Inside Jordan warehouse where Gaza aid held ‘after being refused entry by Israel’ – Sky.com
Published on: 2025-11-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
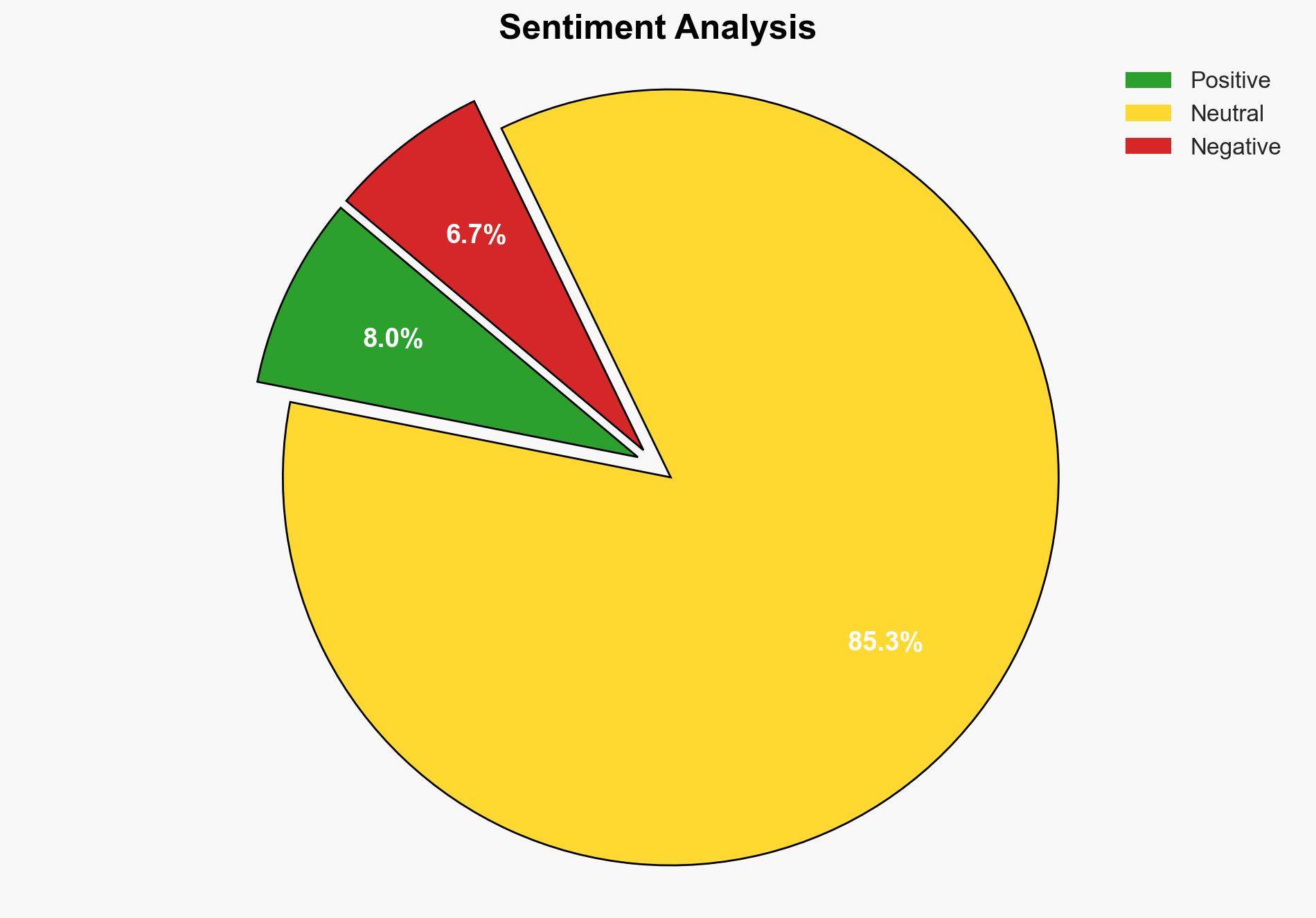
The most supported hypothesis is that the aid blockade at the Jordanian warehouse is primarily due to Israeli security concerns and geopolitical tensions, rather than logistical or humanitarian considerations. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Engage in diplomatic efforts to negotiate humanitarian access while addressing Israeli security concerns.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The aid blockade is primarily due to Israeli security concerns and geopolitical tensions with Jordan and Gaza.
Hypothesis 2: The blockade results from logistical challenges and bureaucratic inefficiencies within the UN and Jordanian authorities.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the historical context of Israeli security policies and recent incidents involving border security, such as the killing of an Israeli soldier. The geopolitical tensions between Israel and its neighbors often influence humanitarian access decisions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: Israel prioritizes security over humanitarian concerns; Jordan and UN are willing to facilitate aid but are constrained by Israeli policies.
Red Flags: Potential bias in reporting from sources with vested interests; lack of transparency in decision-making processes by Israeli authorities.
Deception Indicators: Contradictory statements from Israeli and UN officials regarding the facilitation of aid.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued blockade could exacerbate humanitarian conditions in Gaza, potentially leading to increased regional instability and international criticism of Israel. Escalation scenarios include heightened tensions between Israel and neighboring countries, increased cyber threats targeting Israeli infrastructure, and potential economic repercussions from international sanctions or aid withdrawal.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage in diplomatic dialogue with Israeli authorities to address security concerns while advocating for humanitarian access.
- Coordinate with international organizations to streamline aid distribution processes and ensure transparency.
- Best Scenario: Successful negotiation leads to the opening of aid routes, improving humanitarian conditions in Gaza.
- Worst Scenario: Escalation of regional tensions resulting in military confrontations and further humanitarian crises.
- Most-likely Scenario: Continued diplomatic stalemate with intermittent aid access, maintaining the status quo.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
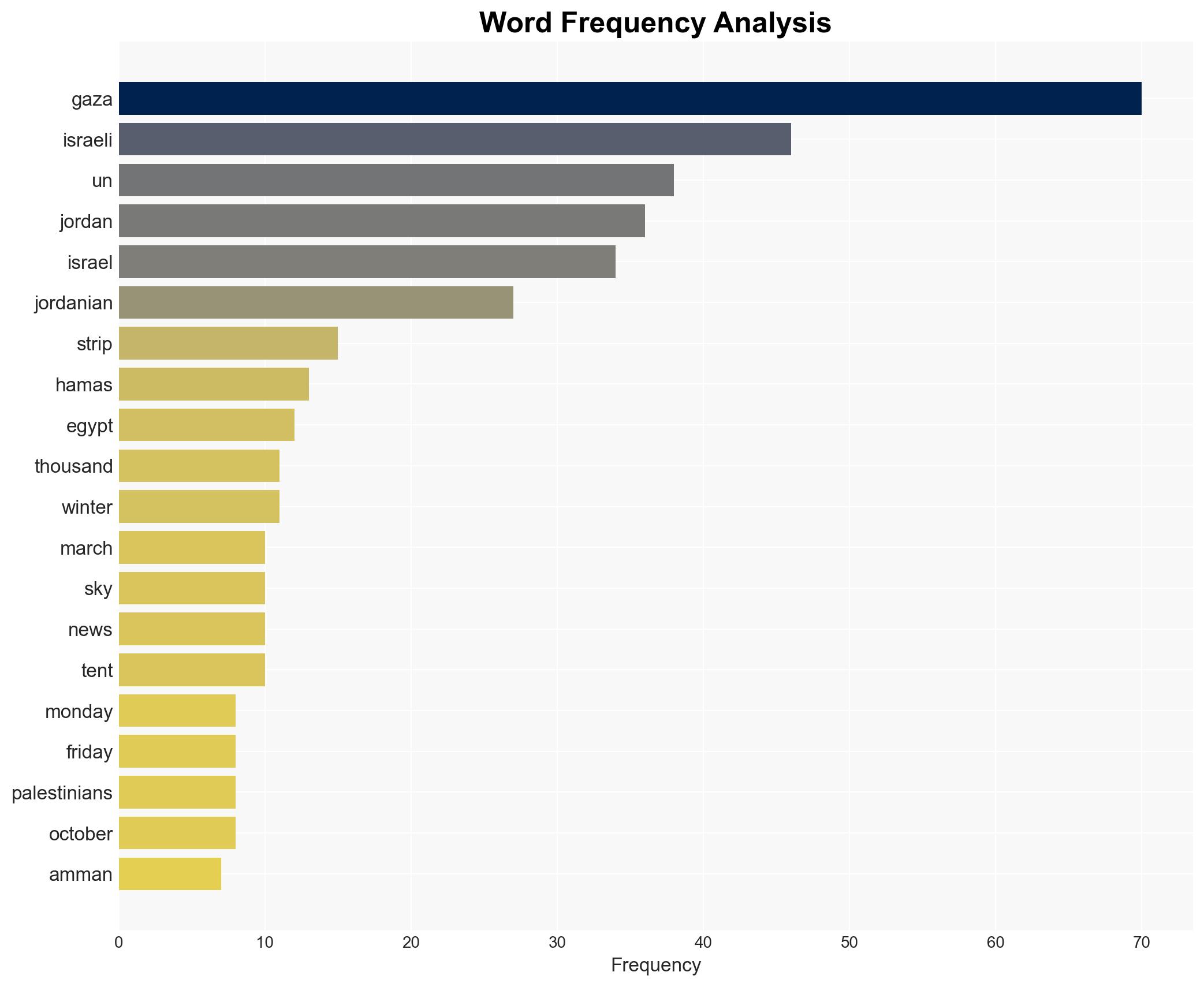
Natalie Boucly (Deputy Commissioner General, UNRWA), Israeli Defense Body (COGAT), UNICEF, Jordanian Authorities.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Middle East, Humanitarian Aid, Israeli-Palestinian Conflict, Geopolitical Tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·