Insurers Paid Nearly 200 Million in Cyber Claims for UK Businesses in 2024 – Insurance Journal
Published on: 2025-11-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Insurers Paid Nearly 200 Million in Cyber Claims for UK Businesses in 2024 – Insurance Journal
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
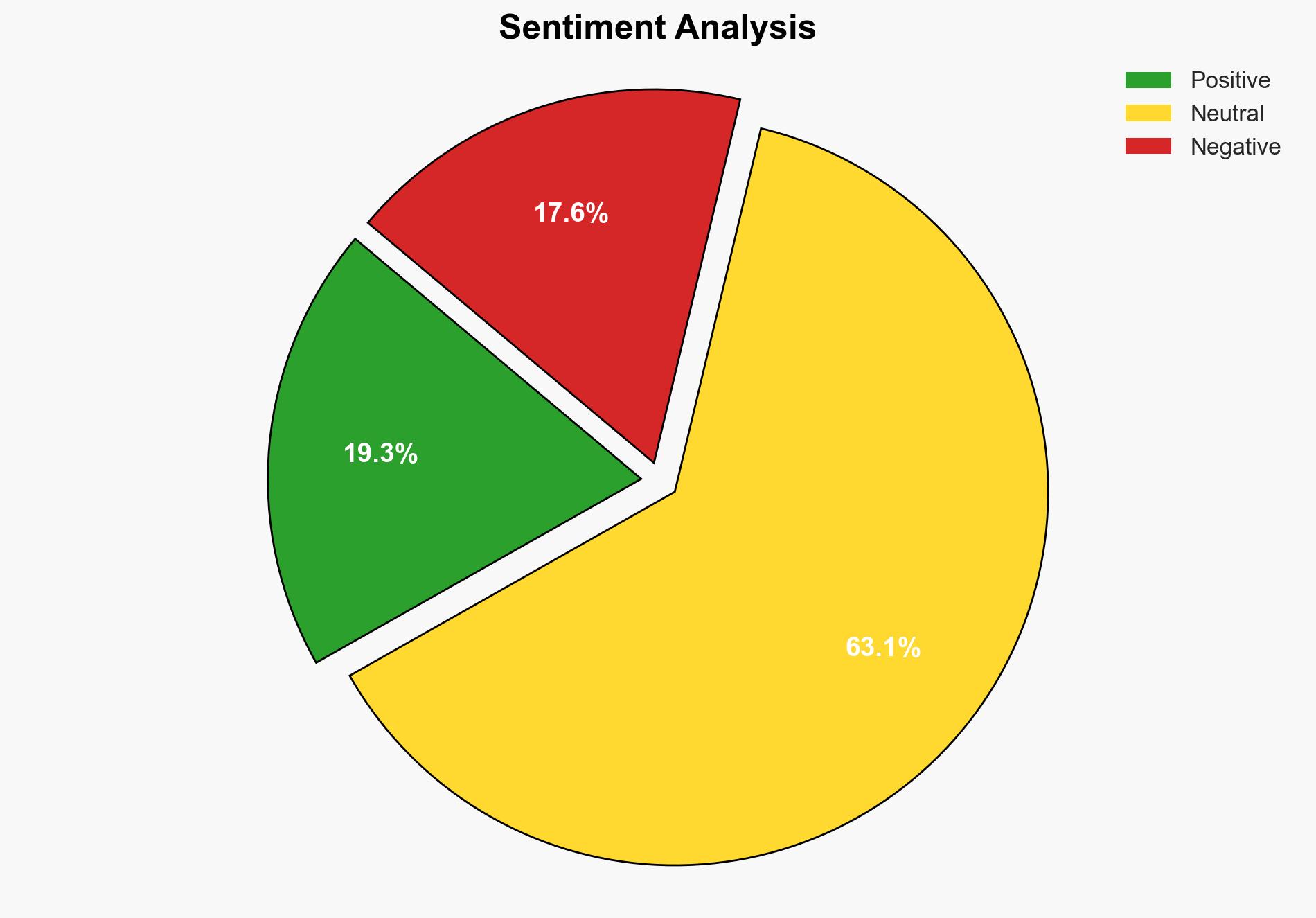
There is a significant rise in cyber insurance claims in the UK, driven by increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. The most supported hypothesis is that this trend will continue, necessitating enhanced cybersecurity measures and regulatory frameworks. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes strengthening cybersecurity infrastructure and regulatory oversight to mitigate risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
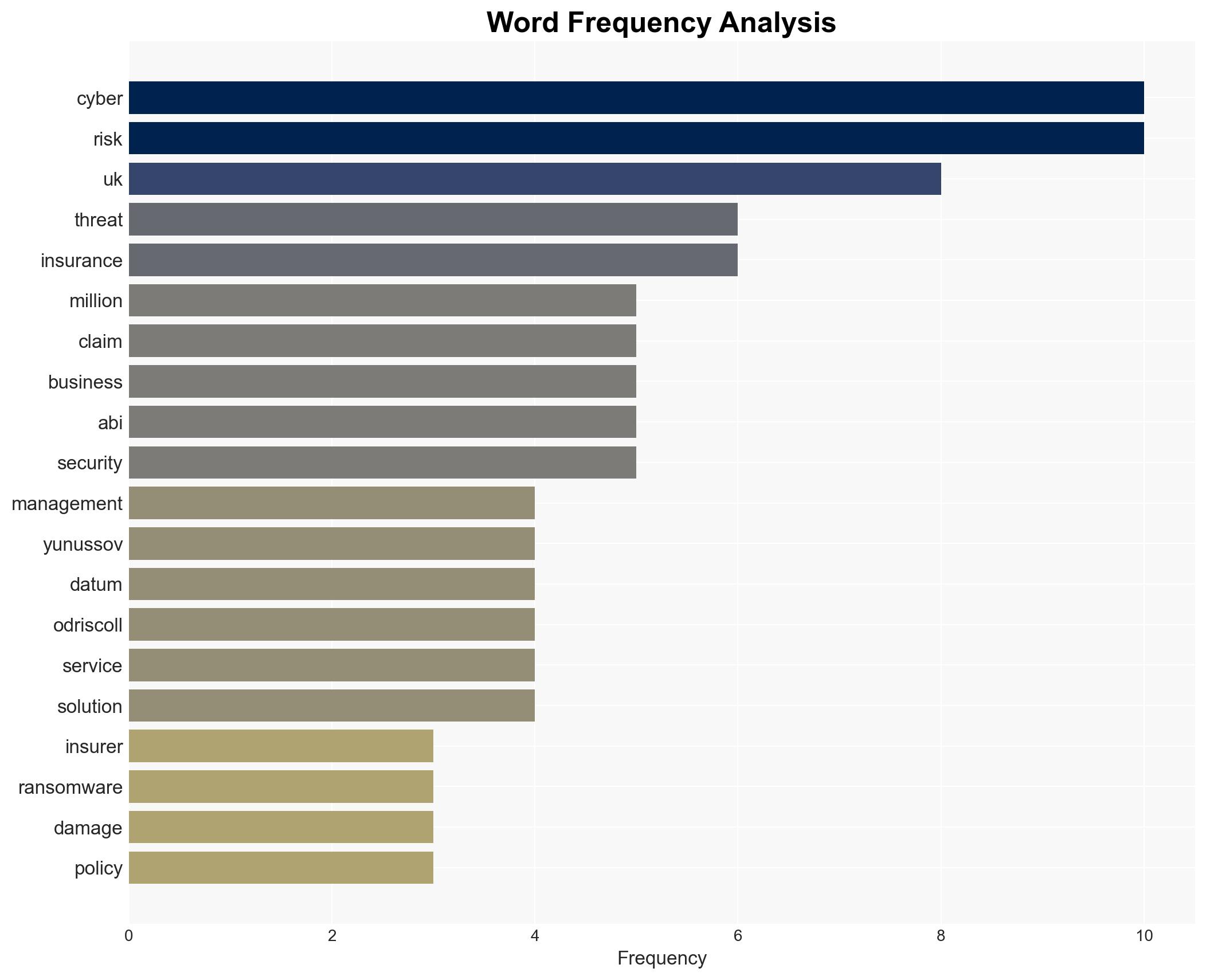
Hypothesis 1: The increase in cyber insurance claims is primarily due to the escalation in the sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks, including ransomware and AI-driven phishing campaigns.
Hypothesis 2: The rise in claims is significantly influenced by increased awareness and adoption of cyber insurance policies by UK businesses, rather than a proportional increase in cyber incidents.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the evidence of sophisticated cyber threats and the commentary from experts highlighting the evolving nature of these threats. Hypothesis 2 is plausible but less supported by direct evidence in the report.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the data provided by the Association of British Insurers (ABI) is accurate and comprehensive. Another assumption is that businesses are accurately reporting cyber incidents.
Red Flags: Potential bias in reporting from insurance companies aiming to justify premium increases. Lack of detailed breakdown of the types of claims and their specific causes could obscure understanding of the threat landscape.
Deception Indicators: No clear indicators of deception, but the possibility of underreporting cyber incidents due to reputational concerns by businesses exists.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increase in cyber claims suggests a growing vulnerability in UK businesses to cyber threats, which could lead to significant economic and reputational damage. The potential for cascading threats includes increased regulatory scrutiny and potential geopolitical tensions if state-sponsored cyberattacks are involved. The industrialization of ransomware and AI-driven attacks could further escalate the threat landscape.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Enhance cybersecurity measures within organizations, prioritize employee training, and improve third-party oversight. Advocate for stronger regulatory frameworks to support cybersecurity resilience.
- Best Scenario: Businesses significantly improve their cybersecurity posture, leading to a reduction in successful cyberattacks and insurance claims.
- Worst Scenario: Cyber threats continue to evolve faster than defensive measures, leading to increased financial and reputational losses.
- Most-likely Scenario: Continued rise in cyber claims as businesses gradually adapt to the evolving threat landscape, with incremental improvements in cybersecurity measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Jonathan Fong, Head of General Insurance Policy at ABI; Anton Yunussov, Director and Head of Cyber Security at Forvis Mazar; Warren O’Driscoll, Head of Security Practice at NTT Data UK.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·