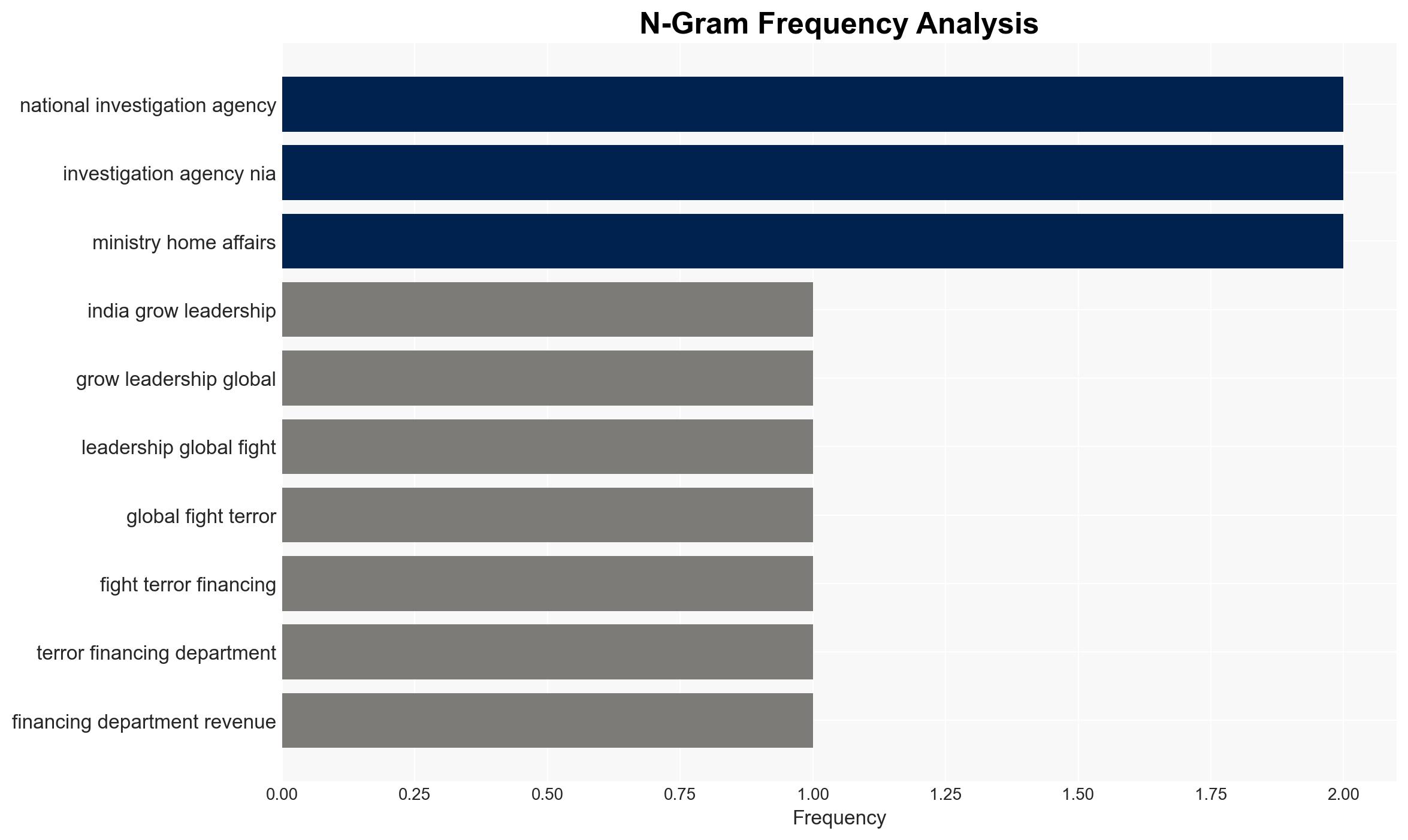
- National Investigation Agency (NIA)
- Minister of State in the Ministry of Home Affairs, Shri Nityanand Rai
7. Thematic Tags
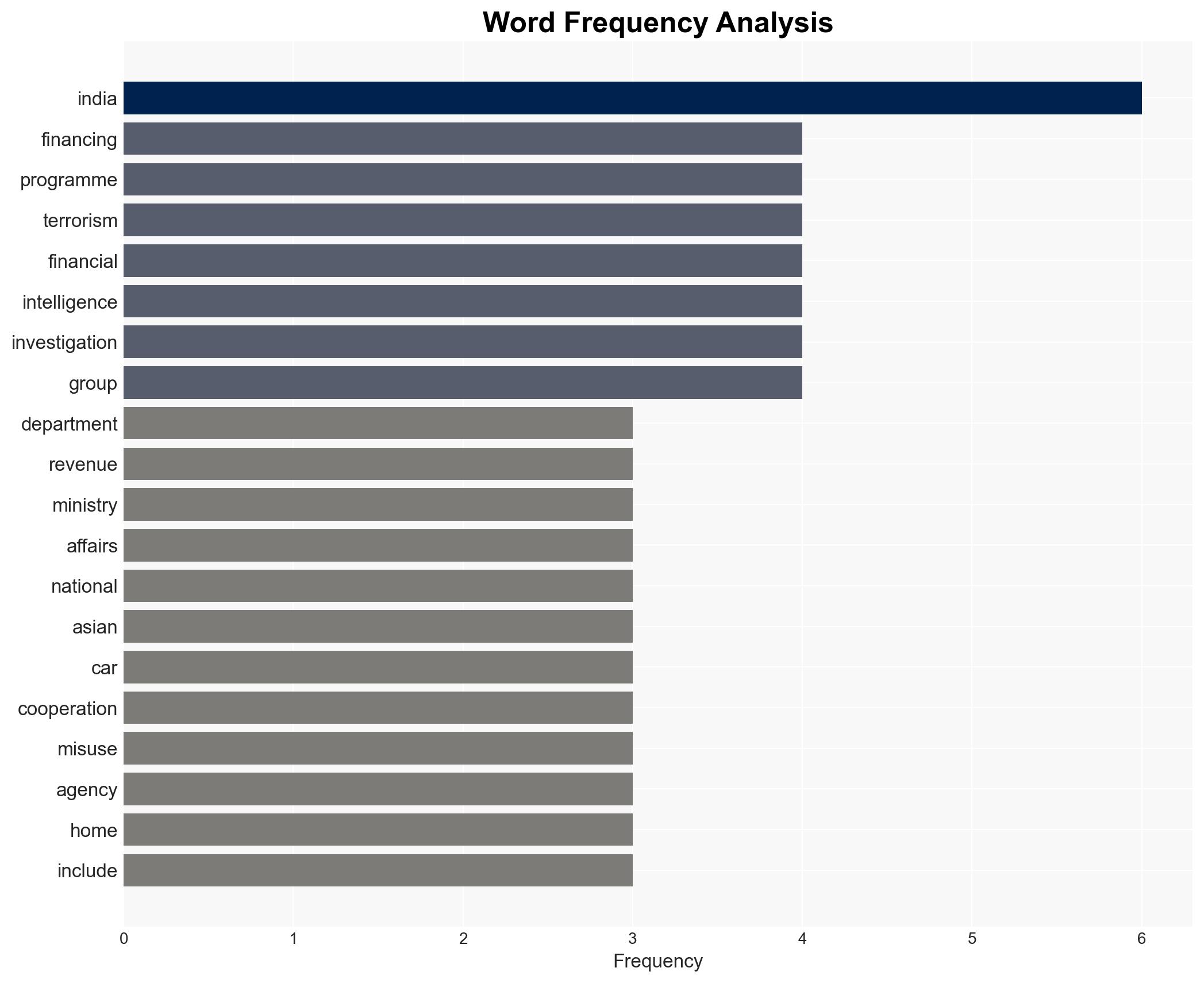
Counter-Terrorism, terrorism financing, cryptocurrencies, Central Asian Republics, capacity building, geopolitical strategy, digital security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us