Japan’s Nuclear Debate: Balancing Deterrence Needs Against Pacifist Legacy Amid Rising Regional Threats
Published on: 2025-12-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Japans NUCLEAR dilemma Rising tensions spark debate over pacifist principles
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
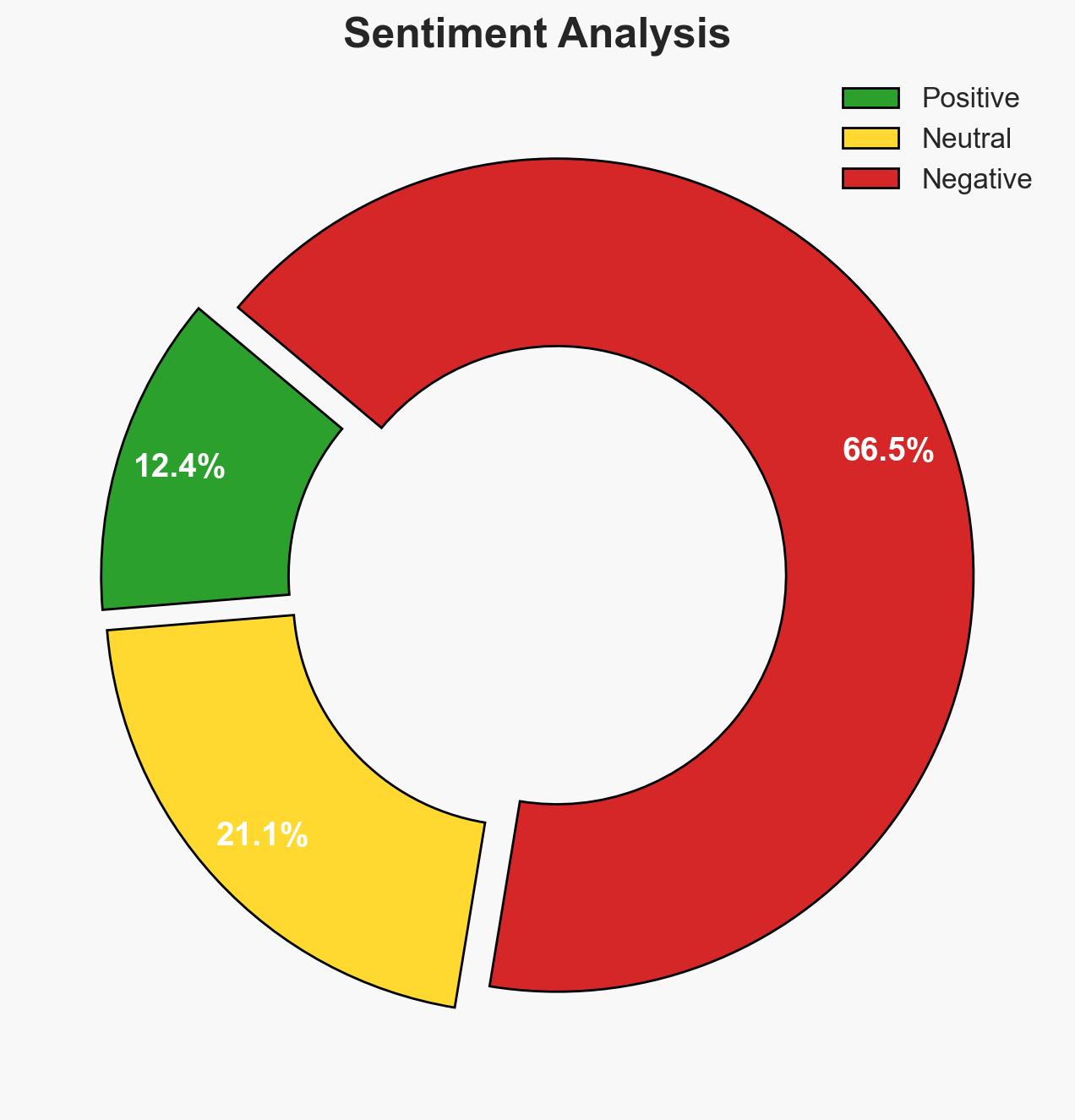
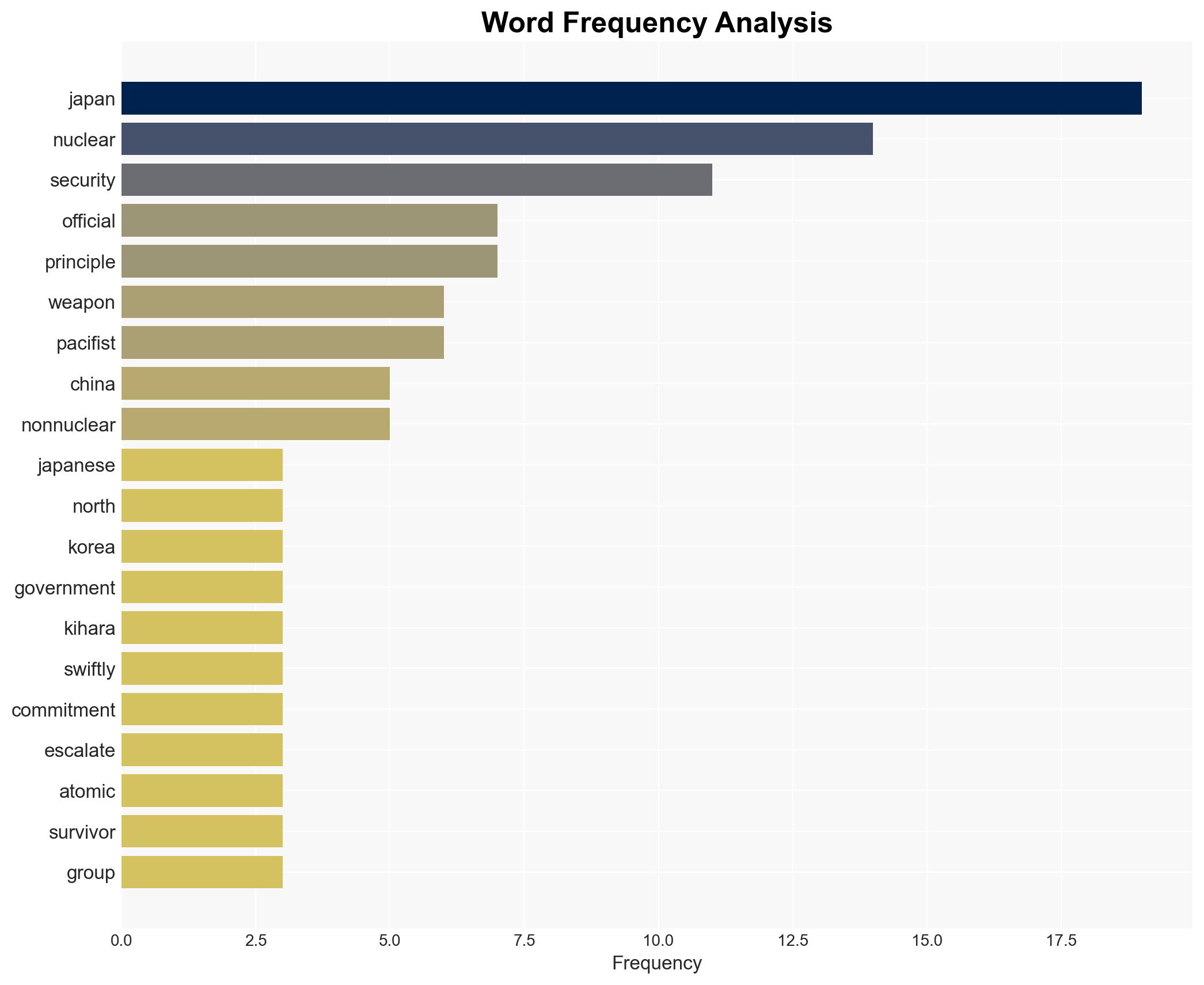
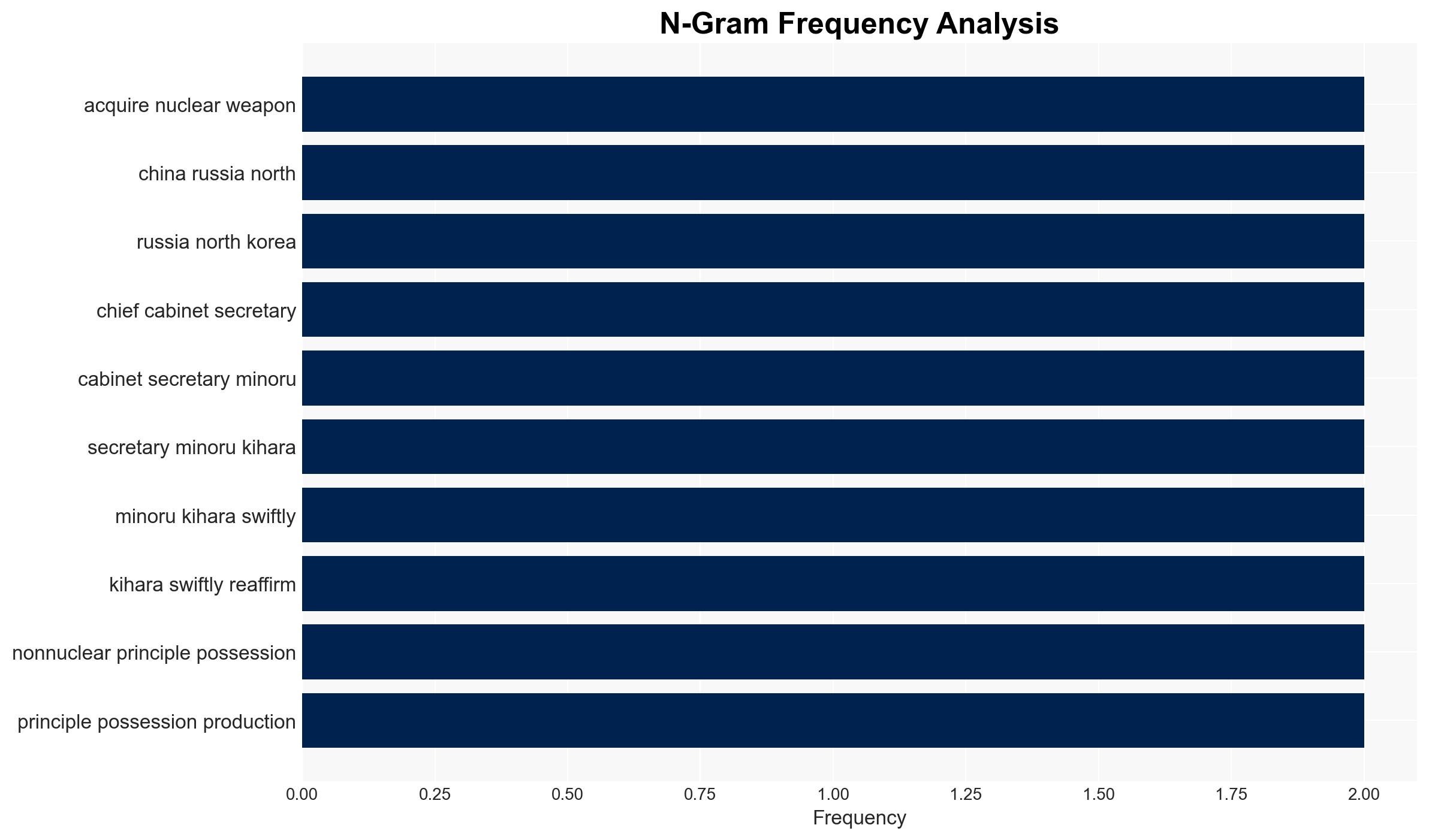
Japan is experiencing internal debate over potentially acquiring nuclear weapons, driven by perceived threats from China, Russia, and North Korea. This marks a significant shift from its pacifist principles, with divisions evident within the government. The most likely hypothesis is that Japan will maintain its non-nuclear stance due to domestic and international pressures, with moderate confidence.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Japan will maintain its Three Non-Nuclear Principles, as reaffirmed by Chief Cabinet Secretary Minoru Kihara, due to strong domestic and international opposition and the historical significance of its pacifist identity. However, internal pressures and regional security dynamics challenge this stance.
- Hypothesis B: Japan will shift towards developing a nuclear arsenal as a deterrent, driven by a growing faction within the government and doubts about U.S. security guarantees. This hypothesis is less supported due to the immediate backlash and the political and logistical challenges of nuclear acquisition.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, given the reaffirmation of non-nuclear principles by key government figures and the significant domestic and international opposition. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in U.S. security commitments or increased regional threats.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Japan’s government will continue to prioritize its pacifist principles; U.S. security guarantees remain credible; domestic opposition to nuclear armament remains strong.
- Information Gaps: Details on the size and influence of the pro-nuclear faction within the Japanese government; specific U.S. responses to Japan’s security concerns.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from sources with vested interests in either maintaining or altering Japan’s nuclear stance; manipulation risks from adversarial states aiming to influence Japan’s policy decisions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regional tensions and influence Japan’s strategic alignments. The debate may affect Japan’s domestic politics and its international relations, particularly with the U.S. and neighboring countries.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on Japan’s relations with China and South Korea; increased pressure on U.S.-Japan security arrangements.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible escalation in regional arms race dynamics; heightened threat perceptions among neighboring countries.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber espionage targeting Japan’s defense and policy sectors; potential information warfare campaigns by adversaries.
- Economic / Social: Domestic unrest or protests from anti-nuclear groups; potential economic sanctions or diplomatic fallout if Japan pursues nuclear armament.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor government statements and policy shifts; engage with U.S. counterparts to assess security guarantee commitments; track public opinion and media narratives.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen diplomatic engagements with regional allies; enhance intelligence capabilities to monitor regional military developments; invest in public diplomacy to manage domestic and international perceptions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Japan reaffirms non-nuclear stance, enhancing regional stability.
- Worst: Japan pursues nuclear armament, triggering regional arms race.
- Most-Likely: Japan maintains non-nuclear principles while seeking enhanced security assurances from the U.S.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Minoru Kihara – Chief Cabinet Secretary
- Unnamed senior Japanese security official
- Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi’s administration
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, nuclear policy, Japan security, regional tensions, pacifism, U.S.-Japan relations, China-Japan relations, non-proliferation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us