Ivanti issues temporary fixes for critical EPMM zero-day vulnerabilities amid active exploitation threats
Published on: 2026-01-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Ivanti provides temporary patches for actively exploited EPMM zero-day CVE-2026-1281
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
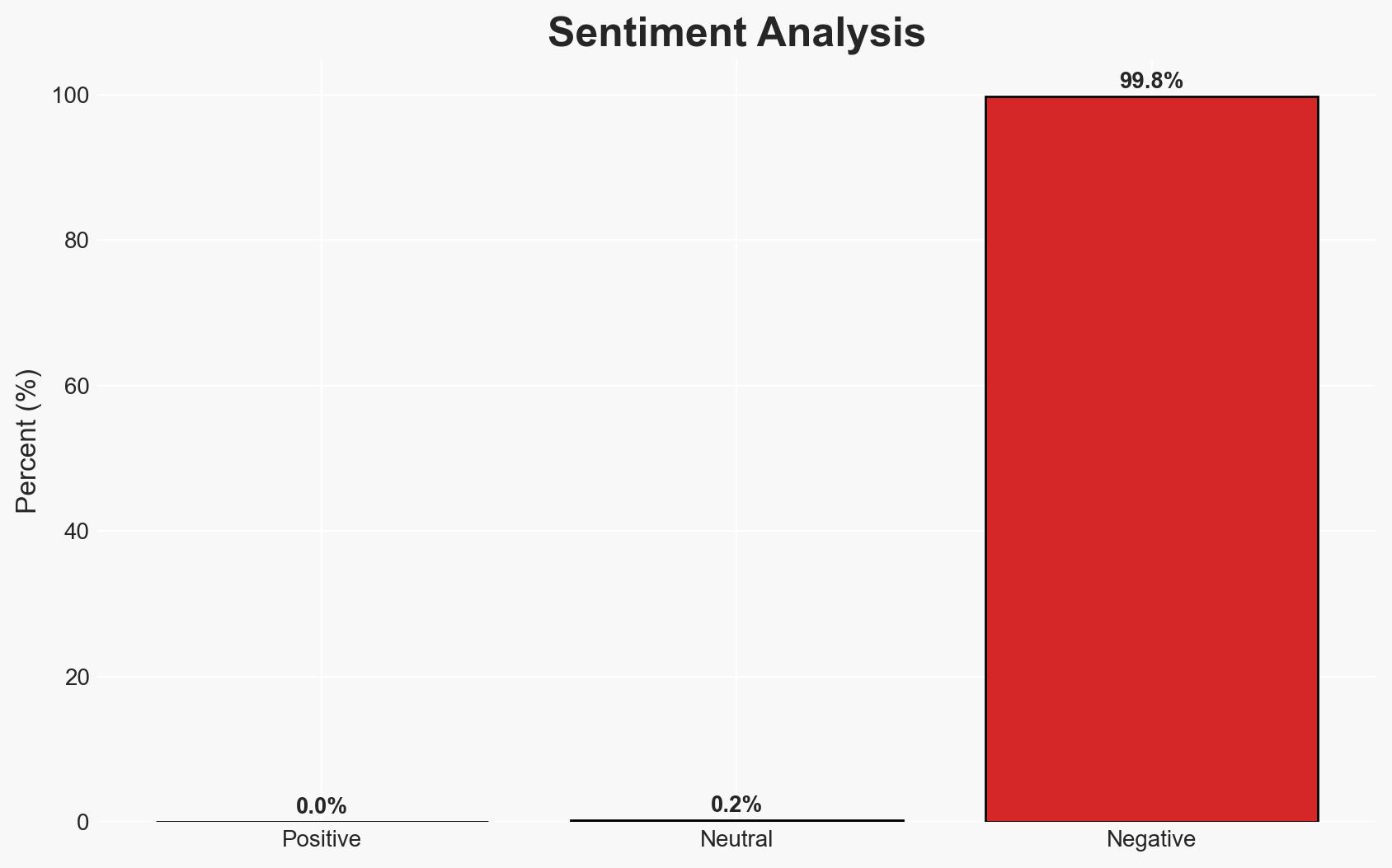
Ivanti has issued provisional patches for two critical vulnerabilities in their Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM), one of which (CVE-2026-1281) is actively exploited. The vulnerabilities allow remote code execution, posing a significant risk to on-premises EPMM installations. The immediate threat is limited, but the potential for broader exploitation exists. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on threat actor tactics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The exploitation of CVE-2026-1281 is limited to a small number of targeted attacks. This is supported by Ivanti’s statement of a “very limited number of customers” affected. However, the lack of detailed threat actor tactics introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities could be leveraged for broader, opportunistic attacks. The potential for remote code execution on vulnerable systems supports this, but there is no current evidence of widespread exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Ivanti’s specific observations of limited exploitation. Indicators such as increased log anomalies or broader reports of compromise could shift this assessment towards Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerabilities are primarily exploited in targeted attacks; Ivanti’s patches are effective; attackers have not significantly tampered with logs.
- Information Gaps: Detailed threat actor profiles and tactics; comprehensive data on the scope of exploitation across different sectors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting by affected organizations; Ivanti’s vested interest in minimizing perceived risk.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to increased scrutiny of Ivanti’s security posture and potential regulatory actions. If broader exploitation occurs, it may necessitate significant security overhauls for affected organizations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic tensions if state actors are involved in exploitation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage activities targeting vulnerable systems.
- Economic / Social: Financial impacts on affected organizations; potential loss of consumer trust in Ivanti products.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Organizations should apply patches immediately, monitor logs for anomalies, and conduct forensic analysis of potentially affected systems.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop enhanced threat detection capabilities and establish partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful mitigation with no further incidents. Worst: Widespread exploitation leading to significant data breaches. Most-Likely: Limited additional exploitation with increased security measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerability, remote code execution, threat mitigation, Ivanti, endpoint management, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us