India trims Russian oil imports by 29 in September broadens energy sourcing to Nigeria Angola and Trkiye – BusinessLine
Published on: 2025-11-03
Intelligence Report: India trims Russian oil imports by 29% in September; broadens energy sourcing to Nigeria, Angola, and Türkiye – BusinessLine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
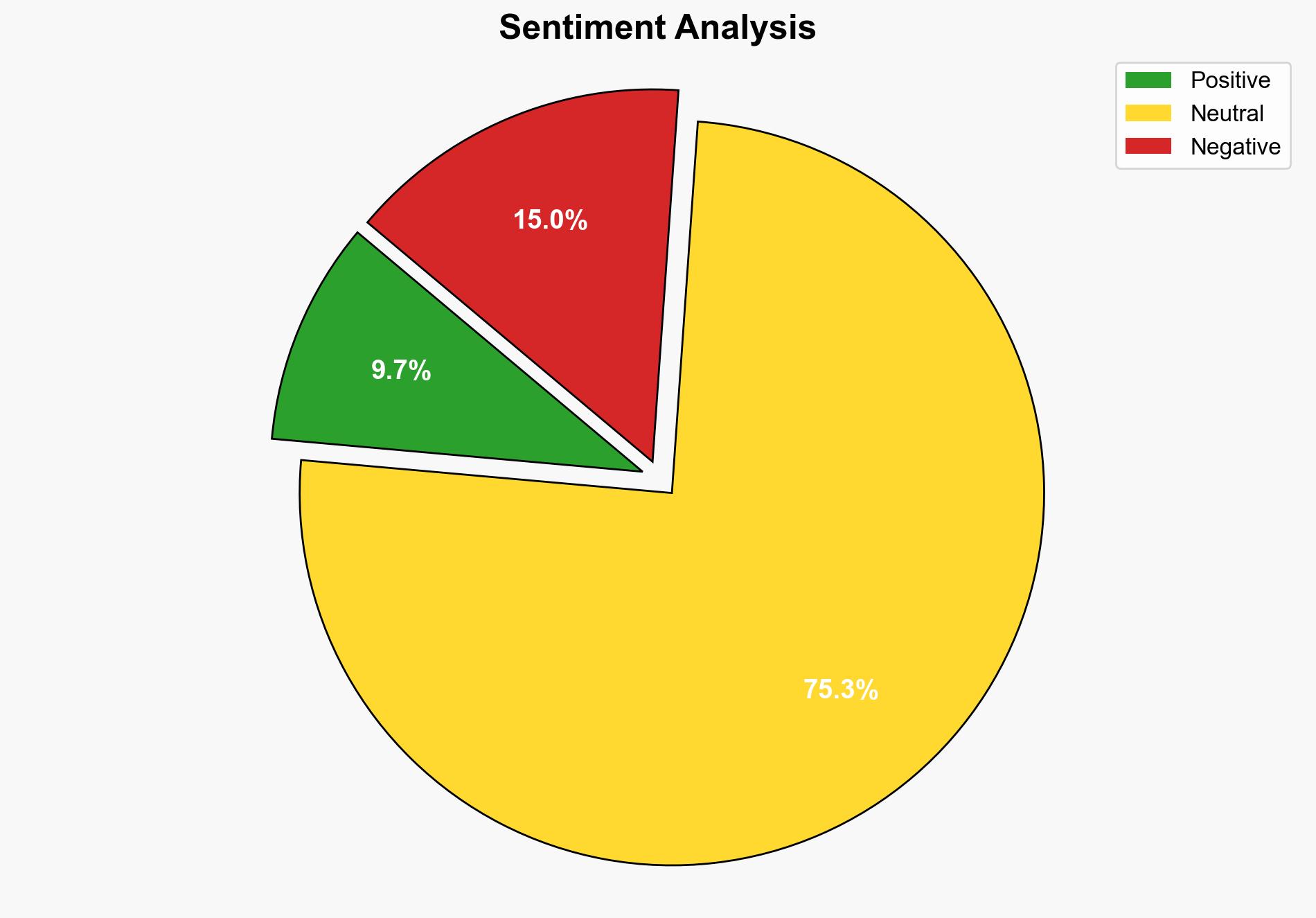
India’s strategic shift away from Russian oil imports, reducing them by 29% in September, is driven by economic pragmatism and geopolitical realignment. The most supported hypothesis is that India is diversifying its energy sources to mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on any single supplier, particularly in light of geopolitical tensions and economic sanctions. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes further diversification of energy sources and strengthening diplomatic ties with new suppliers.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: India is reducing Russian oil imports primarily due to economic sanctions and increased tariffs, which make Russian oil less economically viable.
2. **Hypothesis B**: India is strategically diversifying its energy sources to reduce dependency on Russia and enhance energy security amidst global geopolitical shifts.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis B is better supported due to the broader diversification strategy observed, including increased imports from Nigeria, Angola, and Türkiye, despite the higher costs associated with these sources.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that India has the capacity to absorb higher costs from alternative suppliers without significant economic strain. Another assumption is that geopolitical tensions will persist, necessitating diversification.
– **Red Flags**: The potential for cognitive bias exists in underestimating the economic impact of higher-cost imports. There is also a risk of over-reliance on new suppliers who may not be as stable or reliable.
– **Inconsistent Data**: The report lacks detailed analysis of the long-term economic impact on India’s refinery margins and trade deficit.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic Risks**: Increased import costs could pressure India’s refinery margins and contribute to retail fuel inflation, impacting the broader economy.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: A shift in energy alliances might strain India’s relations with Russia, potentially affecting other areas of bilateral cooperation.
– **Strategic Risks**: Over-reliance on new suppliers could expose India to supply chain vulnerabilities if these regions face instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Mitigate Risks**: Enhance diplomatic engagement with new suppliers to ensure stable and reliable energy imports.
- **Exploit Opportunities**: Invest in renewable energy sources to further diversify the energy mix and reduce dependency on imported oil.
- **Scenario Projections**:
– **Best Case**: Successful diversification leads to stable energy supply and reduced geopolitical risk.
– **Worst Case**: Increased costs and supply disruptions from new suppliers strain the economy.
– **Most Likely**: Gradual adjustment to new suppliers with manageable economic impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Indian Ministry of Commerce
– Major oil suppliers: Saudi Arabia, UAE, Nigeria, Angola, Türkiye
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, energy security, geopolitical strategy, economic diversification