IT Leaders Express Growing Concerns Over Cybersecurity and AI Challenges Ahead of 2026
Published on: 2025-12-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: From AI to cyber risk why IT leaders are anxious heading into 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
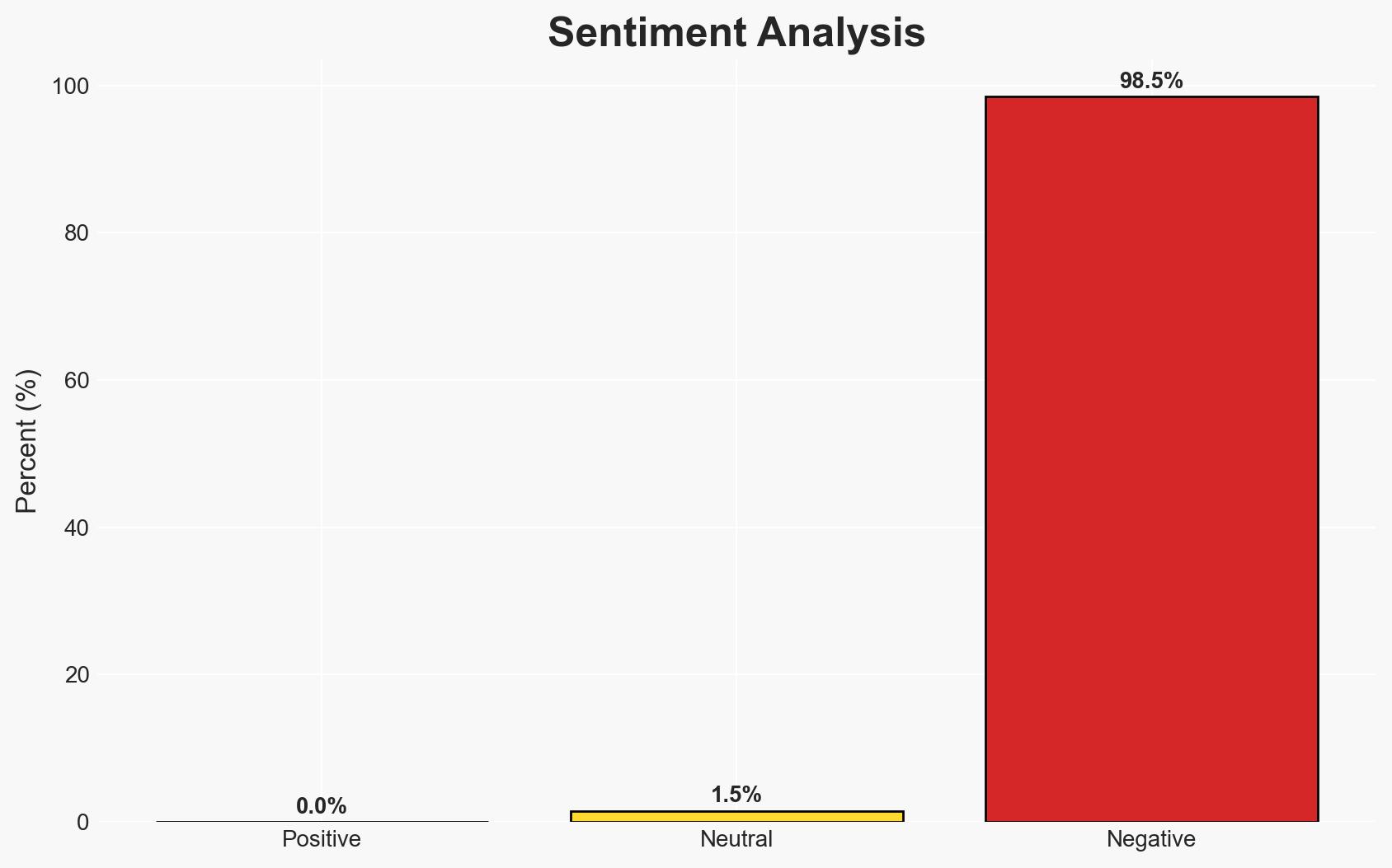
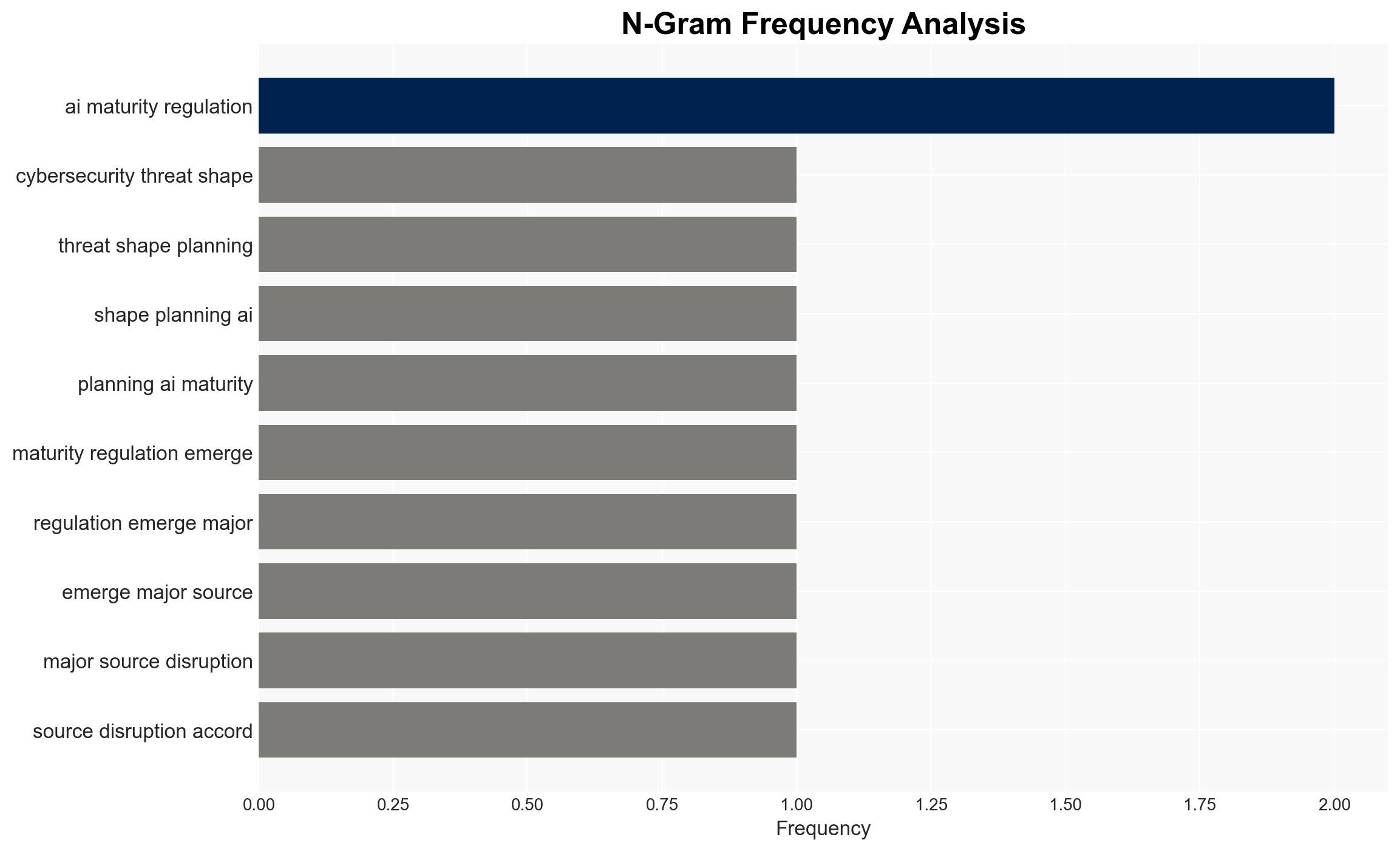
Cybersecurity threats are the primary concern for IT leaders as they plan for 2026, with AI maturity and regulation also significant disruptors. The survey indicates a lack of preparedness for cyberattacks and AI-driven threats, with a moderate confidence level in the assessment. Affected parties include IT and business decision-makers worldwide.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: IT leaders are primarily concerned about cybersecurity threats due to the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, which are exacerbated by AI advancements. This is supported by the survey indicating cybersecurity as the top disruptor and AI-generated attacks as a significant threat. However, the exact nature and evolution of these threats remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Concerns about AI maturity and regulation are equally significant as cybersecurity threats, driven by regulatory pressures and the rapid pace of AI development. While AI and regulation are noted as disruptors, they rank lower than cybersecurity threats, suggesting less immediate concern.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the higher prioritization of cybersecurity threats in the survey. Indicators such as increased AI-driven attack sophistication could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The survey accurately reflects global IT leader concerns; AI-driven threats will continue to evolve; regulatory environments will become more stringent.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the types of AI-driven threats and their potential impact; regional variations in threat perceptions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in survey responses due to self-reporting; possible underreporting of AI-related risks due to lack of understanding.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The focus on cybersecurity and AI regulation will likely drive significant changes in IT strategies and investments. This could lead to increased regulatory compliance costs and shifts in global cybersecurity policies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international collaboration on cybersecurity standards and AI regulation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape with more sophisticated cyberattacks leveraging AI technologies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater emphasis on data protection and resilience, with potential for increased cyber defense spending.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic strain from increased regulatory compliance and cybersecurity investments.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-driven threat developments; initiate cross-sector dialogues on cybersecurity best practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for AI and cybersecurity research; invest in workforce training to address skills shortages.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened global cybersecurity frameworks reduce threat levels.
- Worst: Rapid AI threat evolution outpaces defensive capabilities, leading to widespread disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in readiness and resilience, with sporadic high-impact incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
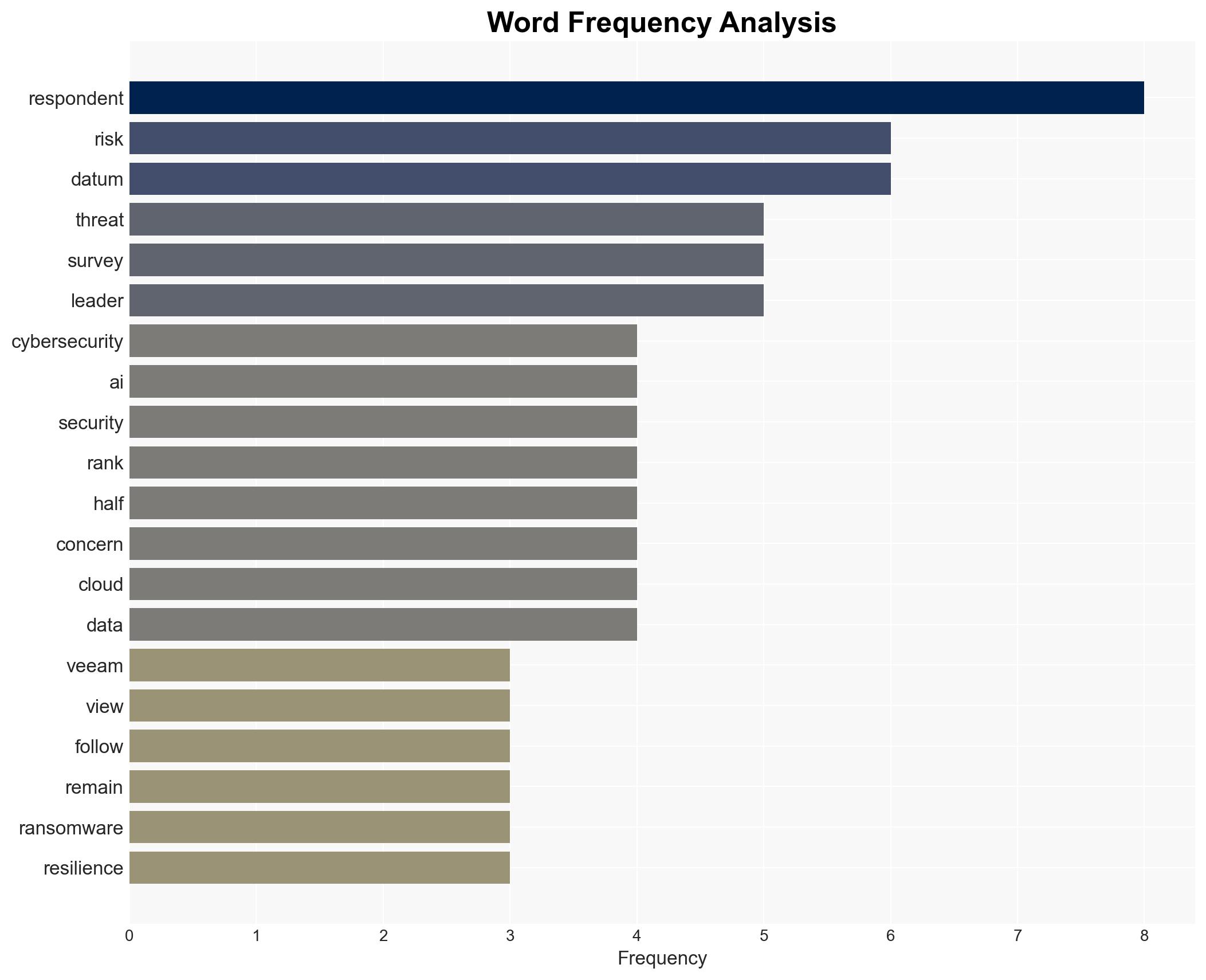
cybersecurity, AI regulation, data resilience, IT strategy, cyber threats, regulatory compliance, ransomware
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us