Iranian Hacker Breaches Data of 50 Global Firms Using Infostealers and Stolen Credentials
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Lone Hacker Used Infostealers to Access Data at 50 Global Companies
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
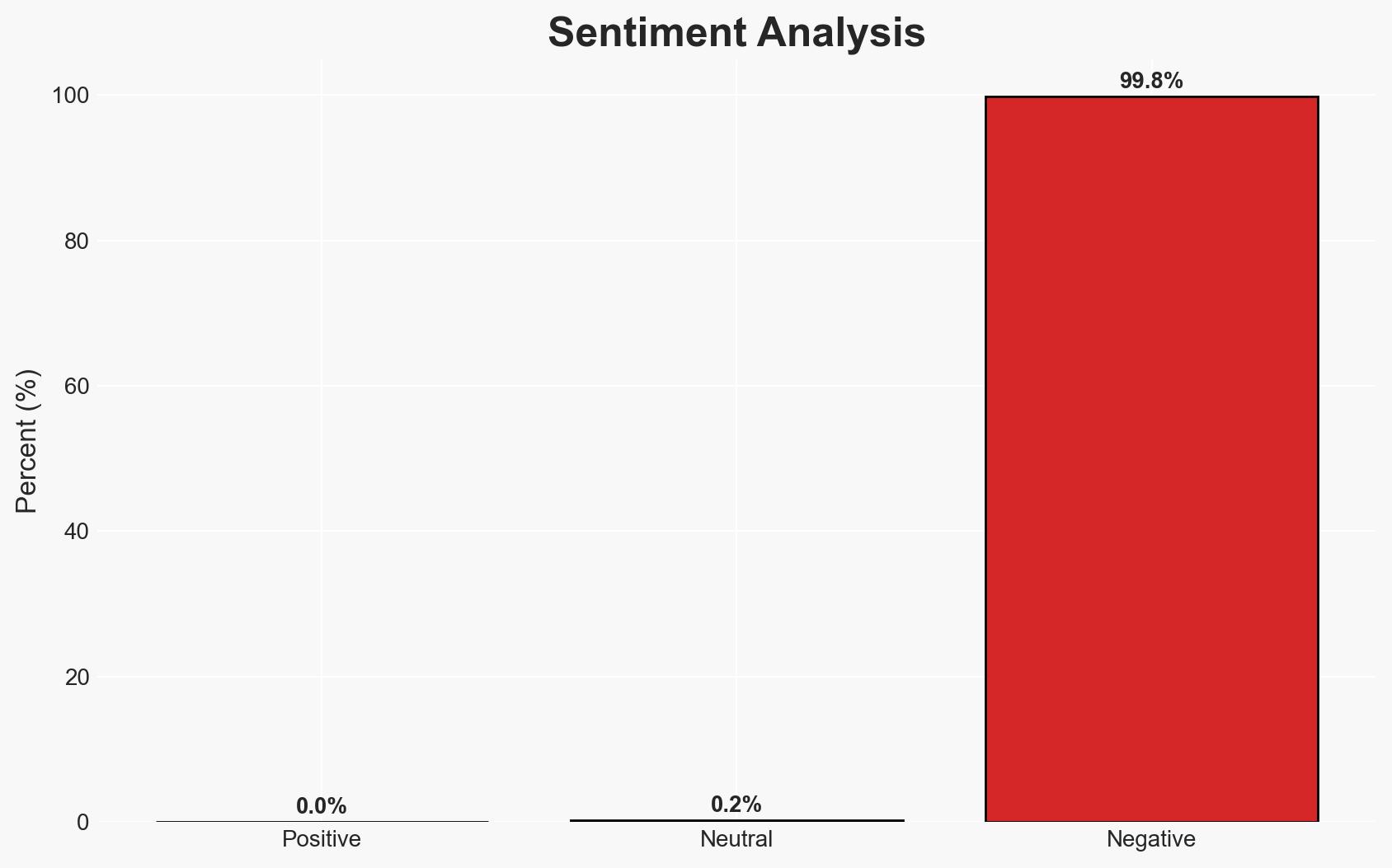
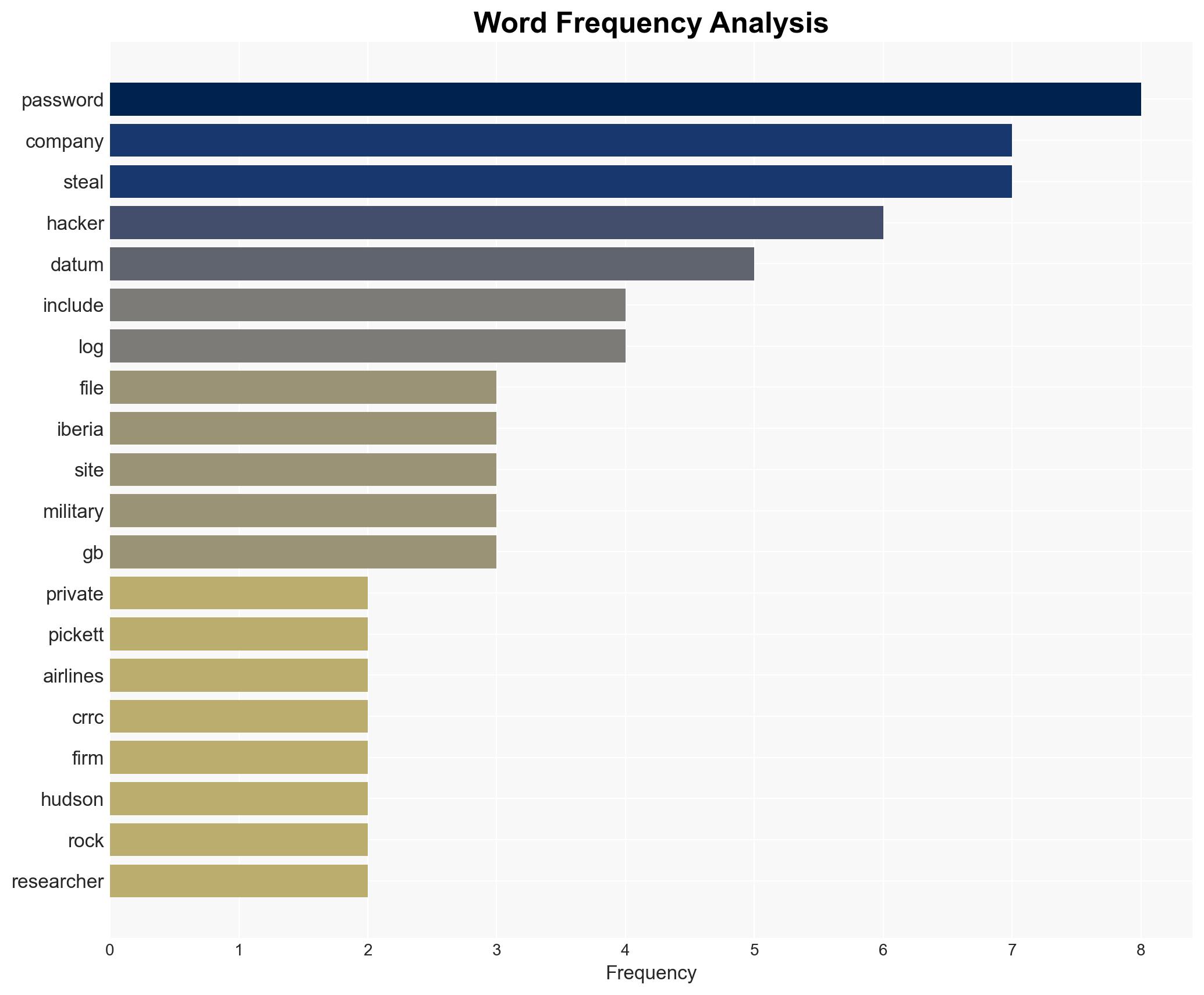
A lone hacker, identified as an Iranian national, exploited weak security practices to access data from 50 global companies using infostealers. The hacker is auctioning the stolen data on dark web forums. The primary vulnerability was the lack of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the reliance on a single source and potential for deception.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The hacker acted independently using infostealers to exploit weak security protocols. This is supported by the simplicity of the attack method and the lack of MFA. However, the identity and motivations of the hacker are not fully verified, introducing uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The hacker is part of a larger coordinated effort, possibly state-sponsored, to gather intelligence or disrupt operations. This is contradicted by the lack of sophisticated techniques typically associated with state actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the straightforward nature of the attack and the lack of evidence indicating a broader conspiracy. Indicators such as the hacker’s online behavior and the nature of the data auction could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The hacker’s identity as an Iranian national is accurate; the companies’ security practices were uniformly weak; the hacker’s actions were primarily financially motivated.
- Information Gaps: Verification of the hacker’s identity and affiliations; the full extent of data compromised; potential connections to other cyber incidents.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from the cybersecurity firm due to vested interests; deception by the hacker regarding identity and motivations to mislead investigators.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development highlights significant vulnerabilities in corporate cybersecurity practices, particularly the lack of MFA, which could lead to increased cyber threats if not addressed. The incident may prompt regulatory scrutiny and impact international relations if state involvement is suspected.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions if the hacker’s nationality is confirmed and linked to state activities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of similar attacks exploiting weak security protocols in critical sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and potential for increased cybersecurity measures across industries.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for affected companies and potential reputational damage, leading to broader economic impacts.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Companies should immediately implement MFA and conduct security audits; law enforcement should monitor dark web forums for data sales.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop industry-wide cybersecurity standards and increase collaboration between private and public sectors for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Companies enhance security measures, reducing vulnerability to similar attacks.
- Worst: Continued exploitation of weak security practices leads to more significant breaches.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security practices with occasional breaches due to lagging implementation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Zestix/Sentap (alleged hacker)
- Hudson Rock (cybersecurity firm)
- Pickett & Associates, Iberia Airlines, CRRC MA, Intecro Robotics, Maida Health (affected companies)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, infostealers, MFA, corporate vulnerability, dark web, Iranian hacker
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us