Indonesia Implements Biometric System for Seamless Immigration Processing at Airports
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: This country now lets travelers clear immigration without stopping
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
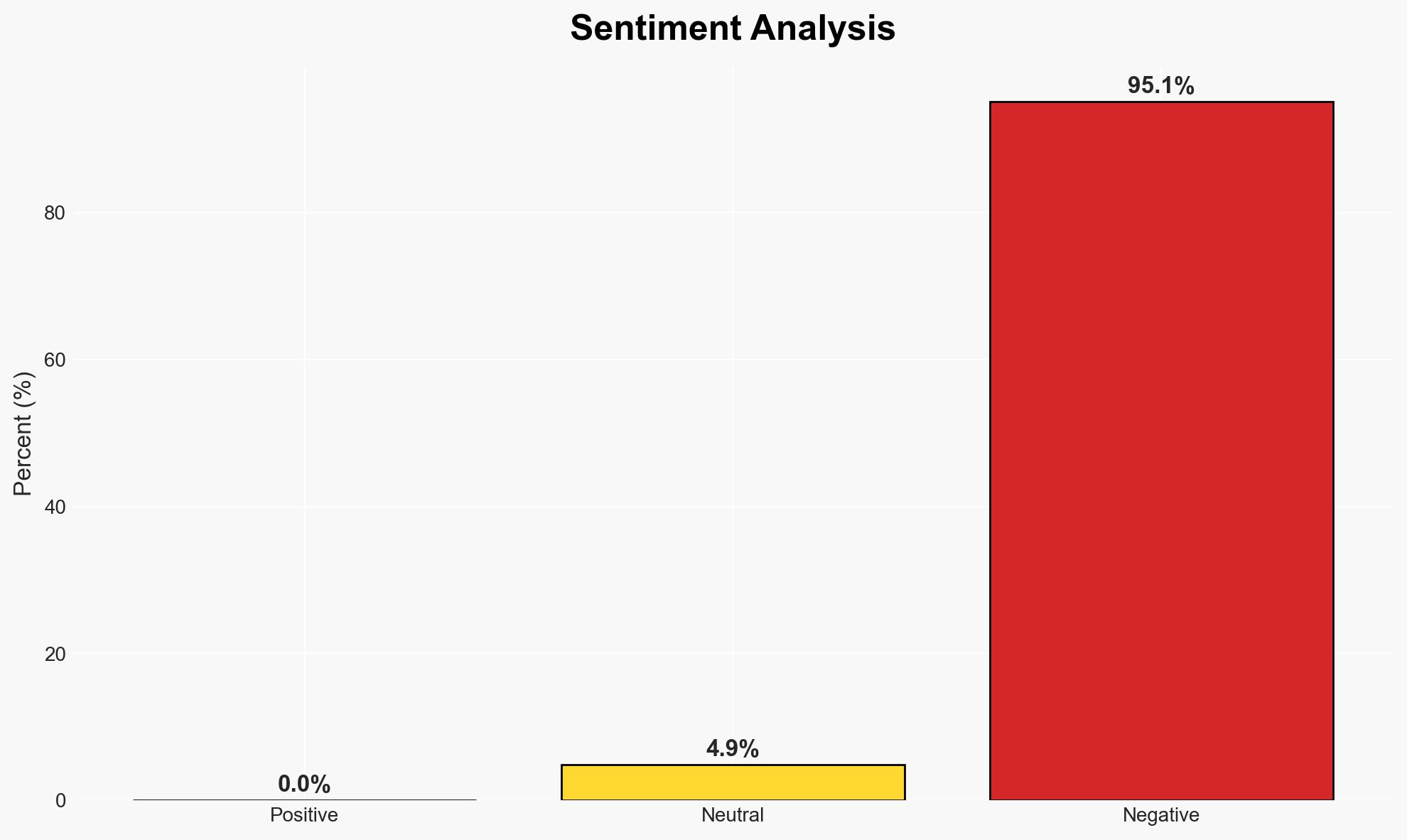
Indonesia has implemented a biometric system at select airports allowing travelers to bypass traditional immigration checks, potentially streamlining passenger flow and enhancing border security. This development primarily affects international travelers and airport operations. The most likely hypothesis is that this system will improve efficiency and security, with moderate confidence due to existing uncertainties in system implementation and user adoption.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The biometric system will significantly enhance airport efficiency and security by reducing queues and improving identity verification. Supporting evidence includes the integration of advanced biometric and AI technologies and successful initial operations in Jakarta and Surabaya. Key uncertainties include the system’s scalability and user acceptance.
- Hypothesis B: The biometric system may face operational challenges that limit its effectiveness, such as technical failures, privacy concerns, or resistance from travelers. Contradicting evidence includes potential technical issues and privacy risks that could undermine system reliability and public trust.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the successful initial deployment and strategic partnerships with technology firms. However, indicators such as technical malfunctions or public backlash could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The biometric system will function as intended; travelers will adopt the new system without significant resistance; data privacy measures are adequately addressed; the system will be scalable to other airports.
- Information Gaps: Detailed performance metrics of the system; traveler feedback and adoption rates; specific privacy protection measures in place.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on vendor-provided data; confirmation bias towards technological optimism; lack of transparency in system failures or privacy breaches.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to broader adoption of biometric systems globally, influencing airport security protocols and international travel norms. However, it may also provoke privacy debates and regulatory challenges.
- Political / Geopolitical: Could set a precedent for other countries, impacting international travel agreements and security collaborations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced identity verification may improve counter-terrorism efforts but could also be targeted by cyber threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased risk of biometric data breaches and cyberattacks targeting the system’s infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Potential to boost tourism and airport efficiency, but may also raise social concerns over surveillance and privacy.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor system performance and traveler feedback; assess privacy measures and potential vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop contingency plans for system failures; engage in public awareness campaigns to address privacy concerns; explore partnerships for further technological enhancements.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: System operates smoothly, enhancing security and efficiency, leading to wider adoption.
- Worst: Technical failures and privacy breaches lead to public backlash and regulatory challenges.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement and expansion with ongoing adjustments to address technical and privacy issues.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Rudy Daniello, Executive Vice President, Amadeus
- Andy Syach, CEO, Sinergi Teknoglobal Perkasa
- Amadeus
- Sinergi Teknoglobal Perkasa
- Indonesia Immigration Department
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us