Ineffective tools hinder effective vulnerability management and extend remediation timelines for organization…
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
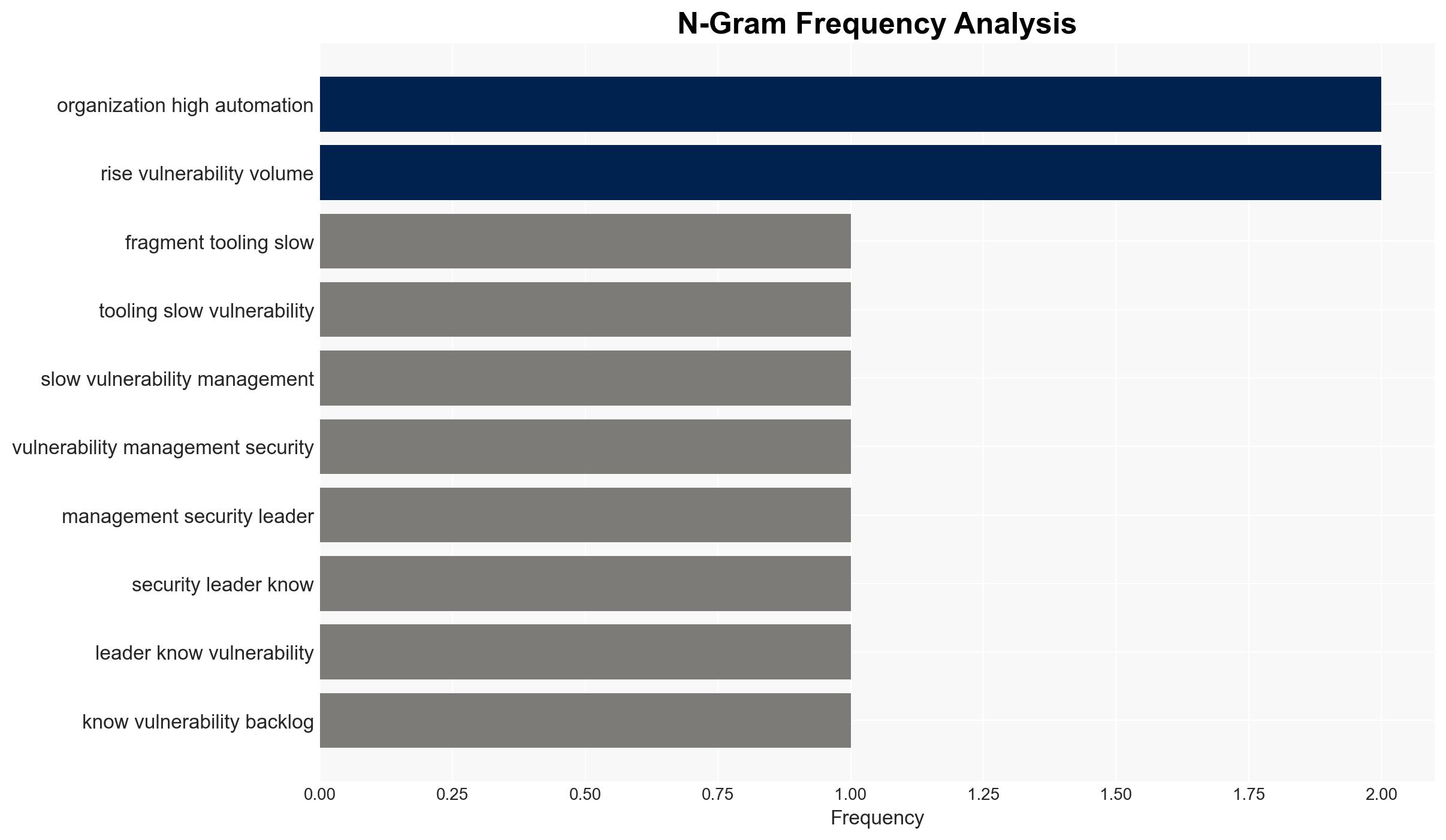
Intelligence Report: Fragmented tooling slows vulnerability management
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
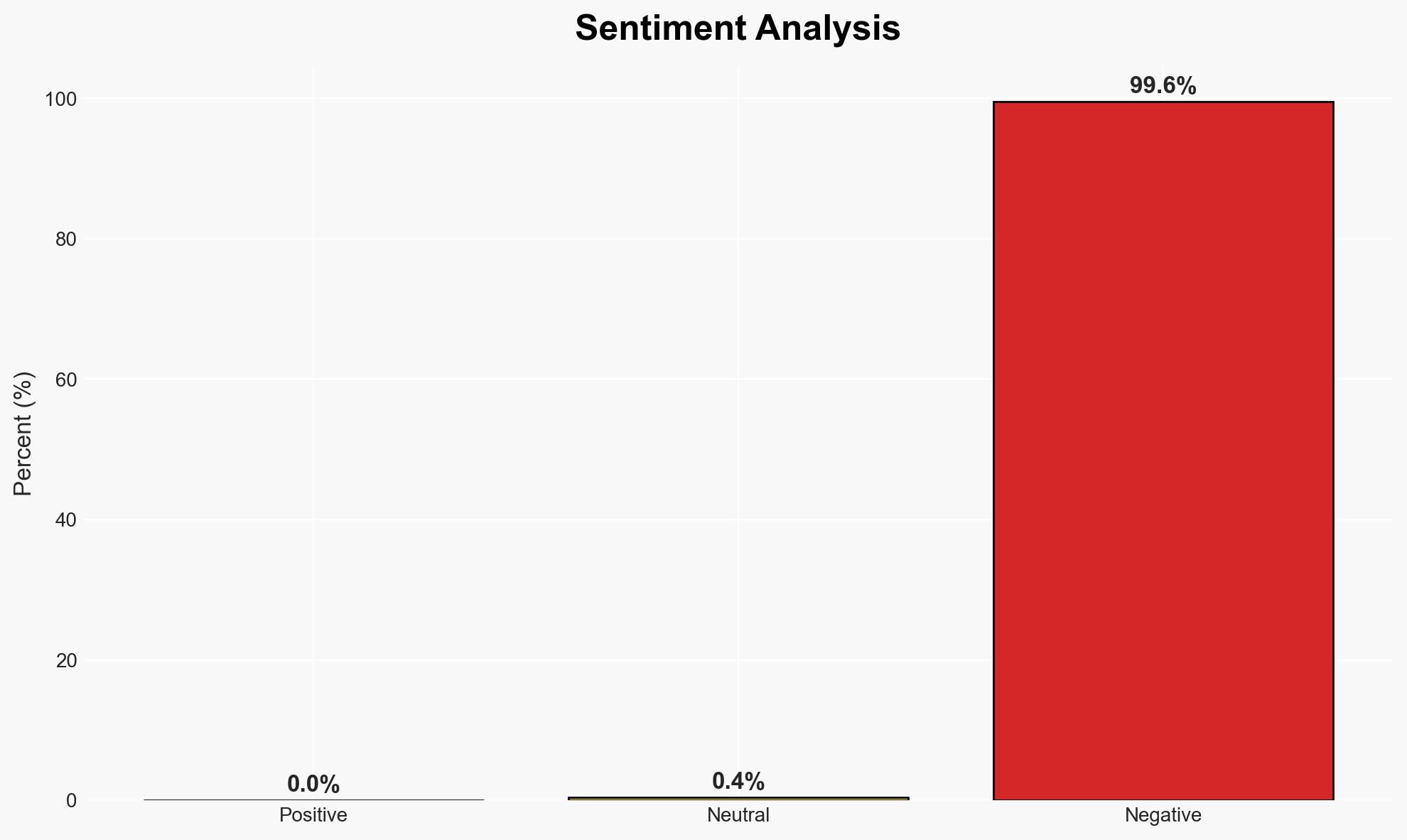
The current state of vulnerability management is hindered by fragmented tooling and manual processes, leading to increased exposure and resource strain. Organizations with high automation are better positioned to manage vulnerabilities effectively. This situation affects cybersecurity teams and broader organizational security posture. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Fragmented tooling and manual workflows are the primary causes of slow vulnerability management. Evidence includes reliance on multiple detection tools and manual triage processes. Key uncertainties include the extent of automation adoption and its impact on remediation speed.
- Hypothesis B: Organizational structure and resource allocation are the main factors affecting vulnerability management efficiency. Evidence includes the role of cybersecurity teams in remediation and the impact of internal processes on prioritization. Contradicting evidence is the reported benefit of automation in improving prioritization.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the clear linkage between fragmented tooling and slow remediation. Indicators that could shift this judgment include data on resource allocation and organizational structure changes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations have the capability to adopt higher levels of automation; Current tooling fragmentation directly impacts remediation speed; Manual processes are less efficient than automated ones.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the adoption rate of automation across different sectors; Specific metrics on the impact of automation on MTTR.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in self-reported data from organizations; Over-reliance on automation as a panacea without considering other factors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The persistence of fragmented vulnerability management could lead to increased cyber risks and operational inefficiencies. Over time, this may necessitate strategic shifts in cybersecurity policy and resource allocation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny on cybersecurity practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of exploitation by threat actors due to slow remediation processes.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased vulnerability to cyber-attacks and data breaches.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses and reputational damage from security incidents.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct an audit of current vulnerability management processes and tooling; Prioritize automation of high-impact areas.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with technology providers to enhance automation capabilities; Implement continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) frameworks.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Full automation leads to rapid remediation and reduced exposure. Worst: Continued fragmentation results in significant security breaches. Most-Likely: Gradual improvement with partial automation adoption.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
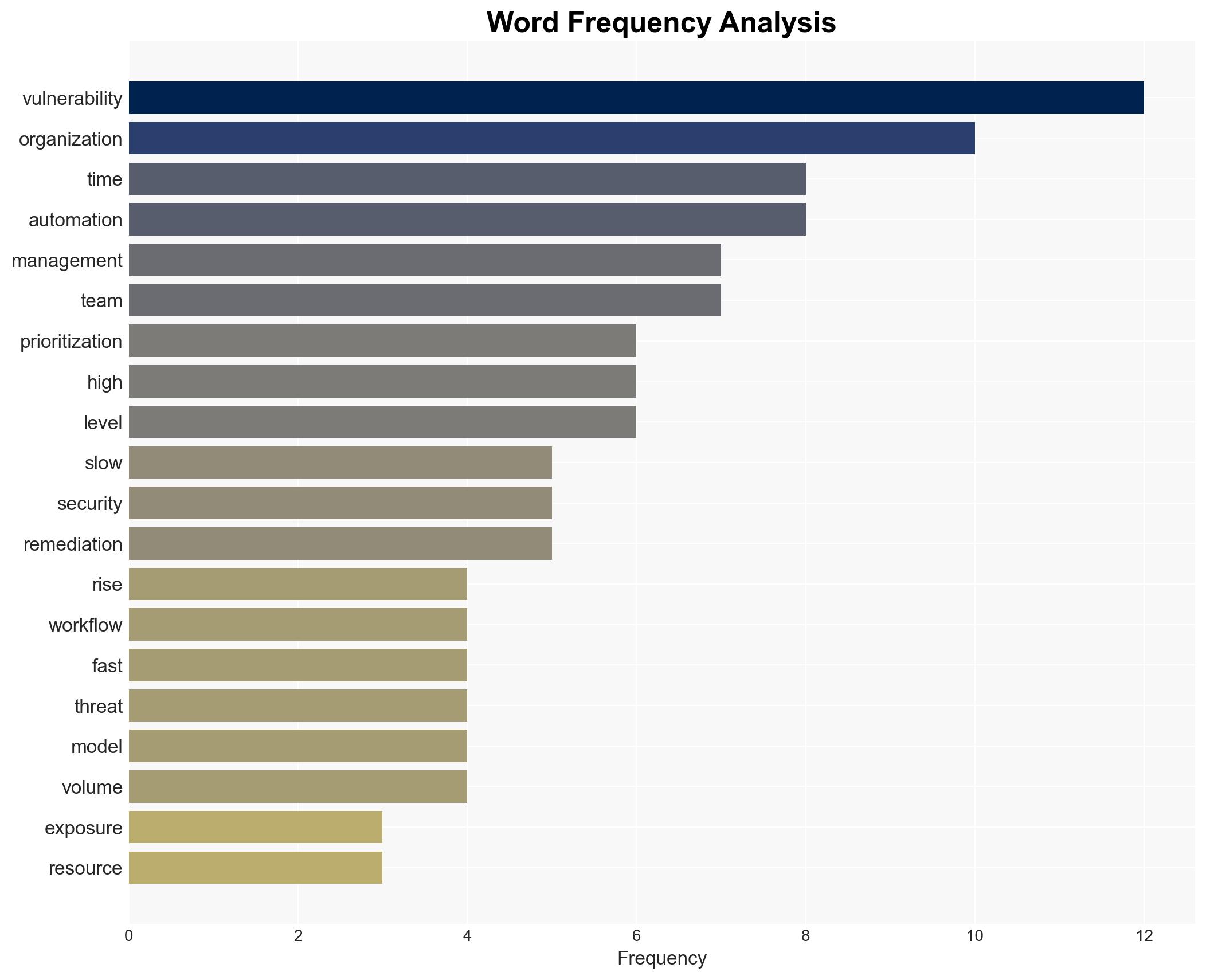
Cybersecurity, vulnerability management, automation, risk management, threat intelligence, organizational efficiency, cyber resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us