India Requires Smartphone Manufacturers to Preload State Cybersecurity App on New Devices
Published on: 2025-12-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
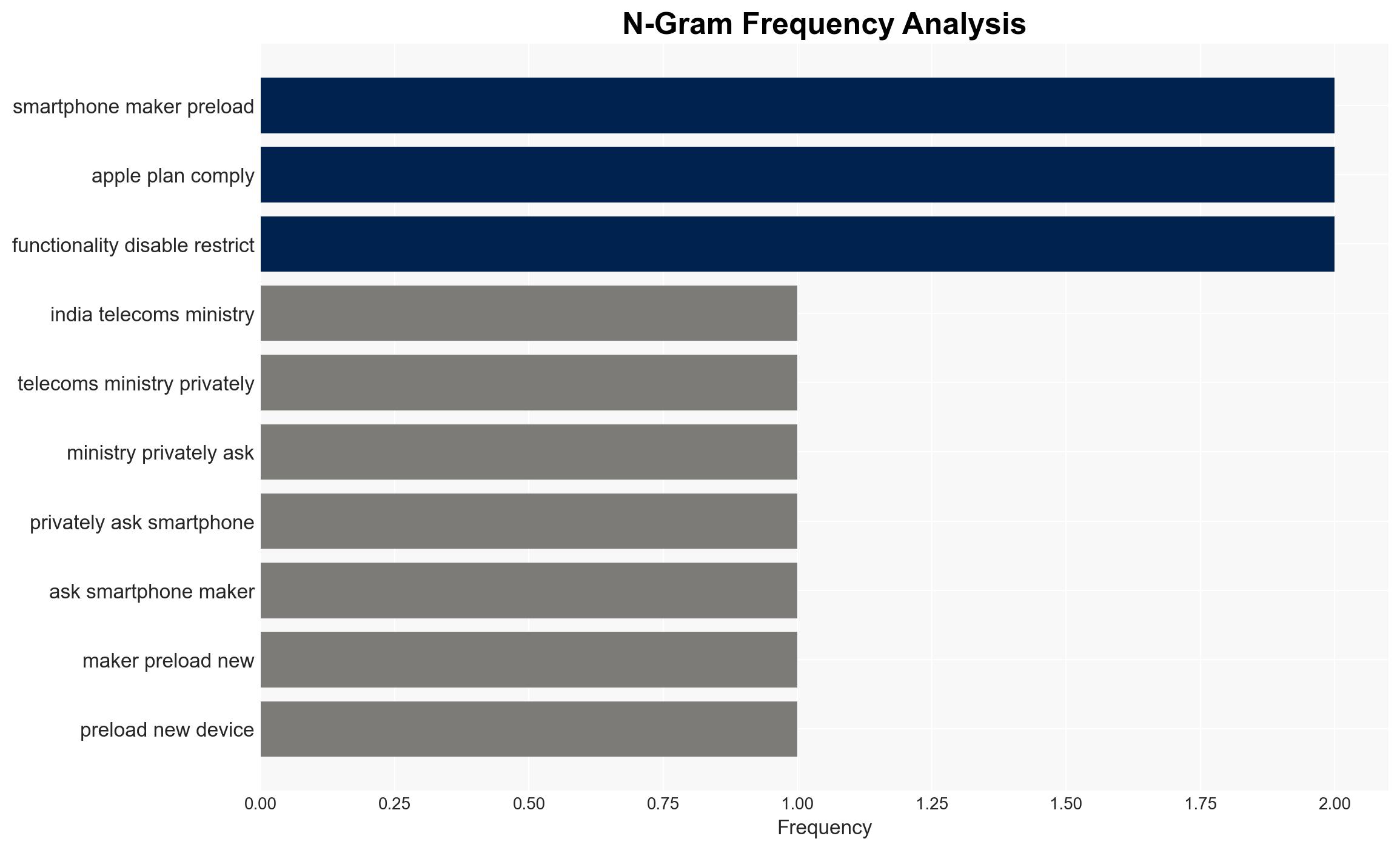
Intelligence Report: Mandate to Pre-Install iOS App in India
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
India’s directive to preload a state-owned cybersecurity app on smartphones is likely to face resistance from Apple and privacy advocates, potentially leading to geopolitical and economic tensions. The mandate aims to combat cybercrime but raises significant privacy concerns. The most likely hypothesis is that India will enforce compliance, impacting foreign tech companies. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: India will enforce the mandate, compelling smartphone manufacturers to comply. This is supported by the government’s firm directive and the precedent of similar actions in other countries. However, the lack of clarity on enforcement mechanisms and potential legal challenges from companies like Apple are uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: India will face significant pushback from international tech companies and privacy advocates, leading to a relaxation or modification of the mandate. This is supported by Apple’s stated non-compliance and potential international pressure. However, the Indian government’s previous actions suggest a strong commitment to cybersecurity measures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the government’s clear directive and the global trend of increased cybersecurity measures. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include legal challenges, international diplomatic pressure, and public backlash within India.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Indian government prioritizes cybersecurity over potential economic repercussions; Apple and other tech companies will prioritize privacy and security concerns; The directive is technically feasible for smartphone manufacturers to implement.
- Information Gaps: Details on enforcement mechanisms and potential penalties for non-compliance; Reactions from other major smartphone manufacturers; Public sentiment within India regarding privacy versus security.
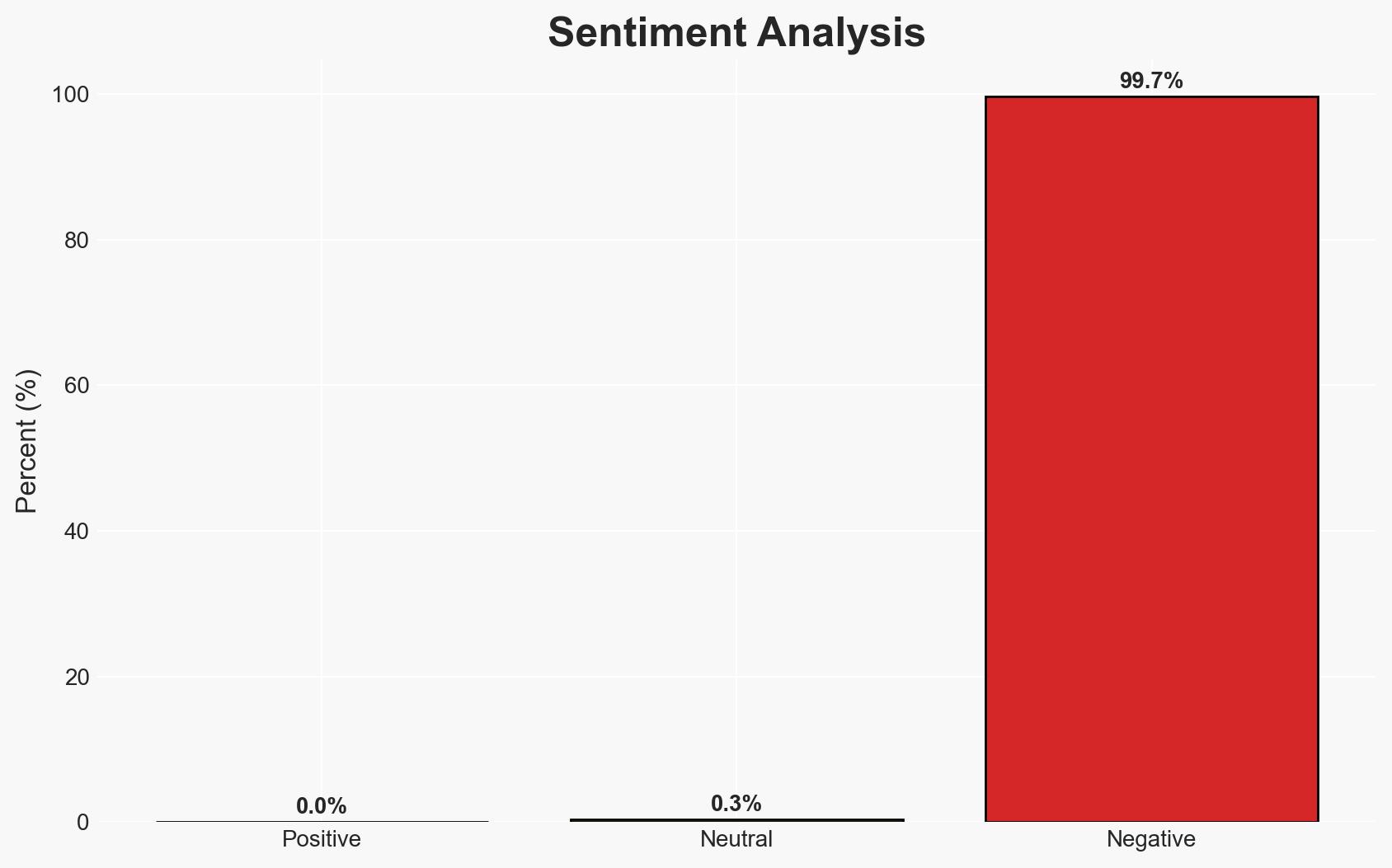
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from sources close to Apple; Government statements may underplay the coercive nature of the mandate; Risk of strategic deception by stakeholders to influence public opinion or policy decisions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions between India and foreign tech companies, potentially impacting trade relations and foreign investment. The mandate may also influence global cybersecurity policy trends.
- Political / Geopolitical: Possible strain in India-U.S. relations if American companies are adversely affected; potential for India to align more closely with countries implementing similar measures.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capability to combat cybercrime and illegal telecom activities; potential misuse of the app for surveillance purposes.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased scrutiny on India’s digital policies; potential for cyber retaliation from affected entities.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on smartphone sales and market dynamics in India; public debate on privacy rights versus national security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor compliance responses from major smartphone manufacturers; engage in diplomatic dialogues to address privacy concerns; assess public sentiment and potential backlash.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential economic impacts; foster partnerships with international cybersecurity entities; enhance legal frameworks to balance security and privacy.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: India revises the mandate to address privacy concerns, maintaining strong international relations. Worst: Escalation of trade tensions and legal battles, harming India’s tech market. Most-Likely: Partial compliance with ongoing negotiations and adjustments to the directive.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
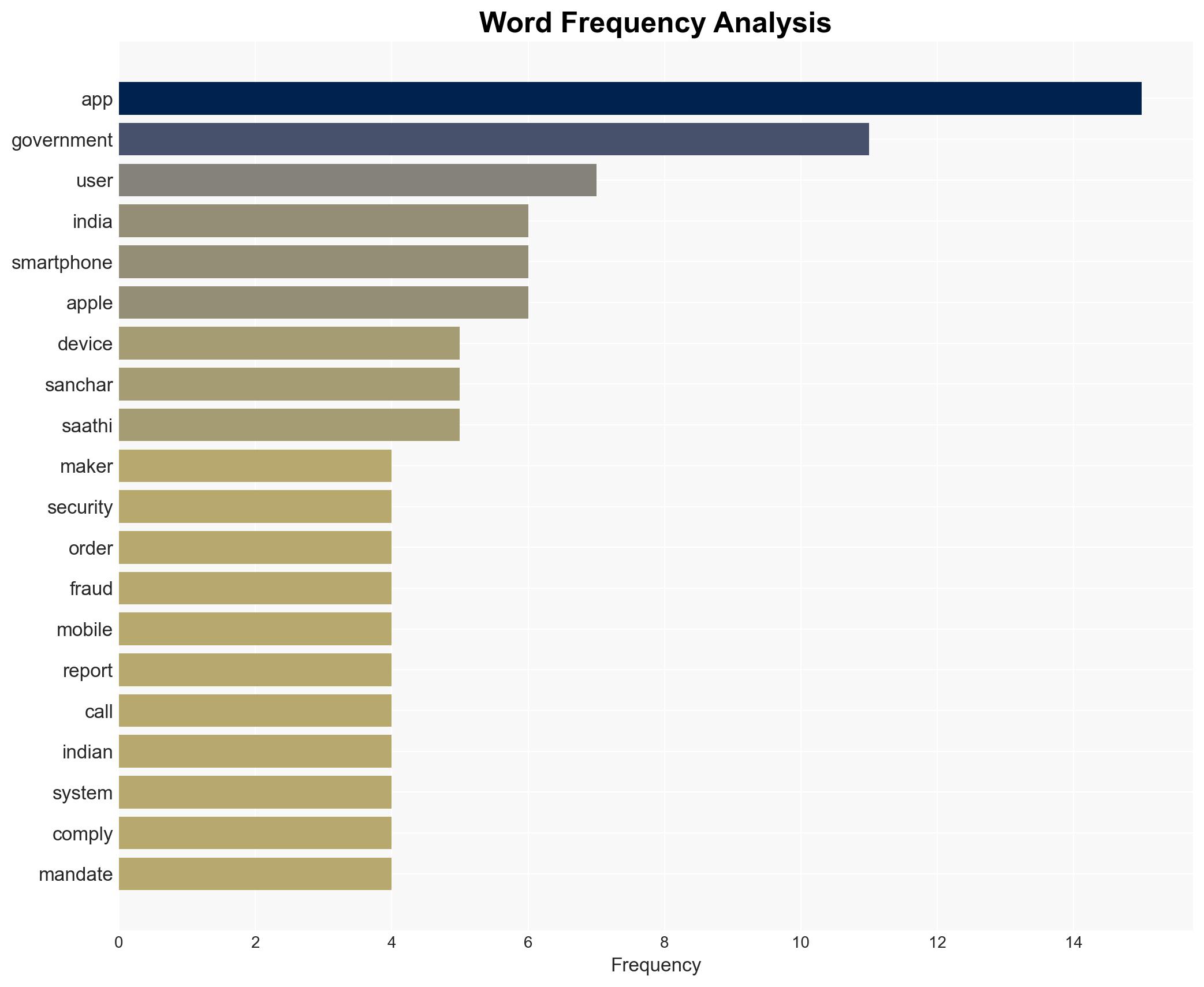
- Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, India’s telecom minister
- Apple Inc.
- India’s Department of Telecommunications (DoT)
- Sanchar Saathi app
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, privacy, international trade, smartphone industry, government policy, India, technology compliance
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us